I MEAN, so effective was President Obama’s delivery that huge swaths of the American public who had come to hold him in clear disdain were safely put back under his spell. So self assured and competent was he that the only explanation his audience can now conjure for Obama’s dismal failures thus far, now called his partial-successes, is resignation about the political adversaries being obviously too great. They argue the presidency has only limited power, the ruling oligarchs hold all the cards, Obama has achieved wonders all things considered. Apparently the President of the United States has such diminished authority he can’t even explain all that in plain English to his national audience. You think he could defy the corporate media to pull the plug on a wardrobe malfunction. Obama would have a popular uprising of Tunisian magnitude if he lent his oratory skills to putting the public wrath in gear. Instead, more unbearable demispeak — I had to unplug from the news cycle. The Tucson tragedy became Obama’s Oklahoma City Moment, another Waco for American aspirations for change.
Tag Archives: Tucson
Palin signed off on Giffords shooting, grizzly lipstick plot to direct gunmen
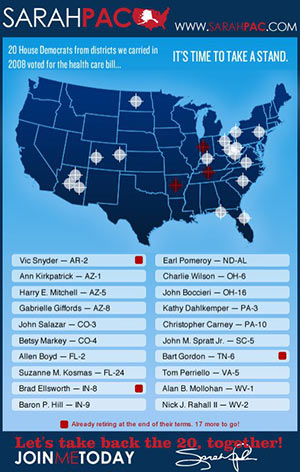 AZ representative Gabrielle Giffords was one of twenty crosshairs on Sarah Palin’s checklist directing political assassinations.
AZ representative Gabrielle Giffords was one of twenty crosshairs on Sarah Palin’s checklist directing political assassinations.
Whether Jared Lee Loughner was a lone gunman, or in a TP or al-Qaeda cell, shouldn’t the DOJ investigate the grizzly mastermind who is inciting these acts? While they’re at it, Vice President Biden for illegally targeting Wikileaks’ Julian Assange, and Boss Obama who commands extrajudicial assassinations via military/CIA drones. If this was a GPS map of Pakistan the “unhinged shooters” would be Predator Drone operators.
Michael Moore tweeted these interesting links:
Dem Rep Giffords shot in head in Az. Sarah Palin had put CROSSHAIRS/ BULLSEYE on Giffords on her website! OUTRAGE!
When Rep Giffords voted in favor of health care bill, her office in Tucson was attacked & vandalized.
Palin “set gun sights on 20 Dems (including Giffords).” Palin site now seems 2 b 2 taking down crosshairs map!
In 2009, another gun nut showed up where Rep Giffords was speaking (at another Safeway) & dropped his gun
Giffords opponent held June event 2 “Shoot a Fully Automatic M16” to “Get on Target” & “Remove Gabrielle Giffords”
When Palin put crosshairs on a map w/ Rep. Giffords & 19 other Dem congressmen/women, she urged followers to “reload” & “aim” for Democrats.
Stunning admission by Tucson sheriff: Arizona “a mecca” of hate & bigotry which unhinges the unbalanced Wow.
Christina Green was the 9yr old killed. She was born on 9/11. Was on student council & only girl on baseball team.
If a Detroit Muslim put a map on the web w/crosshairs on 20 pols, then 1 of them got shot, where would he b sitting right now? Just asking.
Ward Churchill speaks on which settler invasion wrote the book on Apartheid

Ward Churchill spoke in Tucson on Friday and Brenda Norrell has posted the footage. Watching the ex-CU professor speak, I can’t help but think about the university students’ loss. They’re missing the lamentably rarefied perspectives he offers of course, but more important, the inspiration gained from such an engaging luminary.
Throughout his lectures, Churchill likes to put questions back at his audience. He understands, if I can presume to project his rationale, that a mentor’s role is to bounce ideas around, and be sure his students have minds open enough to let them resonate. It’s also a sign of someone fully confident with what they are teaching. Churchill gives you the impression he’s interested in the best argument you’ve got, and I believe him, but in reality he’s going to have few peers up to the task.
When it’s time for Q and A, Prof. Churchill calls it mud-wrestling, and welcomes all shots, “even spit wads.” He draws the line at brick bats, because he says, one might bounce off his head and hit somebody else. He warns, as if he’s had practice, “because someone might get hurt. I can assure you it won’t be me.”
I wished at that moment that Tucson was not so far from Churchill’s curiously vile detractors, who attended his trial in Denver, and who hold bitch fests online about every Churchinalia for reasons unspecified. I predict they’re remunerated; the love-to-hate pretext is wearing thin, these yahoos are pro-Israeli tea-baggers. So there’s no Drunkablog or Pirate Ballerina there tonight to take the “perfessor’s” challenge. Although wouldn’t such an exchange have been simply tedious? I recall this dismal attempt mounted against “Wart” by a couple CU college Republicans, it was just embarrassing. Have Churchill’s online critics ever confronted him in person I wonder? They can spout off in the safety of anonymity, and that’s about it.
Churchill’s speech to the predominantly Anglo and O’odham border activists was about the bigger issues behind the border wall. The theme of the gathering was Apartheid in America, and Churchill demonstrated how South African Apartheid came of the successful colonial methods practiced in the United States. These were the strategies employed by the Germans in taking and settling the Eastern Front during WWII, and of course the goals of Israel in Palestine.
Churchill described how settler invasions vary from colonial administration. In the latter case, the colonizers can go home, in the former, they stay. Another distinction is critical, the settlers aren’t moving to a land and becoming part of the social system, they remain citizens of the occupying force. They bring their identity and the foreign system with them, to apply against the people indigenous to the land. The process involves two steps: displace enough of the natives to make room for yourselves, but leave just enough to serve as a labor pool, for all the building that is required of empire building. You’ve need of only a portion of the original population, to do the manual labor required of developing the land, but eventually you need them to die off. The Nazi strategy in Poland was to eleminate a great deal via war, then another mass through starvation, ill health and exposure. Methods mirrored today in Gaza. As a USA example, Churchill sited the average life expectancy of a Native American on a reservation in 1975. The age was 44.6 years old. That’s 1/3 less that the G-Pop average, equivalent to thinning the population by a third.
To cut to the quick, Churchill asked his audience how they felt about social challenges like sexism, racism, ageism, classism. All were basically in accord as being against. What’s the problem, Churchill asked. If so many are against these things, why do they persist? Then he threw imperialism into the mix, which had not been mentioned. Churchill said we cannot adequately address the others until we have a clean conscience about the land taken from America’s First Peoples. This must be the priority. First Peoples, First Nations, First Priority.
Below is the video of Friday’s Tohono O’odham event in Tucson. Take note also of the excellent speeches which followed the keynote, by Ofelia Rivas and her brother in particular.
Click ON DEMAND, then select the “Live Show Fri Nov 13 2009 06:20:55 PM” or watch it at Livestream/earthcycles.
Ward Churchill to speak for O’odham
 According to Censored News, Activist and scholar Ward Churchill will speak at the Unitarian Universalist Church of Tucson, 4831 W. 22nd St., on November 13, 2009 at 7:00 p.m. to benefit O’odham VOICE Against the Wall, which since 2003 has organized and advocated for the traditional O’odham leaders and elders of the Tohono O’odham communities in the southern territory of the United States and northern territory of Mexico. Professor Churchill’s talk is part of the “Apartheid in America: Surviving Occupation in O’odham Lands”
According to Censored News, Activist and scholar Ward Churchill will speak at the Unitarian Universalist Church of Tucson, 4831 W. 22nd St., on November 13, 2009 at 7:00 p.m. to benefit O’odham VOICE Against the Wall, which since 2003 has organized and advocated for the traditional O’odham leaders and elders of the Tohono O’odham communities in the southern territory of the United States and northern territory of Mexico. Professor Churchill’s talk is part of the “Apartheid in America: Surviving Occupation in O’odham Lands”
O’odham activist Ofelia Rivas will also participate. The event is sponsored by the Dry River Radical Resource Center, the Earth First! Journal, and Voices against the Wall.
Here’s some background on the O’odham struggle:
By J. D. Hendricks, 2004
TIAMAT PUBLICATIONS #5The People Who Emerged From the Earth
Over two thousand years ago the descendents of the O’odham moved into the southwestern region of the area now claimed by the U.S. as the state of Arizona. 1 The O’odham have had one of the longest histories of contact with the forces of European colonization compared with the rest of the native North American peoples. The O’odham’s first contact with Spanish invaders took place in the mid 16th century; nearly one hundred years before the colonization of the North Atlantic coast and Great Lakes regions were begun by the French and English colonists. As such, the history of the O’odham provides a good context for an investigation of the colonization of Native North America, and more specifically, an investigation of the interplay between, and results of, the varied responses to colonization – that of collaboration, accommodation, and resistance.
Many histories of the O’odham refer to these desert people as the Papago. The term Papago was a name given to the O’odham by the Spanish colonizers, and is likely the result of a Spanish corruption of the O’odham word “papabi” which was the O’odham name for one of their principal bean varieties. Thus, the Spanish colonizers term for the O’odham (Papago) came to mean “the bean eaters.” 2 For the purposes of this study I will refrain from the use of the term Papago and will refer to “the people” 3 by their traditional pre-colonial name. 4
As is often the case, with the name Papago being a good example, European constructs are often imposed upon indigenous peoples by the historians that seek to portray their past. This result can occur when historians seek to glorify European norms and traditions at the expense of indigenous ones, and can also be the result of the subconscious indoctrination of the historian by the dominant culture – in this case that of western style industrial civilization. In other cases it can be the result of a simple uncritical usage of language.
One of the most dominant and reoccurring “civilized” constructs imposed upon indigenous peoples history is the commonly understood notion that the O’odham, or any other indigenous North American culture for that matter, existed as a totality or uniformed mass. This study will seek to use the history of the interaction between the O’odham peoples and the United States, both its government and its peoples, to deconstruct this myth of the totality and provide a history of the O’odham’s varied responses to colonization from an anti-colonial and anti-industrial perspective. By investigating various important case studies in O’odham history, and looking not only at resistance but also accommodation and collaboration, it is hoped that this work will help to provide a more realistic historical picture of the effects of colonization, and the intentions and reactions of both the colonizer and the colonized. Within the previously stated context and theoretical framework, this study will argue that while the O’odham responded to the U.S. invasion of their lands in various ways, the choices to resist, accommodate, or collaborate with the forces of colonization did not affect the overall U.S. policy concerning the O’odham – that policy being the eventual total assimilation of the O’odham into the dominant “civilized” industrial system. 5
This investigation will include a strong focus on O’odham resistance to colonization, as any anti-colonial history should, however it will not discount or ignore the many historical occurrences of accommodation, and in some cases outright collaboration, with the colonizers. It is important to always keep in mind that none of the actions and reactions in any of the case studies looked at are attributable to the O’odham as a “totality,” but rather are attributable only to the various groupings of O’odham, be they incarnated in the form of the individual, the clan, the village, an economic or spiritual grouping, or an established political organization.
A God of Civilization and Coercion Comes to the O’odham
The O’odham’s first encounter with Spanish invaders took place in the mid sixteenth century when a group of conquistadors led by Alvaro Nunez Cabeza de Vaca entered O’odham territory in search of gold. These men did not find the riches they were looking for and left the desert region to return to the Spanish colony. However, soon after word spread of the O’odham villages on the northern periphery of the Spanish colony, missionaries began to travel north to bring God and “civilization” to the native people residing there. By 1686, Catholic missionaries had formed a few small missions in O’odham territory using what they believed to be the influence of their soft power 6 techniques to lure the O’odham into their missions where they were then subjected to a rigorous schedule of cultural indoctrination. Most O’odham historians, including Winston Erickson, 7 and to a lesser extent, Bernard Fontana 8 have, during this time period, focused on the O’odham who chose to reside nearby and within these early missions, thus painting a picture of the O’odham as accepting of Spanish influence and cultural indoctrination.
However a closer look at this time period reveals that mission O’odham were only a small percentage of the total population of O’odham residing in the Sonoran desert 9 and that the ones who were there may not have been so for the reasons that the colonizers believed. San Xavier del Bac, the largest mission in O’odham lands, as well as many other missions, took advantage of the fact that the desert O’odham migrated in the dry winter months to the Northern Piman settlements along the rivers to work the small farm plots for sustenance. 10 The Catholic missions inserted themselves into this traditional pattern. Those O’odham who worked and lived near the missions were, for the most part, seasonal residents, which shows that the missions were viewed merely as being of utilitarian value. Thus, the O’odham as a totality were not necessarily accommodating to or interested in anything the missionaries had to offer per se, and when the missionaries began to employ “hard power” techniques and abuse or overstep the grounds for their welcome it did not go without consequence. 11
Accommodating and ignoring the missionaries was not the only response to colonization practiced by the O’odham during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Although historians such as Erickson feel that “the missions did serve the O’odham well….,” 12 that assertion is contradicted by the fact that there were many large scale rebellions waged against the missions from outside and from within. In 1695, 1751, 1756, and 1776, large scale rebellions occurred in which missionaries were killed and their missions burned to the ground. 13 In some cases these rebellions were the doing of joint O’odham/Apache alliances, which is significant considering that many histories of the O’odham and Apache portray them as immemorial enemies. This may be the result of the fact that by the early nineteenth century the Spanish government initiated a campaign of divide and conquer that was continued later by the Mexican and U.S. governments to turn the O’odham and Apache against one another, thus easing the project of their subjugation.
A Change in the Occupation Government: Washington Enters O’odham Lands
In 1821, Mexican Independence from Spain was achieved and interest in the O’odham dropped away nearly entirely. By 1828, the new and secular Mexican government began the process of shutting down the missions in O’odham territory and by 1842, the last of the missions were closed. Soon after, in 1846, the United Stated initiated a war for territorial expansion against Mexico. This war was not of immediate consequence to the O’odham peoples. Isolated in desert regions, the fighting between the two occupation powers affected them little in the short run. However, the signing of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, which ended the war, would lay the foundations for a series of disastrous events which would affect the O’odham in very negative ways.
Of greatest consequence to the O’odham was the fact that the boundary between the United States and Mexico was not finalized by the treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. The boundary was designated by Article Five of the Treaty as being an arbitrary line roughly following the 32nd parallel, an area which runs through the southern part of modern Arizona. To the east, the border was provided by the Rio Grande. The exact boundary line along the 32nd parallel was to be decided at a later date. It is also important to note here that the Treaty also provided that all Mexican citizens absorbed by the United States were to be granted U.S. citizenship, which included all indigenous peoples in the annexed territory since under Mexican law they were considered citizens. In the treaty the United States also assumed the responsibility for preventing cross border raiding into Mexico by the southwestern tribes, specifically the Apache. 14
In the aftermath of the signing of the treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, it became quickly apparent that an acceptable border between Mexico and the United States along the 32nd parallel would not be achieved. An official survey expedition was assembled by the United States and Mexico in 1849 to trace out the boundary between the two countries with little success. Various borderlines were agreed to and then abandoned and re-made by the United States, sometimes in a unilateral decision that dismissed the positions of the Mexican government altogether. 15
The principal concern for the United States was to secure title to an area of land in northern Sonora, Mexico that was ideally suited for the construction of a portion of the southern continental railroad whose building was being discussed in the U.S. Congress at the time. One of the main advocates for this southern railroad route was a South Carolina man by the name of Colonel James Gadsden. Gadsden’s history of connections to powerful business, military, and political leaders is very interesting and his appointment by the United States to be Minister to Mexico in 1853 serves as a very informative source to gauge the United States’ intentions towards Native Americans and the O’odham in particular.
James Gadsden was born into an influential southern family and graduated from Yale University. After enlisting and serving in the war of 1812, Gadsden was sent to the Florida territory with Andrew Jackson to aid in the campaign of removal and extermination being waged against the Seminole Indians, which took place from 1816-1818. After this war against the Seminole, Gadsden was appointed by President Monroe as commissioner to oversee the removal of the Seminole Indians to Indian Territory. Like the more famous removal of the Cherokee, the removal of the Seminole, and the high death rate suffered as a result, unarguably constituted genocide. 16 As a reward for a job well done, Gadsden was appointed by Monroe to a seat on the legislative council of the territory of Florida, thus beginning Gadsden’s political career. In 1840, Gadsden was elected President of the Louisville, Charleston, and Cincinnati Railroad. In 1853, the Secretary of War, an ardent white supremacist and slavery defender by the name of Jefferson Davis, appointed Gadsden to be Minister to Mexico. 17 As Minister to Mexico, one of Gadsden’s primary missions was to negotiate a final demarcation of the boundary between the U.S. and Mexico. Although Gadsden was a zealous believer in Manifest Destiny, his ideas concerning racial Anglo-Saxonism 18 caused him to be an opponent of the total annexation of Mexico. Gadsden, like many racist U.S. politicians of that time, felt that the total absorption of Mexico and its non-Anglo population into the United States would pollute the Anglo bloodline too much and thus he sought only to gain enough territory for the United States to build the southern pacific route. 19 Thus, a man who had presided over a war of genocide against the Seminole Indians, was a devout racist, and who had obvious conflicts of interest due to his connections to the railroads, was put into a position to determine the territorial boundary between the United States and Mexico and in the process also determine the boundaries of the O’odham’s land. With its appointment of Gadsden, the intent of the U.S. government could not be clearer. Business interests and territorial expansion were to run roughshod, by any means necessary, over any native peoples who stood in the way.
It is no surprise that when James Gadsden finally successfully negotiated a treaty with Santa Anna to secure what is now the southern portion of Arizona, the O’odham were not consulted. In fact, the Gadsden Treaty, signed into law in 1853, did not contain any mention of the O’odham at all. Considering that the new boundary line put in place by the Gadsden Treaty literally split the traditional O’odham lands in two, it is obvious that the intentions of the United States were in no way benevolent. Here it is also important to point out that the terms of the Gadsden Treaty specifically included the same citizenship provisions which were spelled out in the earlier Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. 20 Although the Gadsden treaty was of great significance for the O’odham, their isolation and the outbreak of the Civil War enabled them to live another decade in relative isolation from Anglo encroachment.
Assimilation, Cultural Destruction, Double Speak and Ordained Genocide
The causes which the Almighty originates, when in their appointed time he wills that one race of men – as in races of lower animals – shall disappear off the face of the earth and give place to another race, and so on, in the great cycle traced out by Himself, which may be seen, but has reasons too deep to be fathomed by us. The races of the mammoths and mastodons, and the great sloths, came and passed away: The red man of America is passing away!
–United States Congress Committee on Indian Affairs report, 1865. 21No doubt with similar justifications in mind as those of the Committee on Indian Affairs, Anglo settlers began their invasion of O’odham lands less than a year after the conclusion of the Civil War. The Homestead Act had opened up the lands of Southern Arizona to Anglo squatters and in 1866, one of the first of many bills was passed by Congress granting mineral rights to any citizen who claimed them. 22 Every one of these homesteads opened and every resource extraction operation initiated without the express consent of the O’odham represented an illegal action under the Gadsden Treaty. The citizenship provisions of the Gadsden Treaty had granted citizenship to all former Mexican citizens and the O’odham were, by legal definition, included in this formulation. The United States, however, refused to consider “uncivilized” peoples as being worthy of the protections granted to citizens by the fourth amendment of the U.S. Constitution, which prohibits the expropriation of property. This refusal of the United States government to follow its own laws pertaining to Native Americans when those laws happen to stand in the way of U.S. interests has been a common occurrence in United States Indian policy. This land grab was only the first of many illegalities committed against the O’odham people by the United States and its citizens. In this respect the O’odham are in a special position when compared with many other tribes. While the theft of native lands by the United States Government was usually legally justified by treaty stipulations signed between a tribe and the U.S. government, this justification could not and cannot be used in the case of the O’odham since no treaty was ever signed with the O’odham by the United States Government. 23
For the most part, the O’odham did not resist this initial incursion of Anglo settlement, rather the O’odham practiced accommodation and moved farther out into the desert to shield themselves from the new settlers invading their lands. Traditional ways were maintained with the exception of the introduction of cattle ranching. The O’odham territory was well suited for the raising of cattle and a good number of O’odham became cattle ranchers, both for purposes of subsistence as well as for sale to Anglos residing in and around Tucson. In the 1880s, as increasing numbers of Anglo cattle ranchers began to invade and take over their pasture, some O’odham began to resist.
The O’odham resisted by stealing the Anglo cattle herds which were rounded up and driven south to be sold on the Mexican market. The expropriation of Anglo cattle herds was not isolated, and it became a major concern for the settlers and the government. In at least one case, a large cattle outfit was driven out of business. 24 The concern over this outbreak of O’odham theft of Anglo cattle was large enough that newspapers as far away as Los Angeles ran stories about the phenomenon. For the most part these stories seem to have been deliberately used to justify the enclosure of the O’odham into reservations as the government and Anglo cattle ranchers seized the opportunity to gain even more O’odham land by arguing that it was an unfair burden for the Anglo cattle ranchers to have to “support” the O’odham. 25 Here, in previous case study, we have another common attribute of U.S. Indian policy in general, and one which occurs again and again in the history of O’odham contact with the U.S. government and Anglo settlers – blaming the victim.
Another official position of United States Indian policy during this time period was that everything done to the Indians was, in the words of Indian Commissioner J. Q. Smith, in their own “best interests.” 26 Whether this obvious sham was based on a subconscious guilt and delusion or was a cynical example of “double-speak,” it is obvious that Native American’s best interest’s were the last thing on the government’s mind. Nevertheless, with this reasoning as justification, the first official reservation for the O’odham was created by executive order of President Grant on July 1, 1874. This small reservation surrounded the Old Catholic mission at San Xavier del Bac. It is estimated that only about ten percent 27 of the desert O’odham took up residence within this reservation – these were labeled as “civilized” O’odham by U.S. census takers. The vast majority of O’odham were labeled as “wild” and continued to live in the vast desert regions west of San Xavier del Bac. While it is obvious that the desert O’odham were resisting cultural assimilation by avoidance, even the mission O’odham maintained a resistance to European culture as the next example will illustrate.
While visiting the old mission at San Xavier a newspaper columnist from the Los Angeles Times wrote that upon her visit in 1882, she could see “not a single civilized human habitation within miles.” This writer goes on to state that the O’odham’s dwellings were in the form of “conical mud huts.” In the casual racism and Social Darwinist rhetoric of the period she also adds that,
“The Papagos are but little in advance of gophers and prairie dogs in their habitations.” 28
The point is that after more than 200 years of European influence, even the mission O’odham continued to build their traditional shelters. 29
Progressivism and Cultural Genocide: The Dawes Act
In 1887, the General Allotment Act, also known as the Dawes Act, was signed into law. The Dawes Act was the staging point for the forced assimilation of those remnants of Native American groupings which had not been totally decimated by the preceding period of “Indian Wars” and forced relocations. The essential function of the Dawes Act was to disrupt traditional tribal land holding patterns and thus force Native Americans into the Anglo system of private property. The O’odham, like most other Native American cultures, did not have a concept of private property – land was held in common for the benefit of the village group. Communally held land was an essential pre-requisite for their Anarchistic political system and extremely de-centralized tribal structure. 30
The first section of the Dawes Act provides for equal “sections” of land to be parceled out to each “head of family.” This head of family was always understood to be the father of each family when land was allotted. Thus, this first section of the act not only attempted to destroy the communal land system of Native Americans, it also instituted Patriarchy as the basis for social functioning in Native America. 31 In addition, Section Five of the Act also provides that any un-allotted lands be subject to purchase by the United States government. Section Six and Seven provide that all monies paid by the U.S. for un-allotted Native lands be held for each tribe by the U.S. Treasury and “subject to appropriation” by the U.S. government to repay itself for the implementation of allotment as well as to provide for the “civilization” of Native Americans. 32 In less veiled words, these sections are basically stating that Native Americans will be forced to pay for their own cultural annihilation.
This interpretation of the intent of the Dawes Act becomes clearer when one looks at the arguments and debates that took place in Congress and within self described progressive “Indian rights” groups such as the Indian Rights Association. Critics of the Dawes Act in Congress such as Rep. Russell Errett understood that
“the main purpose of this bill is not to help the Indian troubles so much as it is to provide a method for getting at the valuable Indian lands and opening them up for settlement.” 33
And Senator Dawes, the namesake of the final bill, speaking of the land and resources of Native Americans stated that
“civilization has got after these possessions with a greed never before equaled but it is idle to expect to stay it….” 34
As for the progressive Indian Rights Association, they argued that
“the organization of the Indians into tribes is, and has been, one of the most serious hindrances to the advancement of civilization, and that every effort should be made to secure disintegration of all tribal organizations….” 35
And one of their leaders, Reverend L. Abbott, provided justification with the statement:
“Barbarism has no rights which civilization is bound to respect.” 36
So here we have a self-proclaimed progressive Indian Rights organization arguing for cultural genocide and against the notion that Native Americans have any rights that civilized people are bound to respect! This conclusion provides a perfect example of the essence of “progressive” or “civilized” thought.
The Dawes Act had a much less devastating effect for the O’odham than it did for many other Native American tribes. At the time of its passage, the only official reservation for the O’odham was the San Xavier reservation which, as was stated earlier, was only a small 71,090 acre reservation around the old mission San Xavier del Bac. When the allotment agent came to San Xavier in 1890, he allotted out 41,600 acres of land to the 363 O’odham whom he counted in his census as being resident at the time. 37 The vast majority of the O’odham still continued to live west of San Xavier in the expansive desert regions and were little affected by the allotment schemes. Even those O’odham who lived in San Xavier and were allotted land paid little attention to the artificial boundaries drawn on paper which supposedly privatized their land – they continued to farm and graze the land communally. 38 This refusal to abide by the provisions of the Dawes Act is also a form of resistance to cultural assimilation and adds one more example to show that for those O’odham who resisted, the most often employed method of resistance was non-compliance and avoidance. This specific response to colonization was made possible by the isolation and expansiveness of their desert home, which many Anglo’s continued to view as a “hopeless desert.” 39
The Domestication of the “Wild Papago”
The vast majority of the O’odham continued to resist assimilation and maintained a fairly traditional lifestyle – minus the introduction of cattle herding and horse rearing. In the twenty years following the passage of the Dawes Act, a growing effort was made to enclose the “Wild Papago” 40 and forcibly strip them of their traditional culture and instill them with the “civilized” values of the industrial Anglo. As was mentioned previously in the paper, ranchers and the government used O’odham cattle theft from Anglo ranchers as one tool to justify the enclosure of the O’odham within a reservation. During this period, Anglo Cattle ranchers continued to encroach deeper and deeper into O’odham territory and scuffles began to break out.
In another classic example of the “blame the victim” tactic, a pro-enclosure story was printed in the Los Angeles Times, no doubt to build public pressure for the domestication of the “Wild Papago.” The story concerns a group of O’odham who had resisted an Anglo cattleman’s attempts to enclose one of their water sources. When these O’odham continually tore down the fence that this cattleman had built, the rancher filed a report with the local Indian Agency sheriff to have the men arrested. When the sheriff arrived to arrest the O’odham responsible for defending their water source, he was taken hostage. The sheriff was later released unharmed; however, the incident was used to make the argument that such troubles can only be expected to increase if the O’odham were not enclosed on a reservation where they could be more easily controlled and monitored. 41
The tactic of occupying and diverting natural water sources was one of the tools used by the Anglo settlers and government to destroy the self sufficiency of the O’odham and force them into reservations where they would be dependent on the government for their water and would thus be easier to control and monitor. Some of the O’odham clearly understood what was happening, which is evidenced by instances of resistance both to the enclosure of natural water sources as well as resistance to the drilling of wells. One example of the U.S. government using water as a tool of forced cultural assimilation can be found by looking at an event recorded by an O’odham calendar stick 42 keeper. In 1912, the O’odham residing in the village of Santa Rosa, an isolated and traditional village in the western desert region of O’odham territory, were paid a visit by an Anglo Indian Commissioner who wished to drill a well for them. The Chief of the village objected to the drilling of the well on the grounds that it would disturb their culture, their autonomy and their self-sufficiency. The government agent proceeded to have the well drilled anyway. Upon completion of the well, the Chief of the village, according to the calendar stick keeper, stated that
“the well must be left alone and, in order that the Papagos might continue their old life, water must still be carried from the spring in the foothills.” 43
However, the prohibition by the Chief could not be upheld due to the overwhelming convenience of the new well and after a period of abstaining from its usage, the village of Santa Rosa (including the Chief) gave in and thus was assimilated into the industrial system by being made dependent on the Government well. 44 During this same time period, encroaching Anglo farmers engaged in the diversion of O’odham water sources to irrigate their farms. This practice served as another method of forcing the self sufficient O’odham into a relationship of dependence upon the government. In many areas so much water was diverted that the O’odham could no longer grow their traditional summer crops. 45
In 1919, the first incarnation of an O’odham reservation to enclose the nearly two million acres of desert that the “Wild Papago” were residing in was established. The formation of the desert O’odham reservation in 1919 ushered in a period of exponentially increased government interference in O’odham matters, and of course, the various forms of coercive assimilation were multiplied. By 1933, thirty-two unwanted wells were drilled all over the new reservation. 46 The well drilling was often opposed by those who were trying to maintain the O’odham Him’dag – the traditional ways of the desert people.
Resistance and Collaboration: O’odham Responses to Forced Modernization
In contrast to the traditional O’odham who had maintained resistance to cultural assimilation for the past 300 years, there was also a small number of O’odham based in the new reservation that welcomed collaboration with the forces of Anglo modernization and advocated for cultural accommodation and in some instances for total cultural assimilation. These men would later form an organization called the Papago Good Government League, which would serve as the propaganda arm of the Bureau of Indian Affairs and government policy in general. The leadership of this new faction had been taken from their families as youths and placed in Protestant boarding schools to be culturally indoctrinated. The Tucson Presbyterian Training School was one of the indoctrination centers where many future members of the Good Government League had been sent. 47
Religious indoctrination, whether Catholic or Protestant, has always been one of the most powerful tools of colonization and its justification used by European invaders against the indigenous peoples of the Americas. The necessary counterpart to the forced indoctrination of Christian principals and morals has always been the repression of indigenous spiritual practices. The United States government understood the profound power that traditional spiritual practices had in maintaining group solidarity and cohesion and it is for this reason that such spiritual practices were made illegal and repressed historically. In 1883, a Court of Indian Offenses was established by congress at the request of Secretary of Interior Henry M. Teller to eliminate traditional spiritual practices. In a report to the commissioner of Indian Affairs, Teller laid out his goals and his rationale stating that,
“If it is the purpose of the Government to civilize the Indians, they must be compelled to desist from the savage and barbarous practices that are calculated to continue them in savagery….”
Teller went on to associate those who resisted the repression of their spirituality with the “non-progressive” faction of Indians and labeled traditional spiritualism as “debauchery,” “diabolism,” and “savagery.” The overarching argument of his letter is that in order to civilize the Indians and bring them into the industrial system, their traditional spiritualism must be destroyed. As an initial step towards this end, Teller advised that Medicine Men be “compelled” to desist from their practice of “deception.” 48
Although the Court of Indian Offenses advocated that coercion be used to repress and destroy indigenous spiritualism, it failed to succeed in this project even when it used force to try to stop traditional spiritual rituals. According to Historian Edward Spicer, the only thing the Court succeeded in doing was driving traditional spiritual practices underground. In the case of many resistant O’odham, traditional spiritual practices were continued without regard to regulations or prohibitions against them, and in many cases, federal authorities resorted to repression and arrest to try to stop these practices. One traditional spiritual practice of the O’odham which was particularly hated by the Protestant Missionaries and Indian Agents was the Vi-kita ceremony.
The Vi-kita ceremony of the O’odham has been written about and studied by many Anglo historians and anthropologists, the most prominent being Columbia Anthropologist Ruth Underhill. 49 Before going into a short description of the Vi-kita it is important to understand that this ceremony varied depending on who was conducting it and where it was being conducted. Peter Blaine, an influential O’odham man sympathetic to the traditional ways, wrote in his autobiography about Underhill’s methods. Blaine explained the traditional way for the O’odham to tell about their past was to do it
“in a group so that everybody had a chance to talk and tell it their way. Underhill was talking to just one man…Dr. Underhill was wrong all the way in how she got her information.” 50
As scholars from the dominant culture often do, Underhill had applied her own notions of hierarchy, authority and individualism to her work with the O’odham and totally disregarded their traditional methods of conveying information in a communal fashion.
The Vi-kita itself was a yearly rain and fertility festival preformed to initiate and give thanks for the yearly summer rains. The ceremony itself consisted of the communal singing of rain songs, dancing, intimate encounters, and the consumption of Navait (Saguaro wine), an alcoholic drink made by the fermentation of Saguaro Cactus buds. The consumption of this wine was meant to symbolize the connection between the sky and the earth. The intake of the Navait was representative of the earth’s intake of rain. Participants drank Navait until vomiting occurred as this act embodied the clouds issuing forth rain unto the earth. It was a powerful ceremony that bonded the O’odham with the elements of nature.
When Protestant missionaries, and a small number of Protestant O’odham in the Good Government League, backed by U.S. Indian Agents, began their attempts to usurp power on the newly formed western O’odham (Sells) 51 reservation in the early 20th century, one of the first things they attacked was the practice of the Vi-kita ceremony. In the early 1930s, Peter Blaine explained that the traditional O’odham from the San Xavier reservation would travel to the western reservation for the Vi-kita. He states that,
“In the late 1920s the government tried to stop this wine drinking ceremony on the Sells reservation. But no Papago or Agency police could ever stop it.”
In one instance Blaine tells the story of how he helped defend three traditional O’odham Vi-kita ceremony leaders when they were arrested by agents from the Indian Bureau and jailed in Tucson. During the trial, a group of Protestant O’odham men from the Good Government League 52 argued for the repression of the ceremony – one of these men, Richard Hendrix, would continue to plague the traditional O’odham in future encounters. To respond to the collaborationist Good Government League, the resistant traditional O’odham formed the League of Papago Chiefs to counter the attempts of the Protestant Good Government League to usurp control on the reservation. 53
The Indian Reorganization Act and O’odham land rights
On June 18th, 1934, President Roosevelt signed into law the Indian Reorganization Act which finally stopped the forced allotment process initiated by the Dawes Act in 1887. The Indian Reorganization Act was viewed by its proponents as being in the best interests of the Indians. One of the reasons for this view was the fact that the Dawes Act and its forced allotment provisions had resulted in the loss of 90,000,000 acres of tribal lands and it was hoped by some, including then Indian Commissioner John Collier, that the Indian Reorganization Act could be used to regain some of this lost land.
The public was also encouraged to view the Indian Reorganization Act as being beneficial for Native Americans. A large article in the Los Angles Times entitled “The Bill to Return Indian Rights” stated that:
“After a century of graft, plunder and injustice, this bill has the objective of handing their own souls back to the Indians.” 54
However, such optimism and notions of cultural relativism were not held by all. As a precursor to the Indian Reorganization Act, a report was prepared for the Secretary of the Interior in 1928 to lay out the need for a change in Federal Indian Policy. The report stated that the “great majority of Indians are ultimately to merge into the general population” and that it was the government’s responsibility to assimilate Native Americans into “white civilization” because “the hands of the clock cannot be turned backwards.” Sympathetic attempts to help Native Americans retain their culture were stigmatized as attempts to “preserve them as museum specimens.” 55 Indian Commissioner John Collier was one of those who believed that Native Americans should retain their culture and that “the awakening of the racial spirit must be sustained….” 56 However, although the finalized Indian Reorganization Act did contain elements that were meant to “help” Native Americans, many of its articles were still designed to impose “civilized” systems on Native Americans.
It can be argued that the intent of the finalized Indian Reorganization Act was to initiate a new chapter in the push for the total cultural assimilation of the Native American tribes. The argument that there was no qualitative change between the Dawes Act and the Reorganization Act is legitimate. The Indian Reorganization Act provides the examples for the argument. The main tool of assimilation in the Indian Reorganization Act was the provision in Section 17 which allowed for Native American tribes to form their own tribal governments, constitutions and laws which, although it is not specifically stated, were intended to be Anglo in structure and functioning. In the case that these native governments were not sufficiently acceptable to the U.S. government, section 17 also provided that all Tribal Government formations must be “approved by the Secretary of the Interior.” 57 This clearly shows that the intent of the Act was not to allow Native Americans to become fully autonomous, either culturally or politically. For a tribe such as the O’odham, which had a long history of decentralization and consensus decision making, the imposition of western style liberal democracy, with its attendant centralization and majority rule system, was an obvious method of forced cultural indoctrination. Peter Blaine, who was mentioned earlier, was an O’odham man who had sympathy for the traditional, decentralized and communal way of O’odham societal organization. When the collaborationist Papago Good Government League began to maneuver themselves into the position of representing all of the O’odham, Blaine took it upon himself to lead the charge to discredit their assertions to business interests and the Federal Government that they represented the O’odham. Blaine wrote that:
“This so-called council represented only their own church people, but they took it upon themselves to become a council for all Papagos. They had meetings. Nobody attended them but these four guys because most people didn’t recognize them as leaders.” 58
In 1934 Blaine, along with another O’odham from the Gila Bend reservation named Leon Pancho became the first O’odham to travel to Washington D.C. These two men were sent as representatives of the traditional chiefs of the O’odham villages to argue against a recent court order that closed the Sells reservation to outside, Anglo owned, mining. The court order was a result of a lawsuit brought by the members of the Good Government League, including Richard Hendrix, who had teamed up with outside lawyers. These lawyers were to receive as payment a ten percent share of all land reclaimed from the mining companies, or a monetary equivalent. As this entire procedure was done behind the backs of the majority of the O’odham, when it was revealed, there was great resentment towards the Good Government League by many of the O’odham.
While in Washington D.C., Blaine was informed of the pending Indian Reorganization Act, and he became a supporter of the Act due to its provision allowing for the self government of Native Americans, as well as a provision in section Six that allowed the Secretary of Interior to manage mineral, mining, and livestock on the reservation. 59 In the case of the O’odham this meant that the reservation would be re-opened to mining and they would regain an important means of economic sustenance. According to Blaine, the mines were an important economic resource for the O’odham as they provided jobs and a market where beef and other O’odham products could be sold. 60 This is yet another unfortunate example of how the incursion of Anglo industrial technology served to destroy the self-sufficiency of the O’odham by making them dependent on it for survival.
Whether or not the mines were truly in the best interest of the O’odham is a complex topic which cannot be dealt with here. However it should be stated that Blaine and his companions’ trip to Washington D.C. was financed by the Tucson Chamber of Commerce, an organization that functioned in support of the mining interests, not the O’odham. This Tucson Chamber of Commerce was the same organization that had aggressively petitioned President Wilson to rescind his 1916 act forming the Sells reservation because it prevented Anglo agricultural interests from exploiting the area’s “best agricultural and grazing lands.” 61
Resistance to and Collaboration with the “White Man’s War”
Not long after the passage of the Indian Reorganization Act and the formation of the first O’odham Tribal Government, the United States declared war on Japan, thus entering World War II. The participation of Native Americans in World War II has been well publicized, especially the role the Dineh (Navajo) played as code talkers in the South Pacific. The United States government and the mainstream media portrayed Native Americans as being eager to fight for their homeland, and eager to assimilate into “white civilization” once they returned from the war. Nearly 25,000 62 Native Americans served in the United States military during World War II, many of whom were no doubt under the impression that their service would be rewarded with increased “rights” after the war’s end. Instead, as a “reward” for Native Americans participation in World War II the United States government established the Indian Claims commission in 1946 to legalize the U.S. occupation of Native American Lands never granted to the U.S. by treaty, passed House Concurrent Resolution 108 to terminate tribal recognition as separate entities from the Federal Government, and then instituted a plan in 1954 to relocate Native Americans off the reservation and into “Indian Ghettos” in the nation’s large cities. 63 These were the “rewards” for participation in World War II.
Like many other Native American Tribes, some of the O’odham Nations members participated in World War II. Ruth Underhill claims that the O’odham enlisted to serve in World War II “in droves” 64 and it is documented that the O’odham tribal government bought $10,000 in war bonds. 65 However, the extent of this involvement was distorted by the media, academia, and even some of the O’odham leaders in the tribal government. Richard Hendrix, a former member of the collaborationist Good Government League, had risen to prominence in the new O’odham tribal government by this time and was interviewed by the Arizona Archaeological and Historical Society on November 16, 1942. In this interview Hendrix exposed the extent to which he had allowed his mind to be colonized and assimilated into that of the dominant white culture. Speaking of colonization in general and World War II in particular, Hendrix stated that the O’odham had:
Learned to love the American government and they learned to love the Stars and Stripes. And when the war came and the time came for our boys to be registered, there was no exception. They registered just the same as white boys did. And now they are out fighting alongside the white boys, the American boys. They are just as anxious as the white boys to kill as many Japs, to kill as many Germans, and they are very anxious to win this great war so that the Papago people in this desert land may continue to enjoy the freedom of their homes. 66
Hendrix’s internalization of white supremacist racial notions is a heart breaking and shocking example of the extent to which he had accepted the ideology of “white civilization.” In addition, his assertion that every O’odham boy registered for the war with “no exception” is glaringly false.
Aside from the fact that there are always exceptions to everything, there was also a large scale organized resistance to World War II led by an old Chief and medicine man, Pia Machita, and his band of traditional O’odham who resided in an isolated village in the north western area of the Sells Reservation known as the Hickwan district. According to Peter Blaine, the O’odham residing in some of the most isolated villages in the Hickwan district had not seen a white man until the 1930s, and continued to practice the traditional O’odham Him’dag. 67 When Pia Machita was informed of the compulsory registration of young O’odham boys for induction into World War II, he instructed the youth of his village to refuse to sign the registration forms when they were visited by the local Indian Agent. Pia Machita was a very traditional leader who refused cultural assimilation and would not accept the authority of the Bureau of Indian Affairs or the O’odham tribal government. Finally, after all efforts to persuade Pia Machita’s village to register had failed, the tribal chief of police and a gang of Federal Marshals led by U.S. Marshall Ben McKinney invaded the village at two in the morning on October 16th, 1941, with tear gas bombs and guns drawn – when the Marshals attempted to take Pia Machita into custody some of the young men from the village used force to liberate him and severely beat one of the federal marshals. In the face of this resistance, the government agents and their local collaborators retreated to Tucson. When the Attorney General’s Office heard of the resistance on the O’odham reservation, they immediately got involved in the effort to repress this draft resistance movement as quickly as possible to prevent its possible spread to other reservations. By May 17th, 1941, after a period of about six months of trying to track down Pia Machita and his small band of men, Marshall McKinney and O’odham collaborators including Jose Ignacio from the tribal government, surrounded Pia Machita in the village of Stoa Pitk and took him into custody without incident. 68
Peter Blaine was the O’odham tribal chairman during the time that Pia Machita was leading the draft resistance movement. Although he did not believe that Pia Machita and his men were threats in any way, he was annoyed by what he perceived to be their stubbornness and attributed their draft resistance to his belief that they “didn’t really understand what they were doing.” 69 In reality, it was Blaine who did not understand the reasons behind Pia Machita and his men’s resistance to enlistment. Pia Machita and his men understood very well what they were doing – they were resisting giving aid to a government that they understood was their enemy. Given this understanding, and given the dictionary definition of the word “collaboration,” it becomes necessary to label those O’odham who participated in the arrest of Pia Machita as such – collaborators. The understanding that the U.S. government was the enemy of the traditional O’odham of the Hickwan district was based upon a long history of attempts by the U.S. government to force the Traditional O’odham of that area to abandon the Him’dag and embrace elements of Anglo “progress” such as dams, railroads, wells, and the protestant religion. Despite Peter Blaine’s inability to understand why the O’odham in the Hickwan district rejected Anglo-civilization in its totality, he still maintained sympathy for the people there. When Pia Machita and two co-defendants were finally sentenced to serve 18 months in prison at Terminal Island Federal Prison for their roles in leading the resistance movement, Peter Blaine eventually came to their aid and used his connections as tribal chairman to persuade the sentencing Judge to release Pia Machita early and allow him to return to the reservation and his family. 70
Conclusion
The history of the O’odham’s contact with the United States government has been one marked by a persistent current of resistance to cultural assimilation into “white civilization.” This resistance has included a variety of tactics and actions. The favored tactic of resistance to assimilation for many of the O’odham groupings seems to have been that of avoidance and feigned accommodation to Anglo culture when expedient. However, as was evidenced by the O’odham’s early history of contact with the Spanish, they did not refrain from waging armed resistance to colonization when they were pushed into a situation where other tactics might have been ineffectual.
In addition to resistance and accommodation, it has also been shown that some of the O’odham choose to engage in direct collaboration with the Anglo colonization of their lands and minds. As this paper has shown, the levels of collaborative activity amongst the O’odham varied, and so did the effects of such collaboration. When investigating instances of collaboration it is always important to understand the context which produced them and to remember that the ultimate blame for a situation of oppression should always be placed upon the group committing the acts of repression – in this case the United States government and allied business interests. It is important to show such examples of collaboration and to understand that all human cultures who have been the victim of colonization have invariably contained individuals who chose to collaborate for a variety of reasons. The O’odham are no exception to this rule. Making apologies for collaboration or failing to mention the instances where such collaboration did occur creates a historical distortion and does nothing to aid present struggles for liberation.
The O’odham responses to colonization never represented a totality, but a strong current of resistance is evident throughout their history. In regards to the United States government, it can be said, given the primary sources looked at, and the final drafts of laws signed and policies followed, that the intent of the United States government toward all Native American tribes, when it was not outright genocidal, has been the cultural destruction and absorption of remaining Native Americans into the dominant industrial culture of “white civilization.” Regardless of the varying tactics used, and the various lip service about “best interests” and “justice,” it has been shown that there has never been a qualitative change in United States policy toward the O’odham people and Native Americans in general. The O’odham have maintained aspects of their traditional culture despite the best efforts of the government to force assimilation, not as a result of such efforts. A continuing current of struggle between the forces of colonization and resistance has persisted for centuries, in all its various forms, within the minds and bodies of many O’odham and will continue until liberation.
NOTES:
1
This date is based on archeological evidence gathered by E.W. Haury in Ventana Cave. Haury, E.W. The Stratigraphy and Archeology of Ventana Cave Arizona. Tuscon: University of Arizona Press, 1950. Cited from Williams, Thomas R. “The Structure of the Socialization Process in Papago Indian Society.” Social Forces, Vol.36, No.3. p.253.2
Fontana, Bernard L. Of Earth and Little Rain: The Papago Indians. Tuscon: University of Arizona Press, 1989. pp.37-39.3
The name “O’odham” is roughly translated as “the people” in the Piman dialect spoken by the various O’odham groupings.4
In 1986 the tribal government of the Papago reservation officially changed its name to the Tohono O’odham Nation.5
The term “civilized” is a problematic historical term, and its definition tends to be very subjective. The meaning of the term and its use as a label is heavily influenced by how the author and the reader understand its meaning. For the purposes of this paper, the term “civilized” refers to the totality of the “western” cultural, political, and economic system – and most importantly the belief that technological/industrial progress is inherently beneficial and liberatory. For most, being labeled “civilized” is viewed as a positive and the label of “un-civilized” or “savage” is viewed in the reverse. However, for the purposes of this study it is imperative to understand that this author views “civilization” itself as an inherently oppressive and destructive entity, and this must be kept in mind to correctly understand the arguments and analyses in the paper.6
The term “soft power” refers to the concept of gaining influence and control over another group by means of the attraction of the dominating group’s cultural attributes and the use of commodification rather than using military might and coercion (“hard power”) to gain that influence. See Joseph S. Nye, Jr. Soft Power: The means to success in world politics. New York: Perseus Books, 2004.7
Erickson, Winston T. Sharing the Desert: The Tohono O’odham in History. Tucson: University of Arizona Press, 2003.8
Fontana, Bernard L. Of Earth and Little Rain: The Papago Indians. Tucson: University of Arizona Press, 1989.9
According to Catholic missionary records, the numbers of mission O’odham during this time period were somewhere around 2,000. However, according to population estimates there were at least 10,000 O’odham peoples living in this area. See Fontana, Bernard L. Of Earth and Little Rain . pp.11,46.10
Fontana, Bernard L., p.40.11
It is well documented that many of the Missions resorted to physical abuse, forced confinement and occasional murder to coerce the O’odham into compliance. San Xavier del Bac, the largest and most famous of Catholic missions in O’odham lands was built with forced labor. See Daniel McCool; “Federal Indian Policy and the Sacred Mountains of the Papago Indians.” Journal of Ethnic Studies 9.3 (1981).p59.12
Erickson, Winston P., p.66.13
Fontana, Bernard L., pp.61-64.14
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Feb 2nd, 1848. United States Statutes At Large, pp. 922-94315
For a detailed treatment of this series of events see; Garber, Paul N. The Gadsden Treaty. Glouchester: Peter Smith, 1959.16
For more information on the removal of the Seminole; Stannard, David E. American Holocaust: The Conquest of the New World. New York: Oxford University Press, 1992. P.124. For additional information about the Seminole Wars see; Churchill, Ward. “A Little Matter Of Genocide: Holocaust and Denial in the Americas 1492 to the Present.” San Francisco: City Lights Books, 1997.17
All dates for the political appointments of James Gadsden are cited from Paul Garber’s “The Gadsden Treaty.” Pages 74-81.18
Racial Anglo-Saxonism was a belief popular in the later 19th century which held that Europeans of Anglo-Saxon descent were at the forefront of evolution and were responsible to bring civilization to the world. This ideology was used as a convenient justification for the extermination and removal of Native Americans. For a detailed study of this ideology see: Horsman, Reginald. Race And Manifest Destiny: The Origins of American Racial Anglo-Saxonism. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1981.19
For a detailed investigation of the role that the railroads played in the Gadsden purchase see; Schmidt, Louis B. “Manifest Opportunity and the Gadsden Purchase.” Arizona and the West, vol.3 (autumn 1961).20
Forbes, Jack D. The Papago-Apache Treaty of 1853: Property Rights and Religious Liberties of the O’odham, Maricopa and Other Native Peoples. Davis: Native American Studies Tecumseh Center, U.C. Davis, 1979. p.1.21
United States Congress. Joint Special Committee. Condition of The Indian Tribes. Report of the joint special committee, appointed under joint resolution of March 3, 1865. With an appendix. Washington, D.C.: United States Government Printing Office, 1865.22
Erickson, p.7723
During this time period many treaties were negotiated with native tribes in the regions west of the Mississippi to gain legal justification for the United States’ theft of their lands. For a detailed list of treaties signed between the United States and Native American tribes, see the compendium edited by Charles J. Kappler. Indian Affairs: Laws and Treaties. 7 volumes. Washington, D.C.: Unites States Government Printing Office, 1903-4.24
Spicer, Edward H. Cycles of Conquest: The Impact of Spain, Mexico, and the United States on the Indians of the Southwest, 1533-1960. Tucson: The University of Arizona Press, 1962. p.138.25
“Arizona News; Papago Cattle-thieves Brought to Justice.” Los Angeles Times. Feb 1, 1894. Also see: “Arizona News; Report Showing the Depredations Committed by Papago Indians on Stockmen’s Herds.” Los Angeles Times. June 8, 1895, In addition see; “Arizona News: Papagoes Destroying Cattle in Large Numbers.” Los Angeles Times. Mar 23, 1894.26
Kehoe, Lawrence. “Our New Indian Policy and Religious Liberty.” Catholic World, vol. 26 (Oct. 1887). P.96.27
Erickson p.78.28
“Tucson And Fort Lowell; Notes of a Visitor – The Church of San Xavier.” Los Angeles Times. Nov 18, 1882.29
The Spanish had brought the adobe style of construction to the O’odham but, although the resources for adobe construction were readily available to the O’odham at San Xavier, they continued to build their traditional grass huts.30
For a detailed study of traditional O’odham tribal structure and life style see; Underhill, Ruth M. Social Organization of the Papago Indians. Columbia: Columbia University Press, 1939. ________. Papago Woman. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1979.31
For the most part, traditional Native American societies exhibited gender parallelism and were rarely if ever patriarchal by definition. For a detailed study of gender in Native America see: Allen, Paula G. The Sacred Hoop: Recovering the Feminine in American Indian Traditions. Boston: Beacon Press, 1986.32
All direct quotations from Dawes Act. General Allotment Act (Dawes Act). February 8, 1887. Printed in its totality in: Prucha, Francis, P. ed. Documents of United States Indian Policy. 3rd ed. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000.33
U.S. Congress, House Committee on Indian Affairs, Lands in Severalty to Indians: Report to Accompany H.R. 5038, 46th Cong., 2nd sess., May 28, 1880, H. Rept. 1576, pp.7-10. Reproduced in: Washburn, Wilcomb E. The Assault on Indian Tribalism: The General Allotment Law (Dawes Act) of 1887. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Co., 1975.34
Letter from Henry L. Dawes to Henry M. Teller (Commissioner of Indian Affairs), September 19, 1882. Dawes Papers, Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. Reproduced in: Washburn, Wilcomb E. The Assault on Indian Tribalism: The General Allotment Law (Dawes Act) of 1887. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Co., 1975.35
Washburn, Wilcomb E. The Assault on Indian Tribalism: The General Allotment Law (Dawes Act) of 1887. P.12.36
Washburn, p.16.37
Fontana, pp. 77-79.38
Erickson, p. 92.39
“Baboquivari Peak.” Los Angeles Times. Nov 4, 1894.40
The term “Wild Papago” was a term used by the government and media to marginalize those O’odham who continued to resist “civilization.”41
“The Indian War Cloud.” Los Angeles Times. May 22, 1885.42
The Calendar Stick was a device used by the O’odham as a tool to aid in the remembering of their history. The Calendar Stick itself was a cactus stick on which notches were carved at various intervals which aided the history keeper in the remembrance of events.43
Fontana, p.54.44
This example is meant to show the insidious nature of industrial technology and is not intended to place any blame on this specific group of O’odham for their ultimate choice to begin using the well. This example is given to show how industrial technology always comes with strings attached. In this case, once the village becomes dependent on the well they in turn become dependent on the Anglo civilization which is needed to maintain the functioning of such a well, and thus become less able to resist other Anglo incursions. In addition it must be pointed out here that the traditional water gathering procedure talked about was preformed by O’odham women. Due to this fact, some may feel that by resisting the building of the well, the male O’odham are in fact seeking to perpetuate patriarchy. It is true that the O’odham did have a system of gendered roles, but the overall system made room for exceptions and is best characterized as one of gender parallelism, not patriarchy. It is the Anglo industrial system that brought patriarchy to the O’odham. For more information see: Underhill, Ruth. Papago Woman. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1979. Also see: Allen, Paula G. The Sacred Hoop: Recovering the Feminine in American Indian Traditions. Boston: Beacon Press, 1986.45
Forbes, Jack D. The Papago-Apache Treaty of 1853: Property Rights and Religious Liberties of the O’odham, Maricopa and Other Native Peoples. Davis: Native American Studies Tecumseh Center, U.C. Davis, 1979. pp..5-8.46
Spicer, p. 140.47
Spicer, p.141.48
All quotes taken directly from: House Executive Document no.1, 48th Cong., 1st sess., serial 2190, pp.x-xii. Reproduced in; Prucha, Francis, P. ed. Documents of United States Indian Policy. 3rd ed. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000.49
For a detailed account of the Vi-kita see: Davis, Edward H. The Papago Ceremony of Vikita. New York: Museum of The American Indian, 1920. Also see: Underhill, Ruth. Papago Woman. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1979.50
Blaine, Peter. Papagos and Politics. Tucson: The Arizona Historical Society, 1981. p.42.51
The expansive western O’odham reservation was officially called the Sells reservation. It was named after the first Indian agent in the region, John Sells.52
The Good Government League was formed by a small group of Protestant O’odham who used the organization to advocate for the assimilation of the O’odham into Anglo civilization as well as to promote general U.S. Indian policy.53
Blaine, pp.40-50.54
“Bill To Return Indian Rights ” Los Angeles Times. June 8, 1934.55
Lewis Meriam et al., The Problem of Indian Administration. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press, 1928. Selection printed in: Prucha, Francis, P. ed. Documents of United States Indian Policy. 3rd ed. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000.56
Annual Report of the Secretary of Interior, 1934, pp.78-83. Reprinted in; Prucha, Francis, P. ed. Documents of United States Indian Policy. 3rd ed. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000.57
Wheeler-Howard Act (Indian Reorganization Act) June 18, 1934. U.S. Statutes at Large, 48:984-88. Re-printed in: Prucha, Francis, P. ed. Documents of United States Indian Policy. 3rd ed. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000.58
Blaine, p.50.59
Wheeler-Howard Act (Indian Reorganization Act) June 18, 1934. U.S. Statutes at Large, 48:984-88. Re-printed in: Prucha, Francis, P. ed. Documents of United States Indian Policy. 3rd ed. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000.60
Blaine, pp.50-53.61
McCool, Daniel. “Federal Indian Policy and the Sacred Mountains of the Papago Indians.” Journal of Ethnic Studies 9.3 (1981). p.62.62
Holm, Tom. “Fighting A White Mans War: The Extent and Legacy of American Indian Participation in World War II.” The Journal of Ethnic Studies. 9.2. p.70.63
For more on this aspect of the Indian Claims Commission, and a discussion about the termination act see: Forbes, Jack D. The Papago-Apache Treaty of 1853: Property Rights and Religious Liberties of the O’odham, Maricopa and Other Native Peoples. Davis: Native American Studies Tecumseh Center, U.C. Davis, 1979.64
Underhill, Ruth. Papago Woman. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1979. P.94.65
Blaine, p.115.66
Hendrix, Richard. Talk by Richard Hendricks, Prominent Papago Indian, Given at the Arizona Archaeological and Historical Society, November 16, 1942. The Kiva, vol. 8 (Nov. 1942).67
Blaine, p.92.68
Flaccus, Elmer. “Arizona’s Last Great Indian War: The Saga of Pia Machita.” The Journal of Arizona History, vol. 22 (1981).69
Blaine, p.101.70
Blain, pp.103-4.© 2004, REPRODUCTION FOR NON-PROFIT INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES IS ALLOWED
High Country Earth First Denver Meeting
 High Country Earth First is hosting the EF! ROADSHOW, in DENVER, May 25-26: Monday 2pm in Cheesman Park, and Tuesday 6pm at the Gypsy House.
High Country Earth First is hosting the EF! ROADSHOW, in DENVER, May 25-26: Monday 2pm in Cheesman Park, and Tuesday 6pm at the Gypsy House.
Four ongoing EF! projects in Colorado: DENVER: Stop I-70 Expansion through North Denver; SAN LUIS VALLEY: Halt gas drilling in Baca National Wildlife Refuge: and WESTERN SLOPE: Red Cliff mine campaign and Feral Futures (May 24 – June 7).
From “Rockslide,” High Country Earth First!
The need for resistance in solidarity with the wild has never been louder or clearer than it is today; the EF! roadshow is a great tool for growing that resistance. There are countless examples to draw from in the story of radical movements before us: militant labor organizing tours, anti-fascist resistance recruitment and international speaking tours to build cross-border solidarity. The origin of Earth First! itself is credited to a few roadshows that kicked it all off in the early 1980s. We are building on this tradition; akin to a fellowship crossing Middle Earth to amass insurgents to face Mordor head-on.
List-serves and websites aren’t enough
This Roadshow’s primary intention is to strengthen our radical grassroots ecological network. For almost 30 years, we have been an organized voice bridging conservation biology with grassroots community organizing, road blockading and eco-sabotage. In the past 5 years we have seen numbers and experience-level in the EF! movement decline drastically. Yet, our place has never been more urgent. New groups are popping up across the country, but they are detached from many of the groups, history, and skills that came before them. We can’t afford to stumble and make the same mistakes over again.We are at the tail end of a decade where corporate globalization rooted itself in the US and spread across the planet like a plague. And now that the reality of climate change is finally sinking into the mainstream consciousness, the same superpowers that pushed so-called ‘free trade’ policies to exploit wild nature more efficiently are promoting carbon trading in attempt to make a profitable industry out of the disasters they’ve created. The spineless Big Green environmental NGOs are scrambling for crumbs and cutting deals with the industry for shallow public relations victories. Earth First! must rise and recognize that it’s presence is a strong component of making the broader environmental movement truly effective. We are its spine, or as an EF! co-founder, Howie Wolke, has put it, we are the lions of a movement ‘ecosystem’. Our niche is critical, and its presence (or absence) is felt deeply by our surroundings.
We need to reconnect the multi-generational aspect of Earth First! that has fallen by the wayside in recent years. We need to broaden our network’s base—from radical rural grandparents to revolutionary urban youth. We need re-establish lost relationships with scholars and scientists who resonate with us. We need to re-inspire musicians and artists to contribute their passion to our battles.
When it comes down to it, solid movements are based on strong personal relationships; and real relationships don’t go very far over the internet. We need face-to-face interaction to build trust with—and support for—each other.
From EF! Here is a glimpse of ongoing local and national campaigns and projects related to EF!. They could all use your support in a variety of ways—from fundraising to showing up in person. Please contact the organizing groups directly to find out what they need most:
Northern California Redwood Defense
Since the fall of Maxxam/Pacific Lumber, forest defenders in the Redwoods have been directing attention on another logging empire: Green Diamond Resource Company (formerly Simpson). In the last 10 years they have clear-cut 52,000 acres of Northern California forests. They are killing off endangered Spotted Owls and have aspirations to sell off thousands of acres in Humboldt County for Salmon killing suburban development. We have set up multiple treesit villages to oppose the destruction, and we need your help TODAY.
www.efhumboldt.org
Appalachian Anti-Mountain Top Removal
The presence of coal plants are threats to the lives within both the human community and the mountain ecosystem. One of the most biologically flourishing areas of the world is being environmentally and socially impoverished by companies practicing mountain top removal. Mountain top removal clogs streams, destroys forests, threatens biodiversity and forces coalfield residents into the unjust choice between income and well-being.
www.blueridgeef.com
Stop I-69 in Indiana
I-69 is a NAFTA superhighway, already constructed from Canada to Indianapolis and projected to extend down into Mexico. This highway is intended for the mass transportation of goods and resources, to further exploit workers and the land, and to lessen companies’ accountability in terms of human and environmental rights. In 2008, they began construction of this road through southwestern Indiana, which will evict hundreds of rural families, destroy hundreds of acres of land, and devastate the habitats of countless species of animals, including the endangered Indiana Bat. www.stopi69.wordpress.com
Fight Development in the North Woods of Maine
The largest piece of undeveloped land east of the Mississippi is under attack. Plum Creek, the nation’s largest corporate landowner, is in the process of rezoning 20,000 acres of the Moosehead Lake region in Maine for luxury house and resorts, while trying to balance it off with a fraudulent conservation easement plan. This plan would still allow timber harvesting, commercial water extraction and the building of new infrastructure, among many other ecologically devastating practices. www.maineearthfirst.wordpress.com
Defend the Last Free-Roaming Wild Buffalo in Montana
The Buffalo Field Campaign (BFC) is the only group working in the field, everyday, to stop the slaughter and harassment of Yellowstone’s wild buffalo. Volunteers from around the world defend buffalo on their traditional winter habitat and advocate for their protection. Our daily patrols stand with the buffalo on the ground they choose to be on, and document every move made against them. Tactics range from video documentation to nonviolent civil disobedience. www.buffalofieldcampaign.org
Fight new Copper Mines and Roads in the Deserts of Arizona
Chuk’shon Earth First! is fighting the proposed Rosemont Copper Mine in the Santa Rita Mountains, which is greenwashing itself by claiming a need for increased copper extraction for the solar panel industry. The group is also opposing the expansion of I-10, part of the Department of Transportation’s “Corridors of the Future” program to increase capacity of global industrial commerce. The proposed I-10 Bypass would bisect wild/rural lands and facilitate more sprawl between Tucson and Phoenix. www.chukshonef.wordpress.com
Blue Mountain Biodiversity Project in eastern Oregon
Blue Mountains Biodiversity Project (BMBP) formed in 1991 to increase regional and national awareness of the Blue Mountains ecosystems, to ensure the protection for and reintroduction of diverse native wildlife species, to promote ecologically sound restoration and address the root causes of ecological and community instability. They have trained countless EF!ers is forest monitoring. They are one of the country’s premier grassroots ‘paper-wrenchers’, filing legal challenges that help make our blockades successful. They can be reached at 541-385-9167
Stop Florida Power & Light from trashing the Everglades
Everglades Earth First! (EEF!) have been battling FPL’s plans to build the country’s largest fossil fuel power plant in the Loxahatchee Basin; a headwaters to the remaining Everglades ecosystem. EEF! Is also challenging over 500 miles of new gas pipelines and 2 new Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) facilities. Get more details: www.evergladesearthfirst.org
Stop Gas Drilling in Western New York
There is a proposal on the table to begin one of the largest fossil fuel exploration projects in the country. This project would result hundreds of millions of tons of CO2 emissions, along with the impacts of pipelines, power plants, and new LNG storage facilities. Get in touch with Shale Shock: www.shaleshock.org
Bank of America, Stop Funding Coal!
A national campaign is well underway to stop Bank of America (BoA), who is the largest investor to Mountain Top Removal coal mining. The company recently offered lip-service to address their support for the coal industry, but have made no real steps towards cutting ties with King Coal. With BoA locations in cities across the U.S., this campaign can easily be supported in a decentralized fashion. Give ‘em hell! For more info: www.ran.org
No 2010 Olympics
The Native Youth Movement and other First Nations groups in occupied Canada have called for full-scale resistance to the Winter Olympics proposed in British Colombia. The Olympics proposal includes a mess of development, ski-resorts and infrastructure on indigenous land. Learn more at: www.no2010.com
Root Force
This project is a research database and strategic think tank for direct action intended to target corporate/colonial infrastructure, such as: roads, dams, power plants, and mines. Their website offers background information on transnational companies, government agencies and their local affiliations across the United States. www.rootforce.org
Air National Guardsmen are aiming Preditor and Reaper Drones from home
Bush has brought the Global War On Terrorism to American shores! Air National Guardsmen deployed at stateside bases are piloting and aiming the Predator and Reaper drones against peoples in Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and victims yet unreported. Do you doubt they might be Filipinos, Colombians, Bolivians and South Georgians? If any of those aforementioned want to defend themselves, they could only attack those shooting at them from Arizona, California, Nevada and Texas.
Residents of those states should know they are living in war zones if they live adjacent these installations. Do you know any of these soldiers? The specialists who guide and track the munitions directly to their target’s alarmed faces are called “Sensor Operators” and have been experiencing PTSD right at home!
214th Reconnaissance Group
Tucson, Arizona
163rd Reconnaissance Wing & 196th Reconnaissance Squadron
March Air Reserve Base, California
432nd Reconnaissance Wing
Creech Air Force Base, Nevada
14th Reconnaissance Wing
Ellington Field Joint Reserve Base, Houston, Texas
In case the CBS article is removed, we’ll mirror it here:
The Air National Guardsmen who operate Predator drones over Iraq via remote control, launching deadly missile attacks from the safety of Southern California 7,000 miles away, are suffering some of the same psychological stresses as their comrades on the battlefield.
Working in air-conditioned trailers, Predator pilots observe the field of battle through a bank of video screens and kill enemy fighters with a few computer keystrokes. Then, after their shifts are over, they get to drive home and sleep in their own beds.
But that whiplash transition is taking a toll on some of them mentally, and so is the way the unmanned aircraft’s cameras enable them to see people getting killed in high-resolution detail, some officers say.
“When you come in (with a fighter jet) at 500-600 mph, drop a 500-pound bomb and then fly away, you don’t see what happens,” said Col. Albert K. Aimar, who is commander of the 163rd Reconnaissance Wing here and has a bachelor’s degree in psychology. “Now you watch it all the way to impact, and I mean it’s very vivid, it’s right there and personal. So it does stay in people’s minds for a long time.”
He said the stresses are “causing some family issues, some relationship issues.” He and other Predator officers would not elaborate.
But the 163rd has called in a full-time chaplain and enlisted the services of psychologists and psychiatrists to help ease the mental strain on these remote-control warriors, Aimar said. Similarly, chaplains have been brought in at Predator bases in Texas, Arizona and Nevada.
In interviews with five of the dozens of pilots and sensor operators at the various bases, none said they had been particularly troubled by their mission, but they acknowledged it comes with unique challenges, and sometimes makes for a strange existence.
“It’s bizarre, I guess,” said Lt. Col. Michael Lenahan, a Predator pilot and operations director for the 196th Reconnaissance Squadron here. “It is quite different, going from potentially shooting a missile, then going to your kid’s soccer game.”
Among the stresses cited by the operators and their commanders: the exhaustion that comes with the shift work of this 24-7 assignment; the classified nature of the job that demands silence at the breakfast table; and the images transmitted via video.
A Predator’s cameras are powerful enough to allow an operator to distinguish between a man and a woman, and between different weapons on the ground. While the resolution is generally not high enough to make out faces, it is sharp, commanders say.
Often, the military also directs Predators to linger over a target after an attack so that the damage can be assessed.
“You do stick around and see the aftermath of what you did, and that does personalize the fight,” said Col. Chris Chambliss, commander of the active-duty 432nd Wing at Creech Air Force Base, Nev. “You have a pretty good optical picture of the individuals on the ground. The images can be pretty graphic, pretty vivid, and those are the things we try to offset. We know that some folks have, in some cases, problems.”
Chambliss said his experience flying F-16 fighter jets on bombing runs in Iraq during the 1990s prepared him for his current job as a Predator pilot. But Chambliss and several other wing leaders said they were concerned about the sensor operators, who sit next to pilots in the ground control station. Often, the sensor operators are on their first assignment and just 18 or 19 years old, officers said.
While the pilot actually fires the missile, the sensor operator uses laser instruments to guide it all the way to its target.
On four or five occasions, sensor operators have sought out a chaplain or supervisor after an attack, Chambliss said. He emphasized that the number of such cases is very small compared to the number of people involved in Predator operations.
Col. Rodney Horn, vice commander of the 14th Reconnaissance Wing at Ellington Field Joint Reserve Base near Houston, said his unit went out of it way to impress upon sensor operators the sometimes lethal nature of the job. “No one’s walking into it blind,” he said.
Master Sgt. Keith LeQuire, a 48-year-old sensor operator here, said the 163rd asks prospective sensor operators whether they are prepared for the deadly serious mission. “No one’s been naive enough to come in to interview but not know about that aspect of the job,” he said.
Unlike soldiers living together in the war zone, the Predator operators do not have the close locker-room-style camaraderie that allows buddies to talk about the day’s events and blow off steam. But many Predator operators at Creech employ a decompression ritual during the long ride home, said Air Force Lt. Col. Robert P. Herz.
“They’re putting a missile down somebody’s chimney and taking out bad guys, and the next thing they’re taking their wife out to dinner, their kids to school,” said Herz, a Ph.D. who interviewed pilots and sensor operators for a doctoral dissertation on human error in Predator accidents.
“A lot of them have told me, `I’m glad I’ve got the hour drive.’ It gives them that whole amount of time to leave it behind,” Herz said. “They get in their bus or car and they go into a zone _ they say, `For the next hour I’m decompressing, I’m getting re-engaged into what it’s like to be a civilian.'”
Col. Gregg Davies, commander of the 214th Reconnaissance Group in Tucson, Ariz., said he knows of no member of his team who has experienced any trauma from launching a Predator attack.
Himself a Predator pilot, Davies said he has found the work rewarding. The Arizona Air National Guard unit flies Predators in both the Iraq and Afghanistan war zones. It has often provided protection for American convoys, and its personnel have seen insurgents planting roadside bombs.
“If we can have an effect there where we can take people out, that’s a real plus in terms of saving American lives,” Davies said. “Our folks look at it as they’re in the fight, they’re saving lives. They don’t feel too bad about that.”
Stop the War in Iraq and BTTHN
Open National Conference to Stop the War in Iraq and Bring the Troops Home Now
Cleveland, Ohio, June 28-29, 2008
National Assembly Endorser List (Partial Listing)
( * = organization or position for identification only)1. Cindy Sheehan, Gold Star Families for Peace*
2. Howard Zinn, Author, Historian, Social Critic, Political Scientist, Playwright
3. U.S. Labor Against the War (USLAW)
4. Veterans for Peace
5. Vietnam Veterans Against the War, Utah Chapter
6. National Lawyers Guild
7. North Shore AFL-CIO Federation of Labor (Formerly Cleveland AFL-CIO)
8. Donna Dewitt, President, South Carolina AFL-CIO*
9. Navy Petty Officer Jonathan W. Hutto, Author of “Anti-War Soldier” and Co-Founder of Appeal For Redress*
10. Los Angeles County Federation of Labor, AFL-CIO, Los Angeles, CA
11. Progressive Democrats of America
12. A.N.S.W.E.R. Coalition (Act Now to Stop War and End Racism)
13. The Iraq Moratorium
14. United Teachers Los Angeles
15. Northeast Ohio Anti-War Coalition (NOAC)
16. Ramsey Clark, former U.S. Attorney General
17. Green Party of Ohio
18. Progressive Action, a coalition of the Duluth Central Labor Body, Democratic Farmer-Labor Party, and the Duluth Area Green Party
19. Scott Ritter
20. Anti-War Committee of the Thomas Merton Center, Pittsburgh, PA
21. Colia Lafayette Clark, Chair, Richard Wright Centennial Committee, Philadelphia, PA
22. Ohio State Council UNITE HERE
23. Women Speak Out for Peace and Justice – the Cleveland Branch of Women’s International League for Peace and Freedom
24. Chris Silvera, Secretary-Treasurer, Teamsters Local 808*, Long Island, NY
25. Cleveland Peace Action
26. Peninsula Peace and Justice Center, Palo Alto, CA
27. Greater Boston Stop the Wars Coalition (STWC)
28. John W. Braxton, Co-President, American Federation of Teachers Local 2026*; Faculty and Staff Federation of Community College of Philadelphia*
29. Eduardo Rosario, Executive Board, NY City Chapter – Labor Council for Latin American Advancement*
30. RI Mobilization Committee to Stop War and Occupation
31. Steve Early, Member, National Writers Union/UAW*, Labor Journalist
32. Bethlehem Neighbors for Peace
33. Northeast Ohio American Friends Service Committee
34. Cynthia McKinney, Former Congresswoman from Georgia
35. Allen Cholger, United Steelworkers Union Staff Representative*, Southfield, MI
36. Malcolm Suber, Reconstruction Activist; 2007 City Council Candidate in New Orleans, LA
37. Greg Coleridge, Coordinator, Northeast Ohio Anti-War Coalition; Economic Justice & Empowerment Program Director, Northeast Ohio American Friends Service Committee
38. Marilyn Levin, Member, Coordinating Committee, Greater Boston United for Justice with Peace; Founder, Middle East Crisis Coalition
39. Jeff Mackler, Founder, Mobilization for Peace, Jobs and Justice, San Francisco, CA
40. Jerry Gordon, former National Co-Coordinator of the Vietnam-era National Peace Action Coalition (NPAC); Member, U.S. Labor Against the War Steering Committee, Cleveland, OH
41. Barbara Lubin, Director, Middle East Children’s Alliance
42. Jamilla El-Shafei, Kennebunkport, Maine, (the Kennebunkport Peace Department)
43. Mumia Abu-Jamal
44. Alan Netland, President of the Duluth Central Labor Body and AFSCME Local 66*
45. Will Rhodes, Chair, Minnesota 8th Congressional District, Green Party; Steering Committee of the Duluth Area Green Party
46. Leonard Weinglass, Attorney for the Cuban Five
47. Gail Schoenfelder, Co-Chair, Clayton-Jackson-McGee Memorial; Board Member of the Duluth League of Women Voters*
48. California Peace and Freedom Party
49. Greater Cleveland Immigrant Support Network
50. Wasatch Coalition for Peace and Justice of Northern Utah
51. Alan Benjamin, Member, Executive Board, San Francisco Labor Council; Member, National Steering Committee, U.S. Labor Against the War
52. Rev. Dr. Diana Gibson, Co-Director, Council of Churches of Santa Clara County, San Jose, CA*
53. Sacramento Chapter, Labor Council for Latin American Involvement (LCLAA), AFL-CIO, Sacramento, CA
54. Iranians for Peace and Justice, CT and Texas Chapters
55. Youth Against War & Racism, MN
56. Samina Faheem, Executive Director, American Muslim Voice
57. National Education Association Peace and Justice Caucus
58. Union de Trabajadores Inmigrantes (Union of Immigrant Workers), Madison, WI
59. The L.A. Palestine Labor Solidarity Committee, Los Angeles, CA
60. San Jose Peace and Justice Center
61. Andy Griggs, Board of Directors, United Teachers Los Angeles; Chair, National Education Association Peace and Justice Caucus; Continuations Committee, American Federation of Teachers Peace and Justice Caucus*; Steering Committee Member, U.S. Labor Against the War, Los Angeles, CA
62. Office of the Americas, Los Angeles, CA
63. Fernando Suarez del Solar, Founder and Director, Guerrero Azteca Peace Project Escondido, CA
64. Doug Bullock, 1st Vice President, Albany Federation of Labor and Member of the Albany County Legislature
65. Arlington (MA) United for Justice with Peace
66. Sarah Martin, Member, Women Against Military Madness, MN
67. Paul Krehbiel, Iraq Moratorium, Los Angeles, CA
68. Sharon Smith, Haymarket Books
69. Francesca Rosa, Member SEIU Local 1021, Delegate, San Francisco Labor Council*, Member, Bay Area Labor Committee for Peace and Justice*
70. National Benedictines for Peace
71. Elizabeth Aaronsohn, Professor of Education and Faculty in the Peace Studies Program*, Central CT State University, New Britain, CT
72. Adirondack Progressives
73. Pam Africa, International Concerned Family and Friends of Mumia Abu-Jamal and Move Organization
74. AfterDowningStreet.org
75. Kali Akuno, Member, Malcolm X Grassroots Movement, Gulf Coast Reconstruction Movement activist, New Orleans, LA*
76. Richard Brooks Alba, Co-Chair Emeritus, SF Pride at Work (AFL-CIO), Berkeley, CA
77. Mike Alewitz, Labor Art and Mural Project, New Britain, CT
78. All-African People’s Revolutionary Party (G-C), Washington, D.C.
79. Stephen Allen, Steve Allen Painting, Akron, OH
80. Alliance for Global Justice
81. Dr. Sabah Alwan, Associate Professor of Leadership & Organizational Behavior, College of St. Scholastica, Duluth, MN
82. American Federation of Musicians Local 1000, NY, NY
83. Andy Anderson, Veterans for Peace, Chapter 80
84. Jeff Anderson, Duluth City Councilor
85. Thomas Atwood, Community Organizer, Peninsula Interfaith Alliance (PICO); Unitarian Universalist Fellowship of Redwood City, CA*
86. Mark Bailey, member and seminary student, United Church of Christ*, Elyria, OH
87. Jared A. Ball, Producer, Independent/Mixtape Journalism: FreeMix Radio, Words, Beats and
Life Global Journal of Hip-Hop Culture, Washington, D.C.*
88. Russ Banner, Co-Coordinator, Pax Christi – Manasota Chapter, FL
89. Hans Barbe, Iraq Moratorium, Students for a Democratic Society, Grosse Pointe Park, MI
90. Ana Barber, UTLA Board of Directors, Long Beach, CA
91. Bay Area United Against the War
92. Karen Bernal, International Longshore Workers Union Project Organizer, San Francisco, CA
93. Dennis Bernstein, Producer Flashpoint/KPFA Radio, Berkeley, CA
94. Marcia Bernsten, North Shore Coalition for Peace & Justice, Evanston, IL
95. Prof. Hal Bertilson, Professor of Psychology and UWS Psychology Program; Coordinator; Member, Amnesty International; Unitarian Universalist Congregation of Duluth Peace and Justice Committee
96. Thomas Bias, President, Northwest New Jersey Peace Fellowship
97. Stephen Bingham, Attorney, Political Activist, San Francisco, CA
98. Bloomington Peace Action Coalition, Nashville, IN
99. Roy Blount, President, Taxi Workers Alliance of Pennsylvania
100. Iver Bogen, Progressive Action Secretary, Duluth, MN
101. Scott Bol, St. Croix Valley Peacemakers, Stillwater, MN
102. Bolivarian Circle of Los Angeles “Ezequiél Zamora”, Sherman Oaks, CA
103. Blasé Bonpane, Director, Ofice of the Americas, Los Angeles, CA
104. Theresa Bonpane, Executive Director, Office of the Americas, Los Angeles, CA
105. Boston May Day Coalition, http://www.bostonmayday.org
106. Laura Bothwell, Founder of the St. Scholastica College Democrats; Former Director, Programs at the Columbia Univ. Center for the Study of Science and Religion; NY, NY
107. Frank Boyle, Wisconsin State Representative, 73rd Assembly District
108. Patrick Boyle, Progressive Action Steering Committee, Duluth, MN
109. Heather Bradford, Co-Founder, Students Against War, College St. Scholastica
110. Lenni Brenner, Author, Zionism in the Age of the Dictators
111. Lyn Broach, Steve Allen Painting, Akron, OH
112. Brooklyn Greens, Brooklyn, NY
113. Don Bryant, President, Greater Cleveland Immigrant Support Network
114. Cafe Intifada, Los Angeles, CA
115. California Federation of Teachers
116. Joseph Callahan, member, Coalition to March on the Republican National Convention & Stop the War; Iraq Peace Action Coalition; Twin Cities, MN*
117. Campaign for Labor Rights
118. Campus Antiwar Network
119. Campus Anti-War Network, Fordham University Chapter
120. Michael Carano, Ohio Progressive Democrats of America State Co-Coordinator
121. Patrick Carano, Ohio Progressive Democrats of America State Co-Coordinator
122. Steve Carlson, Peace North, Northern Wisconsin Coordinator for the Iraq Moratorium Project
123. Mary Carmichael, Northwoods People for Peace, Ironwood, MN
124. Tim Carpenter, National Director, Progressive Democrats of America
125. Central CT State University Progressive Students Alliance, New Britain, CT
126. Central CT State University Peace Studies Program, New Britain, CT
127. Central Ohioans for Peace
128. Chapter 39 (Northeast Ohio) Veterans for Peace
129. Chatham Peace Initiative
130. Chelsea Unièndose en Contra de la Guerra, Chelsea, MA
131. Chicago Coalition Against War and Racism, Chicago, IL
132. Chicago Labor Against the War, an affiliate of U.S. Labor Against the War
133. Chicago Socialist Party
134. Chippewa County Anti-War Coalition, Dafter, MI
135. Jim Ciocia, Staff Representative, Ohio Council 8, American Federation of State, County and Municipal Employees (AFSCME)*, Cleveland, OH
136. Citizen Soldier
137. Cleveland Middle East Peace Forum
138. Coalition for World Peace (CFWP) – An affiliate of UFPJ, Los Angeles, CA
139. Code Pink, Pittsburgh Chapter
140. Columbus Campaign for Arms Control/For Mother Earth
141. Committee in Solidarity with the People of El Salvador (CISPES – Los Angeles, CA)
142. Common Ground Relief/New Orleans – Malik Raheem, Co-Founder
143. Dave Conley, Douglas County Board Supervisor, WI
144. Jan Conley, Founder and President of Environmental Assn. for Great Lakes Education
145. Polly Connelly, International Representative, United Auto Workers (retired), Tucson, AZ
146. Cliff Conner, Author, “A People’s History of Science” New York, NY
147. Victor Crews, Utah Jobs with Justice, Wasatch Coalition for Peace and Justice, United for Peace and Justice Steering Committee Member
148. Cuba Solidarity, NY, NY
149. Tony Cuneo, Duluth City Council*
150. Denise D’Anne, Senior Action Network, San Francisco, CA*
151. DailyRadical.org, Boston, MA
152. Alan Dale, member, Iraq Peace Action Coalition, MN
153. Warren Davis, Former International Executive Board Member, United Auto Workers, Cleveland, OH
154. De Kalb Interfaith Network for Peace and Justice, De Kalb, IL
155. Declaration of Peace – San Mateo County, San Mateo, CA
156. Declaration of Peace, Bloomington, IN
157. Democratic Socialists of Central Ohio
158. Jesse Diaz, Jr., University of California, Riverside; Political Action Committee – La Hermandad Mexicana Transnacional, Riverside, CA
159. Ron Dicks, International Vice President, Western Region, International Federation of Professional and Technical Employees (IFPTE), San Francisco*
160. Different Drummer
161. Frank Dorrell, Addicted to War, Los Angeles, CA
162. Doug Dowd – Political economist, author, professor, Bologna, Italy
163. Dubuque Peace & Justice, Dubuque, IA
164. Mark Dudzic, National Organizer, Labor Party*
165. Larry Duncan, Labor Beat Co-Producer, Chicago, IL
166. East Central Ohio Green Party
167. Jebb Ebben, lead vocal of The Dear Astronaut band, Milwaukee, WI
168. Charlie Ehlen, Member, Veterans for Peace, Glenmora, LA
169. El Militante Sin Fronteras
170. Erie Benedictines for Peace, PA
171. Every Church a Church of Peace (Duluth, MN area chapter)
172. Farid Farahmand, Iranians for Peace, New Britain, CT
173. Christian Fernandez, Greater Boston Stop the Wars Coalition
174. Bob Fertik, founder of Democrats.com
175. Jeanne Finley, Albany, NY
176. First Presbyterian Church of Palo Alto, CA
177. Milton Fisk, South Central Indiana Jobs with Justice; Emeritus Prof. of Philosophy, Indiana Univ.- Bloomington
178. Jon Flanders, member and past president IAM Local Lodge 1145; Trustee, Troy Area Labor Council, NY
179. Carlos Flores, Secretary-Treasurer, Graphic Communications Conference-IBT Local 4N*
180. Focus the Nation, Portland, OR
181. Folk the War, Kent, OH
182. Dennis Foster, Westlake, OH
183. Christine Frank, Climate Crisis Coalition of the Twin Cities, Minneapolis, MN
184. FreedomJournal.Tv, Akron, OH
185. Freedom Socialist Party, Seattle, WA, Henry Noble, National Secretary
186. Frente de Mexicanos en el Exterior/FME (Front of Mexicans Aboard), Sacramento, CA
187. Anna Fritz, Retiree, Cleveland Heights, OH
188. Emily Gaarder, Assistant Prof. of Sociology/Anthropology, Univ. of MN-Duluth, MN
189. GABNet, a Philippines women’s organization
190. Dennis Gallie, Member UAW Local 235, St. Louis, MO*
191. Sharla Gardner, Duluth City Councilor and Former Executive Board Member of AFSCME Local 66, Duluth, MN
192. Christine Gauvreau, Organizing Committee, CT United for Peace*
193. Gay Liberation Network, Chicago, IL
194. Paul George, Director, Peninsula Peace and Justice Center, Palo Alto, CA
195. Mirène Ghossein, member of Adalah-NY: Coalition for Justice in the Middle East*, WESPAC (Westchester County Peace and Action Network)*
196. Isaac Alejandro Giron, Chairman of the SLC Autonomous Brown Berets
197. Martin Goff, Minnesota UNITE HERE Organizer*
198. David Goldberg, UTLA Treasurer, Los Angeles, CA
199. Sam Goldberger, We Refuse to Be Enemies, West Hartford, CT*
200. Marty Goodman, Transport Workers Union Local 100*, NY, NY, former Executive Board member
201. Dayne Goodwin, Secretary, Wasatch Coalition for Peace and Justice, Salt Lake City, UT
202. Steve Gordon, Former President of UTU Local 1732 & Lead Vocalist for the bands Workerand Black Market Bombs, Conway, SC
203. Kevin Gosztola, Author for OpEdNews; member, Peace Movement
204. Grandmothers for Peace, Northland Chapter
205. Grandmothers for Peace International, Elk Grove, CA
206. Greater Glastonbury for Peace and Justice, Glastonbury, CT
207. Green Party of Brooklyn, Brooklyn, NY
208. Green Party of Rhode Island, Providence, RI
209. Suzanne Griffith, Professor of Counseling, Univ. of Wisconsin-Superior; Member of Women in Black
210. Guerrero Azteca Peace Project, Escondido, CA
211. Cheryl Gustafson, Western University (Salt Lake City) Community Relations*
212. Ioanna Gutas, Middle East Crisis Committee, New Haven, CT*
213. Guyanese American Workers United, New York, NY
214. Jim Hamilton, St. Louis; Member, State Executive Board of American Federation of Teachers, MO*
215. Carol Hannah, Peace North, Hayward, WI
216. Mo Hannah, Ph.D., Chair, Battered Mothers Custody Conference
217. John Harris, Co-Founder, Greater Boston Stop the Wars Coalition, Boston, MA; Co-Founder, Chelsea Uniéndose en Contra de la Guerra, Chelsea, MA; Regional Coordinating Committee member, New England United*
218. Alan Hart, Managing Editor, UE News, United Electrical, Radio and Machine Workers of America (UE)*
219. Hawaii Solidarity Committee, NY, NY
220. Rose Helin, Former President, Students Against War, Univ. of Wisconsin-Superior
221. Stan Heller, The Struggle Video News Network, West Haven, CT*
222. Melissa Helman, former School of the Americas Protest Prisoner of Conscience, Ashland, WI
223. Inola F Henry, UTLA Board of Directors, Los Angeles, CA
224. Laura Herrera, Co-Coordinator, The Mobilization to Free Mumia Abu-Jamal, Northern California
225. Fletcher Hinds, Vietnam Veteran, MN Veterans & Military Families for Progress*, Duluth, MN
226. Fred Hirsch, Plumbers and Fitters Local 393 Executive Board; Delegate to the South Bay AFL-CIO Labor Council, San Jose, CA*
227. Suzanne and William Hodgkins, Niskayuna, NY
228. Marvin Holland, http://www.homestationonline.org, Jersey City, NJ
229. Julie Holzer, Staff Representative, District 12, United Steelworkers Union*
230. Dr. Bill Honigman, Progressive Democrats of America, California State Coordinator, Laguna Hills, CA
231. Kathleen Hopton, Mentor, OH
232. Houston Coalition for Justice Not War, Houston, TX
233. Humanity, Asheville, NC
234. Jeff Humfeld, Board of Directors, KKFI Community Radio, Kansas City, MO*
235. ICUJP-Interfaith Communities United for Justice and Peace, Los Angeles, CA
236. Interfaith Council for Peace in the Middle East, Cleveland, OH
237. International Socialist Organization (ISO)
238. Iraq Peace Action Coalition, Twin Cities. MN
239. Khalil Iskarous, Middle East Crisis Committee, New Haven, CT*
240. lbrahim Jibrell, Trinity College Antiwar Coalition, Hartford, CT*
241. Jeni Johnson, Former News Editor for the Promethean newspaper
242. Laurie Johnson, Former Duluth City Councilor; Business Agent AFSCME Council 5, Duluth, MN
243. Peter Johnson, Progressive Action Steering Committee & Duluth Professional Firefighters Union*, Duluth, MN
244. Todd Jordan, Future of the Union, UAW Local 292*, Kokomo, IN
245. Paul Kangas, Vice President, Veterans for Peace
246. Kansas City Labor Against the War, a U.S. Labor Against the War affiliate
247. Dan Kaplan, Executive Director, AFT Local 1493; San Mateo (CA) Community College Federation of Teachers*
248. David Keil, Greater Boston Stop the Wars Coalition; New England United*
249. Kemetic Inst, Columbus, OH
250. Kent State Anti-War Committee, Kent, OH
251. Sky Keyes, CT United for Peace, Middletown, CT
252. Tim Kettler, Secretary, Green Party of Ohio
253. Joel Kilgour, Truth in Recruiting Committee, Duluth, MN
254. John Kirkland, Stop the War Committee, Carpenters Local 1462*, Bristol, PA
255. Philip Koch, Professor, Maryland Institute College of Art, Baltimore, MD
256. Dr. Gary Kohls, Every Church a Church of Peace
257. Bob Kosuth, Steering Committee of the Northland Anti-War Coalition
258. Gene Kotrba, Northeast Ohio Anti-War Coalition (NOAC), Berea, OH
259. Dennis Kucinich, U.S. Representative, Lakewood, OH
260. Rev. Kurt Kuhwald, Unitarian Universalist Church of Palo Alto, Palo Alto, CA*
261. Rick Kurki, Board Member of the Tyomies Society, Highbridge, WI
262. Zev Kvitky, President, SEIU Local 2007, Stanford, CA
263. La Hermandad Transnacional , Los Angeles, CA
264. Ray LaForest, International Haiti Support Network, New York, NY
265. Lake Superior Greens
266. Werner Lange, Professor of Sociology, Edinboro University of Pennsylvania*
267. Ben Larson, Singer for the band Crew Jones
268. Prof. Mark Lause, Department of History, University of Cincinnati
269. Peter LaVenia, Co-Chair, New York Green Party
270. Paul Le Blanc, Prof. of History, LaRoche College; Member, Anti-War Committee, Thomas Merton Center, Pittsburgh
271. James Marc Leas, National Lawyers Guild
272. Fernando B. Ledezma, UTLA Board of Directors, El Monte, CA
273. Rosemary Lee, Member, CFT Civil, Human and Women’s Rights Committee*, Los Angeles,
CA
274. Pat Levasseur, East Coast Director, Lynne Stewart Defense Committee; former political prisoner, Ohio 7
275. Libertarian Party of Northeast Ohio
276. Liberty Street Agitators, Ann Arbor, MI
277. Jack Lieberman, Jewish Arab Dialog Association*, Miami , FL
278. Jerimarie Liesagang, CT Transadvocacy Coalition, Hartford, CT
279. Peter Linebaugh, Author, Magna Carta Manifesto
280. Michael Livingston, Professor of Psychology, St. John’s University, Collegeville, MN
281. Janet Loehr, Middle East Peace Forum, Cleveland, OH
282. Joe Lombardo, Bethlehem Neighbors for Peace and Coordinator, Northeast Peace and Justice Action Coalition
283. Los Altos Voices for Peace, Los Altos, CA
284. Jennifer Lyon, Iraq Veterans Against the War (IVAW)*, Las Vegas, NV
285. David Macko, Chairman, Libertarian Party, Northeast Ohio*, Solon, OH
286. Dorotea Manuela, Co-Coordinator, Boston May Day Coalition, Boston, MA
287. Jorge Marin, Circula Bolivarimo – Martin Luther King, Jr.*, Boston MA
288. Jennifer Martin-Romme, Editor, Zenith City Weekly Newspaper
289. Logan Martinez, Green Party West Central Ohio
290. Jamshid Marvesti, M.D., Author of four books, most recently “Psycho-Political Aspects of Suicide Warriors, Terrorism and Martyrdom,” Manchester, CT
291. James Mattingly, Kaukauna, WI
292. Mayday Books, MN
293. Bob McCafferty, Andover, NJ
294. Prof. Bud McClure, Faculty Against War, Univ. of Minnesota-Duluth
295. Rick McDowell, Belmont, ME
296. Kay McKenzie, Douglas County Board Supervisor, WI
297. Michigan Emergency Committee Against War & Injustice, Detroit, MI
298. The Middle East Crisis Committee, CT
299. Mimbrez Publishers, Oklahoma City, OK
300. Judy Miner, Office Coordinator, Wisconsin Network for Peace and Justice*, Madison, WI
301. Minnesota Labor Against the War
302. Mobilization to Free Mumia Abu-Jamal
303. Suren Moodliar, Mass Global Action*
304. Hal Moore, Progressive Action Treasurer, Duluth, MN
305. More than Warmth, Nashville, TN
306. Tess Moren, Intl. Peace Studies Student Assn., Univ. of Wisconsin-Superior
307. Dorinda Moreno, Co-Moderator, indyiraqaction; Convenor, Fuerza Mundial Collaborative, Santa Maria, CA*
308. Amy Moses, Leader, Young Adult Group, of the 1st Unitarian Universalist Society of SF
309. Denis Mosgofian, Graphic Communications Conference-IBT Local 4N, past president,
current Delegate to San Francisco Labor Council*
310. Peter and Gail Mott, Co-Editors INTERCONNECT: (national newsletter)
311. David Moulton, Loaves & Fishes Catholic Worker Community, Duluth, MN
312. MoveOn/East Bay, Barrington, RI
313. Bill Moyer and The Backbone Campaign
314. Jorge Mujica, March 10 Coalition*
315. MJ Muser, World Can’t Wait-Cleveland
316. Muslim Solidarity Committee
317. Muslim Youth Brotherhood for Political Action (MYB). Chaplin, CT
318. My Homework Channel, Cambridge, MA
319. National Network on Cuba, San Francisco, CA
320. Native Earth Education Project, Shelburne, MA
321. Kamran Nayeri, Political Economist, University of California
322. Near West Citizens for Peace and Justice
323. Neighbors for Peace, IL
324. Nevada Workers Against the War, Las Vegas, NV
325. New England United
326. New York State Greens/Green Party of New York, New York, NY
327. Nicaragua Network
328. Mary Nichols-Rhodes, Ohio Progressive Democrats of America State CD Organizer
329. Victor Nieto, President of Lodge 1043 Transportation and Communications Union*, Bronx, NY
330. North Shore Coalition for Peace and Justice, IL
331. Northland Anti-War Coalition
332. Jim Northrup, Native American Playwright, Poet, Author and Syndicated Columnist of Column “Fond du Lac Follies”
333. NY Metro Raging Grannies, New York, NY
334. Ohio State Labor Party
335. Barb Olsen, President, Progressive Action, Political Commentator for KUMD-FM Radio and Political Columnist for the Reader Weekly Newspaper
336. Bill Onasch, Midwest Chapter Representative, Labor Party Interim National Council*
337. Steve O’Neil, St. Louis County Board Commissioner, Duluth, MN.
338. Organized Workers for Labor Solidarity, Seattle, WA
339. Debbie Ortman, National Field Director of the Organic Consumers Assn.; Former Hermantown, MN City Councilor; President, Duluth League of Women Voters
340. Our Spring Break, Washington D.C.
341. Pan-African Roots, Washington, D.C.
342. Jeff Panetiere, Western Connecticut State Univ. Youth for Justice, Danbury, CT*
343. Parma Democratic Committee, Hilton, NY
344. Pax Christi Northern California, San Jose, CA
345. PDX Peace Coalition, Portland, OR
346. Peace & Social Justice Committee*, La Roche College, Pittsburgh, PA
347. Peace Action of San Mateo County, San Mateo, CA
348. Peace and Freedom Party, Sacramento, CA
349. Peace and Justice Center of Eastern Maine, Bangor, ME
350. PeaceMajority Report, Lindenhurst, IL
351. Josh Pechthalt, UTLA/AFT Vice President, Los Angeles, CA
352. Paula J. Pedersen: Assistant Professor of Psychology, Univ. of MN-Duluth
353. Penn Action, Pittsburgh, PA
354. Helen Pent, President, Northland College Student Assn.
355. People of Faith CT, West Hartford, CT
356. Peoples Fightback Center, Cleveland, OH
357. John Peterson, National Secretary, U.S. Hands Off Venezuela
358. Millie Phillips, Editorial Board, The Organizer Newspaper*
359. Physicians for Social Responsibility, Hudson-Mohawk Chapter
360. Jan Pierce, Retired National Vice President – Communications Workers of America District One
361. Angela T. Pineros, Greater Boston Stop the Wars Coalition
362. Larry Pinkney, Black Activist Writers Guild & Columnist, Twin Cities, MN*
363. Andy Pollack, Adalah–NY: Coalition for Justice in the Middle East,* Brooklyn, NY
364. Joseph Pollard, Transport Workers Union Local 100*, NY,NY
365. Portage Community Peace Coalition, Brady Lake, OH
366. Michael L. Postell, Transport Workers Union Local 250A, Chairperson, Green Division, San Francisco Municipal Railway*, San Francisco, CA
367. Dolores Perez Priem, Iraq Moratorium and UUs for Peace, San Francisco, CA
368. Progressive Action Steering Committee, Duluth, MN
369. Progressive Democrats of America Los Angeles (PDALA) Los Angeles, CA
370. Progressive Democrats of America – Ohio
371. Progressive Peace Coalition, Columbus, OH
372. Radical Women, San Francisco, CA
373. Radio Free Maine, Augusta, ME
374. Dr. Chengiah Ragaven, Professor of International Relations, Central CT State Univ., New Britain, CT*
375. Rainbow Affinity Tribe/Yippies, Brooklyn, NY
376. Walter Raschik, Host, Walt Dizzo Show on KUWS-FM Radio
377. Jack Rasmus, Co-Chair, Natl. Writers Union, UAW Local 1981, Richmond, CA*
378. Sami Rasouli , Founder & Director, Muslim Peacemaker Teams*, Najaf, Iraq
379. Austin Reams, Oklahoma City, OK
380. Revolutionary Workers Group, San Francisco, CA
381. Rogelio Reyes, California Faculty Association, Calexico, CA *
382. Sergio Reyes, Co-Coordinator, Boston May Day Coalition
383. Marc Rich, Delegate, LA County Federation of Labor
384. Walter Riley, Civil Rights Attorney, Political Activist, San Francisco, CA
385. Adam Ritscher, Douglas County Board Supervisor; Northland Anti-War Coalition
386. Christopher Robinson, Cambridge, MA
387. Rockland Coalition for Peace and Justice, Chestnut Ridge, NY
388. Lorena Rodriguez, International Partnership Coordinator of the Student Trade Justice Campaign, Duluth, MN/Montevideo, Uruguay
389. Mike Rogge, Co-Founder, Students Against War, College of St. Scholastica.
390. Al Rojas, Coordinator, FME (Front of Mexicans Abroad), Sacramento, CA
391. Emma Rosenthal, Los Angeles, CA
392. Martin Rosner, NY Social Activist
393. Donald Rucknagel, M.D., Ph.D., Cincinnati, OH
394. Barb Russ, Progressive Action, Duluth, MN
395. Carl Sack, Northland Anti-War Coalition, former Northland College Student Senator
396. Sacramento for Democracy, Sacramento, CA
397. Sundiata Sadiq, Former President, Ossining, NY NAACP
398. San Diego Coalition for Peace and Justice, San Diego, CA
399. San Mateo County Central Labor Council AFL-CIO, Foster City, CA
400. Ajamu Sankofa, National Conference of Black Lawyers*, Brooklyn, NY
401. Tony Saper, ATU Local 1287 Representative to the Kansas City Regional Transit Alliance, Kansas City, MO
402. Evan Sarmiento, Outreach Coordinator, Greater Boston Stop the Wars Coalition
403. Renee Saucedo, Director, La Raza Centro Legal; Member, SEIU Local 1021, San Francisco*
404. Fred Schnook, former Mayor of Ashland, WI.
405. Ralph Schoenman and Mya Shone, Co-producers, Taking Aim-WBAI Radio-NY, Vallejo, CA
406. Paul Schrade, former International Executive Board Member, United Auto Workers, Los Angeles, CA
407. John Schraufnagle, Northland Anti-War Coalition, Superior, WI
408. Michael Schreiber, Editor, Socialist Action, San Francisco, CA
409. Rodger Scott, Delegate and Past President, American Federation of Teachers Local 2121, City College of San Francisco
410. Mary Scully, member, Iraq Peace Action Coalition, Twin Cities
411. Steve Seal, UTLA Board of Directors/Chair, Human Rights Committee*, Los Angeles, CA
412. Vann Seawell, Assistant Director, UNITE HERE, Columbus, OH
413. Leonard Segal, UTLA Board of Directors, Northridge, CA
414. Rob Segovia-Welsh, Agriculture Rural Labor Inspector for the State of North Carolina
415. Dallas Sells, Director, Ohio State Council, UNITE HERE
416. Shaker Heights High School Students for a Democratic Society (SDS), Shaker Heights, OH
417. Peter Shell, Anti-War Committee of the Thomas Merton Center, Pittsburgh, PA
418. Adam Shils, Vice-President, Aptakisc Education Association (NEA)*
419. Shura Council, Anaheim, CA
420. Joel Sipress, Duluth Area Green Party, former candidate for MN State Senate, Duluth, MN
421. Debbie Ginsberg Smith, Social Activist, New York
422. Michael Steven Smith, Co-Producer, Law and Disorder, WBAI radio
423. Social Action Committee, Unitarian Universalist Fellowship of Redwood City, CA
424. Social Action Committee, West Shore Unitarian Universalist Church, Rocky River, OH
425. Socialist Action
426. Socialist Alternative
427. Socialist Organizer
428. Socialist Party, Boston
429. Socialist Party of CT
430. Socialist Party of Massachusetts
431. Socialist Party USA (National Committee)
432. Socialist Viewpoint
433. Solidarity, Detroit, MI
434. Asiyahola Somburu, Co-Chair of the Emerging Black Leadership Symposium
435. Gary Sorenson, President of Veterans for Peace, Chapter 80
436. South Dakota A.N.S.W.E.R. Coalition, Brandon, State Council
437. Southeast Minnesota Alliance of Peacemakers, Rochester, MN
438. Mark Stahl, Event Coordinator, Rhode Island Community Coalition for Peace
439. Lynne Stewart, Lynne Stewart Organization, NY, NY
440. Judith Stoddard, First Unitarian Universalist Society of San Francisco*
441. Students for a Democratic Society, Kirtland, OH
442. Students for Change, Norwich, CT
443. Hal Sutton, Member, UAW Local 1268 Retirees Chapter, Rockton, IL*
444. David Swanson, Washington Director, Democrats.com and of Impeachpac.org; Co-Founder, AfterDowningStreet.org
445. Shakeel Syed, Executive Director, Shura Council, Culver City, CA
446. Teach Peace Foundation
447. Tennessee Code Pink, Summertown, TN
448. Texans for Peace, Austin, TX
449. Linda Thompson, Guilford Peace Alliance, AFSCME Retirees, CT United for Peace
450. Sara Thomsen, singer/songwriter, South Range, WI
451. Gale Courey Toensing, Editor, The Corner Report, NW CT and Member, Middle East Crisis Committee, CT*
452. Troops Out Now Coalition, New York, NY
453. Troy Area Labor Council, Troy, NY
454. Jerry Tucker, former International Executive Board Member, United Auto Workers, St. Louis, MO
455. Twin Cities Peace Campaign-Focus on Iraq
456. Twin Cities Year 5 Committee to End the War Now
457. U.S. Hands Off Venezuela
458. Imam Warith Deen Umar, Chaplain for 25 years in New York state prisons
459. United Educators of San Francisco
460. Unitarian Universalist Fellowship of Redwood City (entire congregation), Redwood City, CA
461. University of Toledo Anti-War, Toledo, OH
462. Upper Hudson Peace Action, Albany, NY
463. Utah Jobs with Justice, Salt Lake City
464. Utah Peace & Freedom Party, Salt Lake City, UT
465. James E. Vann, Architect; Co-Founder, Oakland Tenants Union, Oakland, CA
466. Chuck Vaughn, UTLA Board of Directors, Pico Rivera, CA
467. Venezuela Solidarity Network
468. Veterans for Peace, Chapter 80
469. Veterans for Peace, Chapter 118, Utah
470. Veterans for Peace – Chapter 153, Iraq Moratorium Project, Peace North, Hayward, WI
471. Carlos Villarreal, Executive Director, National Lawyers Guild*, San Francisco Bay Area Chapter
472. Voters Evolt!, Long Beach, CA
473. Voters for Peace, Baltimore, MD
474. Julie Washington, UTLA Elementary Vice President, Los Angeles, CA
475. Washington Peace Center, Washington D.C.
476. Harvey Wasserman, Founder of Solartopia.org, Bexley, OH
477. WE Project, Los Angeles, CA
478. Carl Webb, Iraq War Veteran; Texas National Guard
479. Tegan Wendland, Douglas County Board Student Representative, WI
480. Coly Wentzlaff, Students for Peace, Univ. of Minnesota-Duluth
481. West Shore Unitarian Universalist Church Social Action Committee, Rocky River, OH
482. Don White, Peace and Justice Activist, Los Angeles, CA
483. Craig Wiesner, President, MicahsCall.org, Palo Alto, CA*
484. David Wilson, Nicaragua Solidarity Network of Greater New York*, NY,NY
485. Marcy Winograd, President, Progressive Democrats of Los Angeles*, Los Angeles, CA
486. Dorothy Wolden, Events Coordinator for the Northland Chapter of Grandmothers for Peace and former Douglas County Board Supervisor, WI
487. Women Against War, Capital District, New York
488. Women for Democracy and Fair Elections, Chicago, IL
489. Women’s International League for Peace and Freedom, Peninsula Branch, Palo Alto, CA
490. Women’s International League for Peace and Freedom, Pittsburgh Chapter, Pittsburgh, PA
491. Women’s International League for Peace and Freedom, U.S. Section; Philadelphia, PA
492. Kent Wong, Founding President of the Asian Pacific American Labor Alliance, Los Angeles, CA
493. Worker to Worker Solidarity Committee, Tucson, AZ
494. Workers International League (Socialist Appeal)
495. World Prout Assembly, Highland Heights, KY
496. Mark Wutschke, UTLA Board of Directors, Los Angeles, CA
497. Gustav Wynn, Writer & Contributing Editor, OpEd News, NY,NY
498. Carol F. Yost, Member, ADALAH-NY Coalition for Justice in the Middle East* Steering Committee Member, Private Health Insurance Must Go Coalition*
499. Youth for International Socialism
500. Marela Zacarias, Founder of Latinos Against the War, Hartford, CT
