
Haha I sympathize with this meme. But it applies to the colonized as well as the colonizers. I do tend to fault impoverished people for shackling themselves to church dogma. Religion rationalizes and preserves inequity. Of course this ignores that African American congregations are community centers above everything else. To cast off religion would deprive believers of their whole social fabric. But isn’t that like arguing that slave plantations were more than places of involuntary employment? Obviously tobacco and cotton plantations were the centers of slave communities. To end slavery threatened a slave’s source of everything: sustenance, shelter, family and community. Small wonder most slaves resisted those agitating for abolition. Slave rebellions were always betrayed by fearful slaves. No churches advocated for abolition. Even the civil rights movement a century later, was resisted by African American churches, except for a tiny few associated with MLK. Everyone today pretends to have marched with MLK, even as they admonish their followers to stay in their pews! Ferguson ignited the Black Lives Matter movement despite local preachers incessantly calling for the protests to cease.
Tag Archives: Shelter
As homeless defendants face camping charges, Denver courts lie to jurors.

DENVER, COLORADO- Trial began yesterday for three homeless activists charged with violating Denver’s Unauthorized Camping Law. An ordinance enacted in 2012 partly as a coordinated response to Occupy Wall Street encampments across the country, partly to smooth the city’s gentrification plans. Though six years old, the ordinance has escaped judicial scrutiny by DPD’s careful avoidance of citing only homeless victims in no position to fight the charges in court. Deliberate civil disobedience attempts have been thwarted by the city bringing other charges in lieu of the “Urban Camping Ban” for which police threatened arrests. Thus Denver Homeless Out Loud’s coup of at last dragging this sham into the Lindsey Flanigan Courthouse has generated plenty of interest. I counted four print reporters and three municipal court judges in the audience! From a jury pool of forty, city prosecutors were able to reject the many who stated outright they could not condemn the homeless defendants for the mere act of trying to survive. At one point the jury selection process was stymied for an hour trying to fill one remaining alternate seat because each successive candidate would not “check their social values at the door.” One potential juror, a hairdresser, became alarmed that all the sympathetic candidates would be purged and so she refused to say how she felt about the homeless. She was removed and they were. As usual jurors were told it was not their place to decide against enforcing bad law. Only those who agreed were allowed to stay. And of course that’s a lie. The only way bad laws are struck down, besides an act of congress, a please reflect how that near impossibility has spawned its own idiom, is when good jurors search their conscience and stand up for defendants.
For those who might have wanted to get out of jury duty, it was an easy day. Show some humanity, provoke authentic laughter of agreement by declaring “Ain’t no way I’m convicting people for camping.” The jury pool heard that Denver’s definition of camping is “to dwell in place with ANY FORM OF SHELTER” which could be a tent, sleeping bag, blanket, even newspaper.
Several jury candidates stated they had relatives who were homeless. Another suggested it would be an injustice to press charges such as these.
“So this isn’t a case for you” the city lawyer asked.
“This isn’t a case for anyone” the prospective juror exclaimed, to a wave of enthusiam from the jury pool and audience.
Another prospect said she didn’t think this case should be prosecuted. The city attorney then asked, “so you couldn’t be fair?”
“I am being fair” she answered. All of these juror prospects were eliminated.
What remained of the jury pool were citizens who swear to uphold whatever law, however vile. One juror that remained even said she gives the benefit of the doubt to police officers. Not removed.
But there is hope because they couldn’t remove everyone. Of the six that remain, one juror agreed to follow the law, even if it was a law which he knew was wrong. That juror works in the legal cannabis industry. He admits he breaks federal law every day. That law is worng he says, but if he has to, he’ll abide by this one.
He admitted, “I can find them guilty. But I’ll have to live with that guilt for the rest of my life.” Ha. Technically the city had to live with that answer.
Another juror recognized that this case was about more than the three homeless defendants. “This case affects not just these three, but the countless homeless outside” gesturing to the whole of downtown Denver.
4/5 UPDATE:
In closing arguments the city lawyers reminded the jury that they swore to uphold the law. No they didn’t, but we’ll see what verdict emerges. After only a couple minutes from beginning deliberations, a juror emerged with this question: if the defendants are found guilty, can the juror pay their fine?
EPILOG:
Well the City of Denver breathes a sign of relief tonight. By which I mean, Denver’s injustice system, Denver’s cops, Denver’s gentrifiers and ordinary residents who are uncomfortable with sharing their streets with the city’s homeless. Today’s offenders were CONVICTED of violating the ordinance that criminalizes the poor for merely trying to shelter from the elements. Today the police and prosecutors and judge and jury acted as one to deliver a message to Denver homeless: no matter the hour, no matter how cold, pick up your things and move along.
This time it wasn’t a jury of yuppy realtors and business consultants that wiped their feet on homeless defendants. It was a cross section of a jury pool that yesterday looked promising.
Today when the jury entered with their verdict the courtroom audience was able to see which juror had been appointed the jury foreman. The revelation wasn’t comforting. Though not the typically dominating white male, this foreman was a female Air Force officer who had declared during voir dire that she had no greater loyalty than law and order. As the jury pool overflowed that first day with professions of sympathy for the homeless, it was the Air Force office, Juror Number Two, who grabbed the microphone to assert that rule of law must always prevail.
Yes, in the interest of optimism I had glossed over those lesser interesting juror statements, in hope that they were only playing to what prosecutors wanted to hear. Left on the jury was a domineering older woman who had said she gives police officers the benefit of the doubt.
An older man, an organist, whose father had been the CEO of a major Fortune 500 company, actually thought that homeless people should be arrested.
I’ll admit now that everyone’s hopes had been pinned on the pot guy who swore he’d have to live with his guilt forever. And so now it’s come to pass.
When those very small people of the jury go home tonight, and eventually read what they’ve done, upheld Denver’s odious, UN-condemned anti-homeless law, they’re going to figure out that they were made to administer the system’s final blow. And Denver couldn’t have done it without them.
The prosecutor had told the jury in her closing statement, that despite the tragic circumstances, everyone was doing their job, the police, the city attorneys, and the judge, and now the jury was expected to do its job. Except that was another lie. It wasn’t the jury’s “job”. They didn’t enlist and they weren’t paid to be executors of the city’s inhuman injustice machine. Whether by ignorance, poor education, or the courtroom team’s duplicity, this jury chose to do it.
But the ignorance runs deep. Judge Lombardi, in her closing remarks to the defendants, reiterated that all the elements had been proved and that justice was served. She praised the jury’s verdict and explained that the only way they could have found otherwise was through “jury nullification”. She said those words after the jury had been dismissed, but she said them on the record, two words that lawyers and defendants are forbidden to utter. In full Judge Lombardi added “and juries are not allowed to do jury nullification.” As if we all can be misled by that lie.
Denver judge rules BEING HOMELESS IS IRRELEVANT to defendants charged with violating city’s urban camping ban

DENVER, COLORADO- A hearing was held today to review motions submitted before the criminal trial of three homeless activists arrested last November for violating Denver’s Urban Camping Ban. Terese Howard, Jerry Burton, and Randy Russel featured in the infamous 2016 video that showed Denver police officers confiscating their sleeping bags and blankets on the snowy steps of city hall. Through attorney Jason Flores-Williams, fellow Denver Homeless Out Loud (DHOL) activists have filed a civil lawsuit to halt the city’s homeless sweeps. In municipal court DHOL hopes to challenge the ordinance being used to harass, displace and imprison the downtown homeless. Already the city’s case appears to be derailing based on developments at the motions hearing. Denver municipal court judge Kerri Lombardi approved all the city’s motions and none for the defense. Lombardi approved the use of 404B evidence for the city, but simultaneously restricted Res Gestae evidence for the defense. In particular, she refused to qualify two experts on homelessness, precluding the accused from arguing a “necessity defense”. Judge Lombardi stated that being homeless was irrelevant to whether they were violating the urban camping ban. When asked to recuse herself, the judge declined, so attorney Flores-Williams declared his intent to file an interlocutory appeal to bump the case to district court. Meanwhile speedy trial was waived and a new court date was set for April 5th.
DHOL’s 2/17 press release:
Yesterday there was a dispositive motions hearing in the Camping Ban criminal cases where homeless and poor people are being charged with crimes for sleeping on the streets with blankets and shelter in Winter. The hearing was noteworthy for the bias and prejudice shown toward Defendants by the Court.
1) At the start of the hearing, prior to any argument, the Judge looked at Defense counsel and said: “The one thing I don’t want is any drama from you, Mr. Flores-Williams.” Defense counsel had never practiced in this court.
2) Without allowing any substantive legal argument, the Court ruled that it was permissible for theProsecution to file a 34-person witness list eight days after the court’s deadline and only two weeks prior to trial.
3) The Court then Excluded all of Defense’s expert witnesses without hearing or testimony, saying that “Homelessness has nothing to do with this case.”
4) The Court then ordered Defense counsel to limit all arguments so that no argument or line of questioning could be construed at trial as an attempt to persuade the jury that the Camping Ban ordinance is itself unjust.
5) At this juncture, defense counsel cited to Fed R. 37(c)and its CO equivalent concerning the prejudice resulting from late disclosure of witnesses. No court response. Defense counsel then quoted from sections from Chambers v. Mississippi, a landmark 1973 civil rights case concerned with due process in which the overall prejudice to defendants becomes so cumulative and egregious that defendants fair trial rights are eviscerated. No response.
6) The Court then took up a Motion from the prosecution that does not exist. A “Res Gestae/404(b) Motion” that wrongfully conflates two different types of evidentiary concepts and underlying analyses. Res Gestae is concerned with the natural narrative of a case. Example: someone robs a liquor store, the fact that they stopped at two bars and to pick up their weapon on the way to the robbery. 404(b)has to do with a very specific set of factors that a defendant leaves at various crime scenes as identifiers. Not to be rude, but the classic example is when serial killer leaves identifiers at numerous crime scenes showing his m.o. The court conflated these two very different legal concepts and construed the “Res Gestae/404b” motion as allowing the prosecution to offer proof of Defendants’ mental states, but not the fact that defendants were homeless. (If this seems like 2+2=5, Wintston, they are….)(The court also disregarded that the motion was filed late and that it was amended without leave of court.)
7) Defense counsel then objected to the fact that the court had asked the prosecution for their jury instructions without asking defense for their jury instructions, and now was reverse injuring the court’s ruling from the prosecutions jury instructions. Objection overruled.
8) Defense counsel made oral motion for the judge to recuse, i.e. that he Judge take herself off the case for bias against defendants. Denied.
9) Defense counsel cited to several cases concerning due process rights, wrongful exclusion of defense witnesses, and the right to fairly address criminal accusations. No response.
10) Defense requested findings of law and fact – none given.
11) Defense counsel asked for a stay of the proceeding to file an interlocutory appeal regarding the court’s rulings.
12) Court stated that interlocutory orders cannot be appealed from municipal court so that none of the court’s decisions are reviewable.
13) Court ruled that the prosecution’s disclosure of 95 police body cameras three days prior to the hearing was permissible, then scolded defense for not reviewing the 95 videos prior to hearing. Defense counsel, concerned that the court would issue sanctions if he responded, had no comment.
We are now seeking an interlocutory appeal of the Court’s rulings.
The trial is scheduled for April 5th, 2017. Mark your calendar.
Pro-immigrant activists with Occupy Denver file suit against DIA and DPD, challenge airport free speech “permit”

DENVER, COLORADO- Civil liberties champion David Lane has filed a complaint in US district court challenging Denver’s office of the city attorney for instituting a permit process at DIA to prevent public protest. Holding signs has become impermissible at the airport, without the issuance of a permit seven days in advnace, although police are not bothering themselves about signs welcoming homecomers or seeking to connect business visitors with their limo service. That selective enforcement is unconstitutional of course, and the lawfirm powerhouse of Kilmer Lane & Newman is filing suit on behalf of two Occupy Denver plaintiffs. last Sunday, January 29, both were threatened with arrest by DIA police. While two earlier attempts to assemble had capitulated to DPD intimidation, the Occupy Denver activists stood their ground. Why did you file your lawsuit? “We know our rights. We want the POLICE to know our rights.”
1. Full text of complaint:
Case 1:17-cv-00332 Document 1
Filed 02/06/17 USDC Colorado Page 1 of 14Civil Action No.
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLORADO
NAZLI MCDONNELL,
ERIC VERLO,Plaintiffs, vs.
CITY AND COUNTY OF DENVER,?
DENVER POLICE COMMANDER ANTONIO LOPEZ, in his individual and official capacity,
DENVER POLICE SERGEANT VIRGINIA QUINONES, in her individual and official capacity,Defendants.
______________________________________________________________________________
COMPLAINT
______________________________________________________________________________
Plaintiffs, by and through their attorneys David A. Lane and Andy McNulty of KILLMER, LANE & NEWMAN, LLP, allege as follows:
INTRODUCTION
1. Plaintiffs Eric Verlo and Nazli McDonnell challenge a regulation of alarming breadth that bans all First Amendment expression at Denver International Airport without a permit.
2. Plaintiffs are concerned citizens who believe that President Donald Trump has overstepped his executive authority by signing the January 27, 2017, Executive Order (hereinafter “Muslim Ban”), which permanently bans Syrian refugees from emigrating to the United States, temporarily bans nationals of seven countries (including permanent legal residents and visa-holders), and suspends all applications to the United States refugee program (even as to vetted entrants currently in transit).
3. Plaintiffs wish to express their disgust with President Trump’s (likely unconstitutional) Muslim Ban. They wish to do so in the same place that hundreds of thousands of Americans across the country have done: standing directly outside of the secure Customs and Border Protection (hereinafter “CBP”) screening area within an airport where immigrants to America enter into the main terminal after clearing customs. Plaintiffs, unlike many citizens across this great nation who have exercised their opposition to the Muslim Ban in airports by chanting, singing, dancing, and praying, simply wish to stand in silent protest, holding signs that express their solidarity with immigrants and the Muslim community.
4. Plaintiffs are banned from doing so by DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50 (hereinafter “Regulation 50”).
5. Regulation 50 states: “No person or organization shall leaflet, conduct surveys, display signs, gather signatures, solicit funds, or engage in other speech related activity at Denver International Airport for religious, charitable, or political purposes, or in connection with a labor dispute, except pursuant to, and in compliance with, a permit for such activity issued by the CEO or his or her designee.” DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.03. In order to obtain a permit, an individual must “complete a permit application and submit it during regular business hours, at least seven (7) days prior to the commencement of the activity for which the permit is sought[.]” DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.04-1.
6. Plaintiffs ask that this Court enjoin the enforcement of Regulation 50 and prohibit Defendants from arresting them for their First Amendment-protected activity of standing in peaceful protest within Jeppesen Terminal. Regulation 50 is overbroad in violation of the First Amendment and vague in violation of the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause.
7. This is a civil rights action for declaratory and injunctive relief as well as fees and costs arising under 42 U.S.C. §§ 1983, 1988 and 28 U.S.C. Section 2201 et seq. due to Defendants’ current and imminent violations of Plaintiffs’ rights guaranteed by the First and Fourteenth Amendments to the Constitution of the United States.
PARTIES
8. Plaintiff Eric Verlo is a citizen of the United States of America. Mr. Verlo wishes to show his resistance to President Trump’s Muslim Ban, so that others will be inspired to join in the resistance.
9. Plaintiff Nazli McDonnell is a citizen of the United States of America. Ms. McDonnell wishes to show her resistance to President Trump’s Muslim Ban, so that others will be inspired to join in the resistance.
10. Defendant City and County of Denver is a municipal corporation and political subdivision of the State of Colorado. Thus, it is an entity subject to the provisions of § 1983.
11. Defendant Antonio Lopez is a Commander with the Denver Police Department. Commander Lopez is responsible for security at Denver International Airport’s Jeppesen Terminal.
12. Defendant Virginia Quinones is a Sergeant with the Denver Police Department. Sergeant Quinones is responsible for security at Denver International Airport’s Jeppesen Terminal.
JURISDICTION AND VENUE
13. Plaintiffs bring this claim pursuant to 42 U.S.C. § 1983; the First Amendment to the United States Constitution, incorporated as against States and their municipal divisions through the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution; and the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.
14. This Court has jurisdiction under 28 U.S.C. § 1331 over Plaintiffs’ claims that “arise[] under the Constitution of the United States.”
FACTS
15. On January 27, 2017, President Donald Trump signed an Executive Order, which permanently banned Syrian refugees from emigrating to the United States, temporarily banned nationals of seven countries (including permanent legal residents and visa-holders), and suspended all applications to the United States refugee program (even as to vetted entrants currently in transit). President Trump’s Executive Order has been subsequently referred to as a “Muslim Ban,” because it both mirrors President Trump’s racist, anti-Islam statements made on December 7, 2015, that he was planning to ban all Muslims from entering the United States until our representatives can “figure out what’s going on” and the ban targets countries whose population is predominantly Muslim and seemingly bears little rational relation to each country’s security threat to the United States.
16. Immediately upon the enactment of President Trump’s Muslim Ban there was an outpouring of outrage from a large proportion of the American population and across the spectrum of political affiliation. This outrage led to resistance in the form of protests.
17. On January 28, 2017, and January 29, 2017, protests erupted in nearly every major city in the United States. The protests organically formed in our nation’s airports. Protesters chose to express their disgust with President Trump’s Muslim Ban in airports (and specifically outside of the secure CBP screening area) because individuals affected by the ban who were in transit to the United States were being held and questioned by CBP agents there. Many of these travelers, including lawful United States residents, were forced to sign documents revoking their lawful status within the United States and deported. Still others were simply deported with no explanation. Others still were held for hours as teams of lawyers rushed to prepare habeas petitions for their release.
18. News reports about the protests make clear that they have been peaceful and non- disruptive despite the gathering of, in some cases, thousands of people.
19. Airport staff have told protesters, and would-be protesters, at numerous airports across the nation, including Kansas City International Airport, that there are no restrictions on their speech and that all protesters who wish to participate in actions against the Muslim Ban are allowed. Protests have continued in other cities to this day.
20. On January 28, 2017, there was one such protest at Denver International Airport, within the Jeppesen Terminal. At approximately 5:00 p.m. hundreds gathered in the Jeppesen Terminal’s atrium, near arrivals, to protest and many others gathered to bear witness.
21. Prior to the protest, leaders had applied for a permit. It was denied. The reason for its denial was that the permit was not requested with seven days advance notice of the protest occurring. Regulation 50 requires seven days advance notice.
22. The January 28, 2017, protest began with speeches, chants, songs, and prayers. It was a peaceful gathering of solidarity for immigrants and Muslims. Every person at the January 28, 2017, protest was contained in an area of the Jeppesen Terminal atrium that is designed as a gathering space for people to sit, relax, and converse. No one was standing in the walkways or passageways of the terminal.
23. Soon after the January 28, 2017, protest began, members of the Denver Police Department arrived on-scene. Commander Antonio Lopez engaged the leader of the protest, Amal Kassir, along with State Representative Joe Salazar and representatives from the ACLU of Colorado, and informed them that the protest was unlawful. Commander Lopez told Ms. Kassir that anything that “could be construed as Free Speech” was prohibited at the Denver International Airport, including within the Jeppesen Terminal, without a permit. See Exhibit 1, January 28, 2017 Video.
24. Commander Lopez also stated that all “First Amendment expression” was prohibited at the Denver International Airport, including within the Jeppesen Terminal, without a permit on Regulation 50. Commander Lopez handed Regulation 50 to multiple protesters, including Ms. Kassir. See Exhibit 2, January 28, 2017 Video 2.
25. Regulation 50 states (in pertinent part): “No person or organization shall leaflet, conduct surveys, display signs, gather signatures, solicit funds, or engage in other speech related activity at Denver International Airport for religious, charitable, or political purposes, or in connection with a labor dispute, except pursuant to, and in compliance with, a permit for such activity issued by the CEO or his or her designee.” DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.03. In order to obtain a permit, an individual must “complete a permit application and submit it during regular business hours, at least seven (7) days prior to the commencement of the activity for which the permit is sought[.]” DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.04-1.
26. Commander Lopez, along with members of Denver International Security, told Ms. Kassir that every portion of Denver International Airport property, which has an approximately fifty square mile footprint, is off-limits for First Amendment expression. They suggested that Ms. Kassir move her protest to Tower Road, which is approximately six miles from the Jeppesen Terminal and, like most of the land surrounding Denver International Airport, adjacent to open prairie land with no inhabitants.
27. Commander Lopez threatened Ms. Kassir and numerous other demonstrators with arrest if they didn’t immediately cease any “First Amendment expression.” According to Commander Lopez’s directives, the individuals gathered in the Jeppesen Terminal could not stand holding signs, sing, speak to others about matters of public concern, hold the United States Constitution above their shoulders, or stand silently with their arms interlocked.
28. Ultimately, to avoid arrest, Ms. Kassir and the demonstrators moved outside of the Jeppesen Terminal to the large area on its south side, adjacent to the escalators leading to the commuter rail and under the Westin Hotel. The protest continued peacefully for a little while longer, then disbursed without issue.
29. The next day, January 29, 2017, Plaintiffs Eric Verlo and Nazli McDonnell traveled to Denver International Airport’s Jeppesen Terminal to express their opposition to President Trump’s Muslim Ban.
30. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell brought with them signs expressing support for immigrants and expressing concern that history was repeating itself with disastrous potential consequences.
31. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell positioned themselves adjacent to the secure CBP screening area within the Jeppesen Terminal at approximately 1:15 p.m.
32. Adjacent the secure CBP screening area at the Jeppesen Terminal is the only place where Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell can reach their intended audience. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell wish to communicate with those who could be swayed by their message and, particularly, with immigrants. International travelers are often immigrants and/or lawful United States residents, including green card and other visa holders, other than citizens. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell wish to express their solidarity with immigrants directly to these individuals. Further, United States citizens who arrive from international locations are also individuals with whom Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell wish to communicate. International travelers have experienced other cultures and are likely to be sympathetic to Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonell’s message.
33. The secure CBP screening area is also the location where the Muslim Ban has been enforced by DHS, both at Denver International Airport and across the nation. Neither Plaintiff attempted to enter any restricted areas of Denver International Airport.
34. While silently displaying their signs, Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell were in the open plaza near the secure CBP screening area within the Jeppesen Terminal and positioned significantly behind the railing, which demarcates where those waiting for loved ones are permitted to stand. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell did not impede the right of way of any passengers hustling to catch flights at the last moment. They simply stood with placards showing their distaste for the Executive Order and the man who executed it.
35. Mr. Verlo and Mr. McDonnell also observed another man in the terminal, named Gene Wells, who was expressing views similar to theirs.
36. Mr. Wells was wearing a sign taped to the back of his shirt.
37. Mr. Wells left the Jeppesen Terminal, but subsequently returned to protest. When he did, he was stopped by Denver Police Department officers who told him that he could not walk around the terminal with the slogan he had affixed to his back. Mr. Wells eventually rejoined Mr. Verlo and Mr. McDonnell at the international arrivals doors, but not without trepidation. He feared he might be arrested.
38. While Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell were displaying their signs, Defendant Sergeant Virginia Quinones approached Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell and threatened them with arrest if they did not leave Jeppesen Terminal. See Exhibit 3, January 29, 2017, Video.
39. Sergeant Quinones handed Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell Regulation 50 and cited it as the reason they would be arrested if they did not leave Jeppesen Terminal. Id. Sergeant Quinones told Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell that they would need a permit in order to stand silently, holding signs in opposition of the Muslim Ban and be in compliance with Regulation 50.
40. Had Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell applied for a permit the second President Trump signed the Executive Order implementing the Muslim Ban, they still would have been unable to engage in protest within the Jeppesen Terminal under the terms and conditions of Regulation 50 on January 29, 2017.
41. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell did not immediately leave the Jeppesen Terminal after being threatened with arrest. However, they were startled by Sergeant Quiones’ threat and feared arrest for the duration of the time they were there.
42. Throughout the time Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell were expressing their views within the Jeppesen Terminal they received numerous shows of support from passersby. Multiple self- proclaimed Muslims expressed heart-felt statements of appreciation to Mr. Verlo, Ms. McDonnell, and others holding signs.
43. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell ultimately left Jeppesen Terminal.
44. Mr. Verlo and Ms. McDonnell wish to return to Jeppesen Terminal to express solidarity with Muslims and opposition to the Muslim Ban, but are reticent to do so for fear of being arrested.
45. Upon information and belief, no individual has been arrested, or threatened with arrest, for wearing a “Make America Great Again” campaign hat without a permit within the Jeppesen Terminal at Denver International Airport.
46. Upon information and belief, no individual has been arrested, or threatened with arrest, for holding a sign welcoming home a member of our military without a permit within the Jeppesen Terminal at Denver International Airport.
47. Upon information and belief, no individual has been arrested, or threatened with arrest, for holding a sign and soliciting passengers for a limousine without a permit within the Jeppesen Terminal at Denver International Airport.
48. Upon information and belief, no individual has been arrested, or threatened with arrest, for discussing current affairs with another person without a permit within the Jeppesen Terminal at Denver International Airport.
49. At all times relevant to this Complaint, Defendants acted under color of law.
CLAIM I: FIRST AMENDMENT
(§ 1983 violation – all Defendants)50. Plaintiffs repeat, re-allege, and incorporate by reference the allegations in the foregoing paragraphs of this Complaint as fully set forth herein.
51. Regulation 50 violates the Free Speech Clause of the First Amendment to the Constitution, on its face and as applied, because it impermissibly curtails Plaintiffs’ free-speech rights.
52. Plaintiffs wish to speak on a matter of public concern. 11
53. Denver International Airport’s Jeppesen Terminal is a public forum.
54. Regulation 50 directly infringes upon and chills reasonable persons from engaging in activity that is protected by the First Amendment.
55. Regulation 50 acts as an unconstitutional prior restraint on speech because it (1) requires a permit before allowing individuals to engage in speech, (2) allows for arbitrary and/or discriminatory permit denials, and (3) requires advance notice that is unconstitutionally excessive.
56. Regulation 50 is overbroad.?
57. Regulation 50 is not narrowly tailored to serve a compelling government interest.?
58. Regulation 50 does not further a substantial government interest.?
59. Regulation 50’s restriction on expressive conduct is greater than necessary to further any
government interest.?60. Defendants’ actions and/or omissions enforcing Regulation 50 caused, directly or
proximately, Plaintiffs to suffer damages.CLAIM II: FIRST AMENDMENT RETALIATION
(§ 1983 violation – all Defendants)1. All statements of fact set forth previously are hereby incorporated into this claim as though set forth fully herein. ?
2. Plaintiffs engaged in First Amendment protected speech on a matter of public concern ?while displaying signs opposing President Trump’s Muslim Ban on January 29, 2017.
3. Defendants jointly and on their own accord responded to Plaintiffs’ First Amendment protected speech with retaliation, including but not limited to threatening Plaintiffs with arrest.
4. Defendants retaliatory actions were substantially motivated by Plaintiffs’ exercise of their First Amendment rights.
5. By unlawfully threatening Plaintiffs with arrest, Defendants sought to punish Plaintiffs for exercising their First Amendment rights and to silence their future speech. Defendants’ retaliatory actions would chill a person of ordinary firmness from engaging in such First Amendment protected activity.
6. Defendants’ actions and/or omissions enforcing Regulation 50 caused, directly and proximately, Plaintiffs to suffer damages.
CLAIM III: FOURTEENTH AMENDMENT DUE PROCESS
(§ 1983 violation – all Defendants)7. All statements of fact set forth previously are hereby incorporated into this claim as though set forth fully herein.
8. The prohibitions of Regulation 50 are vague and not clearly defined. ?
9. Regulation 50 offers no clear and measurable standard by which Plaintiffs and others can ?act lawfully.
10. Regulation 50 does not provide explicit standards for application by law enforcement officers.
11. Regulation 50 fails to provide people of ordinary intelligence a reasonable opportunity to understand what conduct it prohibits, and authorizes or encourages arbitrary and discriminatory enforcement, or both.
12. Defendants’ actions and/or omissions enforcing Regulation 50 caused, directly and proximately, Plaintiffs to suffer damages.
PRAYER FOR RELIEF
WHEREFORE, Plaintiffs respectfully request that this Court enter judgment in their favor and against Defendants, and grant:
(a) Appropriate declaratory and other injunctive and/or equitable relief; 13
(b) Enter a declaration that Regulation 50 is unconstitutional on its face and enjoin its enforcement; ?
(c) Compensatory and consequential damages, including damages for emotional distress, loss of reputation, humiliation, loss of enjoyment of life, and other pain and suffering on all claims allowed by law in an amount to be determined at trial; ?
(d) All economic losses on all claims allowed by law; ?
(e) Punitive damages on all claims allowed by law and in an amount to be determined ?at trial; ?
(f) Attorney’s fees and the costs associated with this action, pursuant to 42 U.S.C. § ?1988; ?
(g) Pre and post-judgment interest at the lawful rate; and ?
(h) Any further relief that this court deems just and proper, and any other relief as ?allowed by law. ?
Dated this 6th day of February 2017.
KILLMER, LANE & NEWMAN, LLP
s/ Andy McNulty___________________________________
David A. Lane
?Andy McNulty?
Killmer, Lane & Newman, LLC
1543 Champa Street, Suite 400 Denver, Colorado 80202?
Attorneys for Plaintiff
2. Full text of Feb 6 motion for preliminary injunction:
Case 1:17-cv-00332 Document 2
Filed 02/06/17 USDC Colorado Page 1 of 23Civil Action No.
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLORADO
NAZLI MCDONNELL,
ERIC VERLO,Plaintiffs, vs.
CITY AND COUNTY OF DENVER,
DENVER POLICE COMMANDER ANTONIO LOPEZ, in his individual and official capacity,
DENVER POLICE SERGEANT VIRGINIA QUINONES, in her individual and official capacity,Defendants.
______________________________________________________________________________
MOTION FOR PRELIMINARY INJUNCTION
______________________________________________________________________________
Plaintiffs, by and through their attorneys David A. Lane and Andy McNulty of KILLMER, LANE & NEWMAN, LLP, hereby submit the following Motion for Preliminary Injunction, and in support thereof, states as follows:
1. Introduction
Over the last four days, many Americans have expressed public disapproval of President Donald Trump’s January 27, 2017, Executive Order, which permanently bans Syrian refugees from emigrating to the United States, temporarily bans nationals of seven countries (including permanent legal residents and visa-holders), and suspends all applications to the United States refugee program (even as to vetted entrants currently in transit). Plaintiffs are concerned and alarmed United States citizens who wish to join the growing chorus of voices expressing opposition to the Executive Order. To do so, they wish to stand in silent protest at the Jeppesen Terminal within Denver International Airport.
Plaintiffs did just this on January 29, 2017, standing in silent protest of the Executive Order outside of the secure Customs and Border Protection (hereinafter “CBP”) screening area within Jeppesen Terminal. Almost immediately, Plaintiffs were threatened with arrest by Denver Police Department Sergeant Virginia Quinones for standing silently and holding signs opposing the Executive Order, despite that fact that the Jeppesen Terminal has previously been used for expressive activity (and that protesters at more than ten major airports nationwide have protested peacefully without major disruption or legal restriction). While silently displaying their signs, Plaintiffs were in the plaza within the Jeppesen Terminal and positioned significantly behind the railing, which demarcates where those waiting for loved ones are permitted to stand, in the open plaza outside of the secure CBP screening area at the Jeppesen Terminal. Plaintiffs did not impede the right of way of any passengers hustling to catch flights at the last moment. They simply stood with placards showing their distaste for the Executive Order and the man who executed it.
Even though Plaintiffs were simply engaged in peaceful First Amendment protected expression, they were threatened with arrest. Sergeant Quinones informed Plaintiffs that, in order to stand silently with political signs, they would need a permit. Without a permit, Sergeant Quinones stated, all “First Amendment expression” at the Denver International Airport was banned.
This was not the first time since the enactment of the Executive Order that the Denver Police Department threatened individuals with arrest for engaging in First Amendment protected activity in Jeppesen Terminal. On January 28, 2016, a protest was held in the plaza of Jeppesen Terminal. During the protest, Denver Police Commander Antonio Lopez instructed multiple individuals, including State Representative Joseph Salazar and representatives from the ACLU of Colorado, that all “First Amendment expression” was banned at Denver International Airport without a permit. See Exhibit 1, January 28, 2017, Video 1; Exhibit 2, January 28, 2017, Video 2. The protesters had, in fact, applied for a permit earlier that day. However, it had not been granted because they had not done so seven days in advance of the protest in compliance with Denver International Airport regulations. Although no arrests were ultimately made, protesters were threatened numerous times by Commander Lopez, and other officers, with arrest.
The Denver International Airport regulation that both Sergeant Quinones and Commander Lopez relied upon in instructing Plaintiffs, and others, that Denver International Airport bans all “First Amendment expression” without a permit is DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50 (hereinafter “Regulation 50”). Regulation 50 states that “no person or organization shall leaflet, conduct surveys, display signs, gather signatures, solicit funds, or engage in other speech related activity at Denver International Airport for religious, charitable, or political purposes, or in connection with a labor dispute, except pursuant to, and in compliance with, a permit for such activity issued by the CEO or his or her designee.” DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.03. In order to obtain a permit, an individual must “complete a permit application and submit it during regular business hours, at least seven (7) days prior to the commencement of the activity for which the permit is sought[.]” DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.04-1.
Plaintiffs wish to return to Denver International Airport to protest the Executive Order, but are reasonably frightened of arrest and, absent action by this Court, must choose between lawfully exercising their First Amendment right and being subject to arrest and/or prosecution.
Plaintiffs ask that this Court enter an injunction prohibiting their arrest for standing in peaceful protest within Jeppesen Terminal and invalidating Regulation 50 as violative of the First and Fourteenth Amendments to the United States Constitution.
2. Factual Background
All statements of fact set forth in the simultaneously filed Complaint are hereby incorporated into this Brief as though set forth fully herein.
3. Argument
3.1 The standard for issuance of a preliminary injunction.
When seeking a preliminary injunction, a plaintiff must establish that (1) he is likely to succeed on the merits; (2) he is likely to suffer irreparable harm; (3) the balance of equities tips in his favor; and (4) that an injunction is in the public interest. Winter v. Nat. Res. Def. Council, 555 U.S. 7, 20 (2008); see also ACLU v. Johnson, 194 F.3d 1149, 1155 (10th Cir. 1999).
The Tenth Circuit has modified the preliminary injunction test when the moving party demonstrates that the second, third, and fourth factors “tip strongly” in its favor. See Oklahoma ex rel. Okla. Tax Comm’n v. Int’l Registration Plan, Inc., 455 F.3d 1107, 1113 (10th Cir. 2006); see also 820 F.3d 1113, n.5 (10th Cir. 2016). “In such situations, the moving party may meet the requirement for showing success on the merits by showing that questions going to the merits are so serious, substantial, difficult, and doubtful as to make the issue ripe for litigation and deserving of more deliberate investigation.” Id. (internal quotation marks omitted). Moreover, this “fair chance of prevailing” test is appropriate in this case because Plaintiffs are challenging a policy, not a statue or ordinance. See Planned Parenthood Minn, N.D., & S.D. v. Rounds, 530 F.3d 724, 732 (9th Cir. 2008) (“[C]ourts should… apply the familiar ‘fair chance of prevailing’ test where a preliminary injunction is sought to enjoin something other than government action based on presumptively reasoned democratic processes.”).
Under either standard, Plaintiffs are able to demonstrate that the issuance of a preliminary injunction is appropriate in this matter.
3.3 Regulation 50 implicates Plaintiffs’ First Amendment rights. 1
When the government regulates the exercise of First Amendment rights, the burden is on the proponent of the restriction to establish its constitutionality. Phelps-Roper v. Koster, 713 F.3d 942, 949 (8th Cir. 2013). Moreover, when assessing the preliminary injunction factors in First Amendment cases, “the likelihood of success will often be the determinative factor.” Hobby Lobby Stores, Inc. v. Sebelius, 723 F.3d 1114, 1145 (10th Cir. 2013). This is because “the loss of First Amendment freedoms, for even minimal periods of time, unquestionably, constitutes irreparable injury,” Heideman v. Salt Lake City, 348 F.3d 1182, 1190 (10th Cir. 2003), and it is invariably in the public interest to protect an individual’s First Amendment rights. See Homans v. City of Albuquerque, 264 F.3d 1240, 1244 (10th Cir. 2001) (noting that “the public interest is better served” by protecting First Amendment rights).
[NOTE 1. It is important to note that facial challenges to government policies and statutes, when based on First and Fourteenth Amendment grounds, are not disfavored. See United States v. Stevens, 559 U.S. 460, 473 (2010); City of Chicago v. Morales, 527 U.S. 41 (1999).]
3.4 Plaintiffs are likely to succeed on the merits.
Plaintiffs are likely to succeed on the merits because Regulation 50 violates the Free Speech Clause of the First Amendment and the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.
3.4(a) Plaintiffs engaged, and wish to engage, in speech on a matter of public concern.
Plaintiffs’ speech is at the core of the First Amendment’s protection because it deals with a matter of public concern. “Speech deals with matters of public concern when it can be fairly considered as relating to any matter of political, social, or other concern to the community, or when it is a subject of legitimate news interest; that is, a subject of general interest and of value and concern to the public.” Snyder v. Phelps, 562 U.S. 443, 453 (2011) (internal quotation marks and citation omitted). “Speech on matters of public concern is at the heart of the First Amendment’s protection.” Id. at 451-52 (alterations and quotation marks omitted). “The First Amendment reflects ‘a profound national commitment to the principle that debate on public issues should be uninhibited, robust, and wide-open.’” Id. at 452 (quoting New York Times Co. v. Sullivan, 376 U.S. 254, 270 (1964)). Plaintiffs wish to engage in expression about President Donald Trump’s January 27, 2017, Executive Order, a topic that has generated nearly unprecedented debate and dissent. See Adrienne Mahsa Varkiani, Here’s Your List of All the Protests Happening Against the Muslim Ban, THINK PROGRESS (Jan. 28, 2017), https://thinkprogress.org/muslim-ban-protests-344f6e66022e#.ft1oznfv4 (compiling list of direct actions planned in response to President Trump’s January 27, 2017, Executive Order). Thus, Plaintiffs’ speech “‘occupies the highest rung of the hierarchy of First Amendment values, and is entitled to special protection.’” Snyder, 562 U.S. at 452 (quoting Connick v. Myers, 461 U.S. 138, 145 (1983)).
3.4(b) Regulation 50 acts as a prior restraint.
The restriction at issue in this matter is a prior restraint. “The term prior restraint is used ‘to describe administrative and judicial orders forbidding certain communications when issued in advance of the time that such communications are to occur.’” Alexander v. United States, 509 U.S. 544, 550 (1993) (quoting M. Nimmer, Nimmer on Freedom of Speech § 4.03, p. 4–14 (1984)). Regulation 50 is in an administrative order that forbids future communication and bases the ability to communicate in the future on the discretion of an administrative official. See DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.03 (“no person or organization shall leaflet, conduct surveys, display signs, gather signatures, solicit funds, or engage in other speech related activity at Denver International Airport for religious, charitable, or political purposes, or in connection with a labor dispute, except pursuant to, and in compliance with, a permit for such activity issued by the CEO or his or her designee.” (emphasis added)). It is a prior restraint.
The burden of proving a prior restraint is permissible is particularly steep. The Supreme Court has repeatedly held that “[a]ny system of prior restraints of expression comes to this Court bearing a heavy presumption against its constitutional validity.” Bantam Books, Inc. v. Sullivan, 372 U.S. 58, 70 (1963). For the reasons outlined infra, Defendants cannot meet this especially significant burden.
3.4(c) Jeppesen Terminal, outside of the passenger security zones, is a traditional public forum.
The Supreme Court has not definitively decided whether airport terminals, including Jeppesen Terminal, are public forums. In Lee v. International Society for Krishna Consciousness, Inc., 505 U.S. 830 (1992) (hereinafter “Lee I”), issued the same day as International Society for Krishna Consciousness, Inc. v. Lee, 505 U.S. 672 (1992) (hereinafter “Lee II”), the Supreme Court struck down a total ban on distribution of literature in airports. In Lee I, the Court issued a one sentence per curiam opinion, which affirmed the Second Circuit for the reasons expressed by Justice O’Connor, Justice Kennedy, and Justice Souter in Lee II. See Lee I, 505 U.S. at 831. Justice Kennedy and Justice Souter’s opinions in Lee II found that “airport corridors and shopping areas outside of the passenger security zones… are public forums, and speech in those places is entitled to protection against all government regulation inconsistent with public forum principles.” Lee II, 505 U.S. at 693 (Kennedy, J., concurring in the judgment); but see Lee II, 505 U.S. at 683 (“”[W]e think that neither by tradition nor purpose can the terminals be described as satisfying the standards we have previously set out for identifying a public forum.”).
Therefore, Plaintiffs ask this Court to find the area of Jeppesen Terminal outside of the passenger security zones to be a public forum. The historical use of the Jeppesen Terminal’s plazas and other areas outside of the passenger security zones (including the area outside of the secure CBP screening area) for political speech (particularly, the history of welcoming of American military personnel home from service, discussion between passengers of matters of public concern, and display of clothing advocating for political views and ideals) indicates that it is a public forum. See First Unitarian Church of Salt Lake City v. Salt Lake City Corp., 308 F.3d 1114, 1130 (10th Cir. 2002) (“Where courts have considered the traditional use of publicly accessible property for speech, they have refused to attribute legal significance to an historical absence of speech activities where that non-speech history was created by the very restrictions at issue in the case.”). Further, that the Jeppesen Terminal is free and open to the public (outside of the passenger security zones), illustrates that it is a public forum. See, e.g., Ark. Educ. Television Comm’n v. Forbes, 523 U.S. 666, 676 (1998); Cornelius v. NAACP Legal Def. & Educ. Fund, 473 U.S. 788, 800, 805, 809 (1985). Finally, Jeppesen Terminal retains characteristics similar to parks: it has large plazas lined with benches, it is surrounded by businesses which are open to the public, and it has dedicated walkways, similar to sidewalks, indicating that it is a public forum. See e.g., Frisby v. Schultz, 487 U.S. 474, 480-481 (1988); United States v. Grace, 461 U.S. 171, 177 (1983). Further, the Supreme Court has not strictly limited the public forum category to streets, sidewalks, and parks. See, e.g., Se. Promotions, Ltd. v. Conrad, 420 U.S. 546 (1975) (finding leased municipal theater is a public forum); Heffron v. Int’l Society for Krishna Consciousness, Inc., 452 U.S. 640 (1981) (finding state fair is a public forum); Edwards v. South Carolina, 372 U.S. 229 (1963) (finding grounds of state capitol are a traditional public forum). Even if the City claims that it has never intended for Jeppesen Terminal to be a public forum, this is not dispositive. See Lee, 505 U.S. at 830 (government policy prohibiting distribution of literature at airport on property struck down); Cornelius, 473 U.S. at 805 (government’s decision to limit access is not itself dispositive). Plaintiffs’ ask that this Court find Jeppesen Terminal, outside of the passenger security zones, a traditional public forum.
Since Jeppesen Terminal is a traditional public forum, any restriction on Plaintiffs’ speech must be content-neutral and narrowly tailored to a compelling government interest. Regulation 50 fails at both.
3.4(d) Regulation 50 is content-based.
Regulation 50 is a content-based restriction of expression. Although the Supreme Court has long held that content-based restrictions elicit strict scrutiny, see, e.g., Carey v. Brown, 447 U.S. 455 (1980), lower courts diverged on the meaning of “content-based” until Reed v. Town of Gilbert, 135 S. Ct. 2218 (2015). 2 Reed clarified that a restriction is content based simply if it draws distinctions “based on the message a speaker conveys.” 135 S. Ct. at 2227. Reed is clear that even “subtle” distinctions that define regulated expression “by its function or purpose . . . are distinctions based on the message a speaker conveys, and therefore, are subject to strict scrutiny.” Id. This accords with Texas v. Johnson, which held that “the emotive impact of speech on its audience is not a secondary effect unrelated to the content of the expression itself.” 491 U.S. 491 U.S. 297, 412 (1989) (internal quotations omitted).
[NOTE 2. Reed involved a municipal “sign code” that regulated signs differently based on the kind of message they conveyed (such as “ideological,” “political,” or “temporary directional”). 135 S. Ct. at 2224-25. The Court rejected the city’s argument that a law had to discriminate against certain viewpoints in order to be a content-based restriction. Id. at 2229.]
Regulation 50 is content-based on its face. It distinguishes between content and requires that an official determine the content of the speaker’s message when enforcing its proscriptions. Reed, 135 S. Ct. at 2227; see DENVER INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT REGULATION 50.03 (“No person or organization shall leaflet, conduct surveys, display signs, gather signatures, solicit funds, or engage in other speech related activity at Denver International Airport for religious, charitable, or political purposes, or in connection with a labor dispute[.]” (emphasis added)). The distinctions drawn by Regulation 50 make it a facially content-based restriction on expression that must elicit “the most exacting scrutiny.” Johnson, 491 U.S. at 412; Reed, 135 S. Ct. at 2227.
3.4(e) Regulation 50 is not narrowly tailored to serve a compelling government interest.
As a facially content-based restriction of expression at traditional public fora, Regulation 50 is presumptively unconstitutional unless Defendant “prove[s] that the restriction furthers a compelling interest and is narrowly tailored to achieve that interest.” Reed, 135 St. Ct. at 2231; accord Johnson, 491 U.S. at 412.
“A statute is narrowly tailored if it targets and eliminates no more than the exact source of the ‘evil’ it seeks to remedy.” Frisby v. Schultz, 487 U.S. 474, 485 (1988) (citation omitted). Regulation 50 reaches more speech than that which would impair the security of the airport or ensure that passengers are not unduly encumbered. In fact, it completely bans all “First Amendment expression.” “A complete ban can be narrowly tailored, but only if each activity within the proscription’s scope is an appropriately targeted evil.” Id.. Regulation 50 is not such a ban. For instance, Plaintiffs’ expression does nothing to jeopardize security at Denver International Airport or to inhibit the free flow of passengers through the airport.
Further, any argument that Plaintiffs can engage in expressive activity in another location lacks merit, as the Supreme Court has held that the First Amendment is violated when one specific location or audience, when important to the speaker, is foreclosed. See McCullen v. Coakley, 134 S. Ct. 2518, 2536 (2014); Schenck v. Pro-Choice Network, 519 U.S. 357, 377 (1997) (invalidating a “floating” buffer zone around people entering an abortion clinic partly on the ground that it prevented protestors “from communicating a message from a normal conversational distance or handing leaflets to people entering or leaving the clinics who are walking on the public sidewalks”); Schneider v. New Jersey, 308 U.S. 147, 163 (1939) (invalidating anti-handbilling ordinances even though “their operation is limited to streets and alleys and leaves persons free to distribute printed matter in other public places”). Regulation 50 lacks the narrow tailoring necessary to survive First Amendment strict scrutiny analysis.
3.4(f) Regulation 50 violates the First Amendment even if this Court determines Jeppesen Terminal is a nonpublic forum.
Regulation 50 bans all “First Amendment expression” absent a permit; it is unconstitutional even when analyzed under the lower standard of scrutiny applied by courts to First Amendment political speech in a nonpublic forum. In Board of Airport Commissioners of Los Angeles v. Jews for Jesus, Inc., 482 U.S. 569 (1987), the Supreme Court considered whether a resolution restricting free speech in the airport was constitutional. The resolution at issue stated that the airport “is not open for First Amendment activities by any individual and/or entity.” Id. at 574. Although the Court did not explicitly find that the airport was a nonpublic forum, it did hold that the resolution restricting speech in the airport was facially unreasonable, even if the airport was a nonpublic forum. Id. at 573. The Court noted that enforcing the resolution would prohibit “talking and reading, or the wearing of campaign buttons or symbolic clothing.” Id. at 574. The Court also noted, “[m]uch nondisruptive speech–such as the wearing of a T-shirt or button that contains a political message–may not be ‘airport related’ but is still protected speech even in a nonpublic forum.” Id. at 575 (citing Cohen v. California, 403 U.S. 15 (1971) (holding that wearing of jacket with offensive language in a courthouse was a form of nondisruptive expression that was protected by the First Amendment)). Thus, although specific conduct was not at issue in the Jews for Jesus decision, the Court nonetheless implicitly held that non-disruptive speech is protected by the First Amendment in nonpublic fora and that restrictions that encumber non-disruptive expression are unreasonable.
In Lee II, Justice O’Connor set forth the test for determining reasonableness in the context of nonpublic fora. 505 U.S. at 687 (O’Connor, J., concurring). 3 She stated, ”[t]he reasonableness of the Government’s restriction [on speech in a nonpublic forum] must be assessed in light of the purpose of the forum and all the surrounding circumstances.” Id. (O’Connor, J., concurring) (quoting Cornelius, 473 U.S. at 809). However, Justice O’Connor noted that while “[o]rdinarily . . . we have . . . been confronted with cases where the fora at issue were discrete, single-purpose facilities,” airports present a different analysis because they are multipurpose facilities. Id. at 688 (O’Connor, J., concurring) (citations omitted). She determined airports to be multipurpose facilities because
the Port Authority [has] chosen not to limit access to the airports under its control, [and] has created a huge complex open to travelers and nontravelers alike. The airports house restaurants, cafeterias, snack bars, coffee shops, cocktail lounges, post offices, banks, telegraph offices, clothing shops, drug stores, food stores, nurseries, barber shops, currency exchanges, art exhibits, commercial advertising displays, bookstores, newsstands, dental offices and private clubs.
Id. This led to the finding that “[t]he reasonableness inquiry, therefore, is not whether the restrictions on speech are consistent with preserving the property for air travel, but whether they are reasonably related to maintaining the multipurpose environment that the Port Authority has deliberately created.” Id. at 689. A complete ban on First Amendment activity at the Jeppesen Terminal, absent a permit that must be obtained by providing seven days advance notice, is not a reasonable restriction. Regulation 50 does not comport with Justice O’Connor’s conclusion that airports are more than simply places where air travel occurs.
[NOTE 3. It is important to note that Lee involved a plurality opinion, joined by Justice O’Connor. Therefore, Justice O’Connor’s concurrence is the “narrowest grounds” that justify the Court’s result and her concurrence holds substantial precedential weight.]
Moreover, Justice O’Connor distinguished between solicitations (which the Supreme Court found could be reasonably restricted) and distributing leaflets (which the Supreme Court found could not be reasonably restricted) in the airport:
[L]eafleting does not entail the same kinds of problems presented by face-to-face solicitation. Specifically, “one need not ponder the contents of a leaflet or pamphlet in order mechanically to take it out of someone’s hand . . . . The distribution of literature does not require that the recipient stop in order to receive the message the speaker wishes to convey; instead the recipient is free to read the message at a later time.”
Id. at 690 (quoting United States v. Kokinda, 497 U.S. 720, 734 (1990)).
Thus, the Court held in Lee II that prohibiting solicitation in a nonpublic forum is not unreasonable, but that prohibiting the distribution of leaflets and other literature at a nonpublic forum is unreasonable. See also Lee, 505 U.S. at 830 (decided the same day as Lee II and striking down a prohibition on the distribution of leaflets and other literature at La Guardia, John F. Kennedy, and Newark International airports) (per curiam). Circuit courts have also recognized the inherent right to distribute paper and other information in nonpublic fora. Following Lee I and Lee II, two circuit courts have held that airports, as nonpublic fora, could not preclude newspaper publishers from placing newsracks in airport terminals. See Jacobsen v. City of Rapid City, South Dakota, 128 F.3d 660 (8th Cir. 1997); Multimedia Publishing Co. of South Carolina, Inc. v. Greenville-Spartanburg Airport Dist., 991 F.2d 154 (4th Cir. 1993). To the extent that the airports were concerned about safety or the impediment of traffic flow, the courts held that the airport may impose reasonable restrictions, but they could not enforce an outright ban on the newspaper racks. See Jacobsen, 128 F.3d at 660; Multimedia Publishing Co. of South Carolina, Inc., 991 F.2d at 154.
Denver, through Regulation 50, has banned all “First Amendment expression” including leafleting and protests. In fact, Plaintiffs expression is arguably less intrusive and disruptive to air travel than the form of expression, namely leafletting, that the Court held could not be reasonably restricted in the areas of an airport that precede the security screening area. It is clear from Lee I, Lee II, and Jews for Jesus that Denver cannot ban all “First Amendment expression” at the Jeppesen Terminal.
3.4(f)(1) Independently, the viewpoint-based prohibition of Plaintiffs’ speech, based on Regulation 50, violates the First Amendment.
Even if Jeppesen Terminal is a nonpublic forum, “this does not mean the government has unbridled control over speech, . . . for it is axiomatic that ‘the First Amendment forbids the government to regulate speech in ways that favor some viewpoints or ideas at the expense of others.” Summum v. Callaghan, 130 F.3d 906, 916 (10th Cir. 1997) (quoting Lamb’s Chapel v. Center Moriches Union Free School Dist., 508 U.S. 384, 394, (1993)). “Restrictions on speech in nonpublic fora must be viewpoint neutral[.]” Warren v. Fairfax Cty., 196 F.3d 186, 193 (4th Cir. 1999) (citing Cornelius, 473 at 809). Defendants’ restriction of Plaintiffs’ speech, under the guise of Regulation 50, discriminates on the basis of viewpoint. Individuals walk through Denver International Airport with political messages and slogans on their shirts and luggage and discuss politics on a daily basis. Counsel for Plaintiffs has worn political shirts while traveling through Denver International Airport and discussed modern politics with fellow passengers on many occasions. However, no other individual, to Plaintiffs or Plaintiffs’ counsel’s knowledge, has been threatened with arrest for engaging in this political speech. Nor has any individual been arrested for displaying pro-President Trump messages, for example a red hat that reads “Make America Great Again.” Only Plaintiffs’ expressive activity against the President’s Executive Order, and others advocating similarly, has been threatened with arrest. Regulation 50 is being enforced as a clearly view-point based restriction. Defendants’ application of Regulation 50 to Plaintiffs speech is view-point based and violates the First Amendment.
3.4(g) The seven day advance notice requirement for obtaining a permit is not a reasonable restriction.
Notice periods restrict spontaneous free expression and assembly rights safeguarded in the First Amendment. Plaintiffs, like many others throughout history, wish to engage in First Amendment expression in quick response to topical events. While even in such time-sensitive situations, a municipality may require some short period of advance notice so as to allow it time to take measures to provide for necessary traffic control and other aspects of public safety, the period can be no longer than necessary to meet the City’s urgent and essential needs of this type. See American-Arab Anti-Discrimination Comm. v. City of Dearborn, 418 F.3d 600, 605 (6th Cir. 2005) (“Any notice period is a substantial inhibition on speech.”).
Advance notice requirements that have been upheld by courts have most generally been less than a week. See, e.g., A Quaker Action Group v. Morton, 516 F.2d 717, 735 (D.C. Cir. 1975) (two-day advance notice requirement is reasonable for use of National Park areas in District of Columbia for public gatherings); Powe v. Miles, 407 F.2d 73, 84 (2d Cir. 1968) (two-day advance notice requirement for parade is reasonable); Progressive Labor Party v. Lloyd, 487 F. Supp. 1054, 1059 (D. Mass. 1980) (three-day advance filing requirement for parade permit approved in context of broader challenge); Jackson v. Dobbs, 329 F. Supp. 287, 292 (N.D. Ga. 1970) (marchers must obtain permit by 4 p.m. on day before the march), aff’d, 442 F.2d 928 (5th Cir. 1971). Lengthy advance filing requirements for parade permits, such as the seven day advance notice requirement imposed by Regulation 50, have been struck down as violating the First Amendment. See American-Arab Anti-Discrimination Comm., 418 F.3d at 605-07 (holding that provision requiring thirty days’ notice is overbroad and is not saved by an unwritten policy of waiving the provision); NAACP, W. Region v. City of Richmond, 743 F.2d 1346, 1357 (9th Cir. 1984) (“[A]ll available precedent suggests that a 20-day advance notice requirement is overbroad.”). Even an advance filing requirement of five days has been held too long to comport with the First Amendment. See Douglas v. Brownell, 88 F.3d 1511, 1523-24 (8th Cir. 1996) (city’s asserted goals of protecting pedestrian and vehicular traffic and minimizing inconvenience to the public does not justify five-day advance filing requirement for any parade, defined as ten or more persons).
It is clear that, in the case at bar, a permit requirement of seven days advance notice is not a reasonable restriction of Plaintiffs’ First Amendment rights. Plaintiffs wish to engage in timely, direct action against, what they perceive as, a tyrannical and unconstitutional exercise of the executive power. If Plaintiffs were to have applied for a permit at the exact moment President Trump signed the Executive Order, they would still have been prevented from engaging in First Amendment activity on January 29, 2017. In direct action, like in most things, timing is everything. As evidenced by myriad protests that occurred across the nation’s airports, which were accompanied by no violence or destruction of property and did not otherwise jeopardize security, accommodation of protest at the Jeppesen Terminal is reasonable. Such a lengthy approval period, with no exceptions for spontaneous, peaceful protests, violates the First Amendment. See Church of the American Knights of the Ku Klux Klan v. City of Gary, 334 F.3d 676, 682 (7th Cir. 2003) (noting that “the length of the required period of advance notice is critical to its reasonableness; and given … that political demonstrations are often engendered by topical events, a very long period of advance notice with no exception for spontaneous demonstrations unreasonably limits free speech” (emphasis added)).
3.4(h) Regulation 50 is overbroad in violation of the First Amendment.
“[A] law may be invalidated as overbroad if ‘a substantial number of its applications are unconstitutional, judged in relation to the [ordinance]’s plainly legitimate sweep.’” United States v. Stevens, 559 U.S. 460, 473 (2010) (quoting Wash. State Grange v. Wash. State Republican Party, 552 U.S. 442, 449 n.6 (2008)). An overbroad statute may be challenged on its face even though a more narrowly drawn statute would be valid as applied to the party in the case before it. City Council of L.A. v. Taxpayers for Vincent, 466 U.S. 789, 798 (1984) (“[B]roadly written statutes may have such a deterrent effect on free expression that they should be subject to challenge even by a party whose own conduct may be unprotected.”). The Supreme Court “has repeatedly held that a government purpose to control or prevent activities constitutionally subject to state regulation may not be achieved by means which sweep unnecessarily broadly and thereby invade the area of protected freedoms.” NAACP v. Alabama ex rel. Flowers, 377 U.S. 288, 307 (1964); see also Grayned v. City of Rockford, 408 U.S. 109, 114-15 (1972) (“The crucial question, then, is whether the ordinance sweeps within its prohibitions what may not be punished under the First and Fourteenth Amendments.”). Courts have “provided this expansive remedy out of concern that the threat of enforcement of an overbroad law may deter or ‘chill’ constitutionally protected speech—especially when the overbroad statute imposes criminal sanctions.” Virginia v. Hicks, 539 U.S. 113, 119 (2003).
Determining whether a law is substantially overbroad requires a two-step analysis. First, a court must “construe the challenged [law]; it is impossible to determine whether a [law] reaches too far without first knowing what the [law] covers.” United States v. Williams, 553 U.S. 285, 293 (2008). Second, based on the first step, a court must determine whether the law “criminalizes a substantial amount of protected expressive activity.” Id. at 297.
Regulation 50 provides that “no person or organization shall leaflet, conduct surveys, display signs, gather signatures, solicit funds, or engage in other speech related activity at Denver International Airport for religious, charitable, or political purposes, or in connection with a labor dispute, except pursuant to, and in compliance with, a permit for such activity issued by the CEO or his or her designee.” Those tasked with enforcing Regulation 50, have stated that it bans all “First Amendment expression.” See Exhibit 1, January 28, 2017, Video 1; Exhibit 2, January 28, 2017, Video 2.
A complete prohibition on First Amendment expression and related activity proscripts a substantial amount of protected expressive activity. See Jews for Jesus, 482 U.S. at 569; Lee, 505 U.S. at 830. It prohibits face-to-face conversations and wearing clothing intended to convey a message, along with leafleting and other traditional First Amendment activity, all of which protected expression. Regulation 50’s overbreadth is stark and violates the guarantees of the First Amendment.
3.4(i) Regulation 50 is unconstitutionally vague.
“A fundamental principle in our legal system is that laws which regulate persons or entities must give fair notice of conduct that is forbidden or required.” F.C.C. v. Fox Television Stations, Inc., 132 S. Ct. 2307, 2317 (2012). “A law’s failure to provide fair notice of what constitutes a violation is a special concern where laws ‘abut[ ] upon sensitive areas of basic First Amendment freedoms’ because it ‘inhibit[s] the exercise’ of freedom of expression and ‘inevitably lead[s] citizens to steer far wider of the unlawful zone … than if the boundaries of the forbidden areas were clearly marked.’” Stahl v. City of St. Louis, 687 F.3d 1038, 1041 (8th Cir. 2012) (quoting Grayned, 408 U.S. at 109). For this reason, a stringent vagueness test applies to a law that interferes with the right of free speech. Vill. of Hoffman Estates v. Flipside, Hoffman Estates, Inc., 455 U.S. 489, 499 (1982). “Where a statute’s literal scope, unaided by a narrowing state court interpretation, is capable of reaching expression sheltered by the First Amendment, the doctrine demands a greater degree of specificity than in other contexts.” Smith v. Goguen, 415 U.S. 566, 573 (1974).
Regulation 50 is vague, and therefore unconstitutional, for two separate reasons. First, Regulation 50 fails “to provide the kind of notice that will enable ordinary people to understand what conduct it prohibits.” City of Chicago v. Morales, 527 U.S. 41, 56 (1999). A law is unconstitutionally vague where it “does not provide people with fair notice of when their actions are likely to become unlawful.” Stahl, 687 F.3d at 1041. Because violators of Regulation 50 are subject to criminal sanction, the strictest vagueness test applies. See Reno v. ACLU, 521 U.S. 844, 872 (1997) (recognizing criminal sanctions might “cause speakers to remain silent rather than communicate even arguably unlawful words, ideas, and images” which, together with the “‘risk of discriminatory enforcement’ of vague regulations, poses greater First Amendment concerns than those implicated by [a] civil regulation[.]”). Whether expressive activity will be deemed “First Amendment expression” in the Jeppesen Terminal is not predictable. Plaintiffs have reasonably refrained from protected speech for fear that someone might consider their expression to be in violation of the regulation. However, officials have failed to enforce the regulation against many others who are seemingly in violation, including those discussing politics with other passengers, wearing clothing meant to make some social or political statement, limo drivers soliciting passengers, and those welcoming home military veterans. Although there might be times when a speaker knows, or should know, that certain speech will violate the statute, in many situations such an effect is difficult or impossible to predict. See Stahl, 687 F.3d at 1041 (finding vagueness because even “[t]hough there are certainly times when a speaker knows or should know that certain speech or activities likely will cause a traffic problem, in many situations such an effect is difficult or impossible to predict.”). Regulation 50 fails to give fair notice and therefore violates the mandates of the Fourteenth Amendment.
Regulation 50 is also unconstitutionally broad because it “authorize[s] and even encourage[s] arbitrary and discriminatory enforcement.” Morales, 527 U.S. at 56. Regulation 50’s terms allow law enforcement officials wide discretion to decide whether any given speech is prohibited and arrest the speaker. “Such a statute does not provide for government by clearly defined laws, but rather for government by the moment-to-moment opinions of a policeman on his beat.” Cox v. Louisiana, 379 U.S. 536, 579 (1965); see Norton v. Discipline Comm. of E. Tenn. State Univ., 399 U.S. 906, 909 (1970) (“Officials of public universities . . . are no more free than policemen or prosecutors to punish speech because it is rude or disrespectful, or because it causes in them vague apprehensions, or because for any other reason they do not like its content.”).
Officers have been observed enforcing Regulation 50 against those protesting President Trump’s Executive Order, but not against those wearing other political shirts or buttons. Officers have not enforced the regulation against other political expression, including those standing in support of military veterans returning home from combat. Seemingly, the only ones who have been subject to this regulation are those who are specifically speaking against President Trump’s Executive Order. “The most meaningful aspect of the vagueness doctrine is . . . the requirement that a legislature establish minimal guidelines to govern law enforcement.” Smith, 415 U.S. at 574. Because the terms allow a police officer leeway to determine that expressive conduct is lawful, or not, they are vague. Regulation 50 permits “a standardless sweep [that] allows policemen, prosecutors, and juries to pursue their personal predilections.” Kolender v. Lawson, 461 U.S. 352, 358 (1983) (internal citations omitted). It is unconstitutional.
3.5 Absent an injunction, Plaintiffs will suffer irreparable harm.
“The loss of First Amendment freedoms, for even minimal periods of time, unquestionably constitutes irreparable injury.” Elrod v. Burns, 427 U.S. 347, 373 (1976); see also Verlo v. Martinez, 820 F.3d 1113, 1127 (10th Cir. 2016); Awad v. Ziriax, 670 F.3d 1111, 1131 (10th Cir. 2012) (“[W]hen an alleged constitutional right is involved, most courts hold that no further showing of irreparable injury is necessary.”); Verlo v. Martinez, 820 F.3d 1113, 1127 (10th Cir. 2016).
Moreover, Plaintiffs’ expression is a time-sensitive response to a nearly unprecedented action by our federal government. But see C. Norwood, A Twitter Tribute to Holocaust Victims, THE ATLANTIC (January 27, 2017), https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2017/01/jewish-refugees-in-the-us/514742/ (describing the rebuff of refugees fleeing Nazi Germany in 1939, many of whom would be murdered during the Holocaust); Korematsu v. United States, 323 U.S. 214 (1944). Delaying Plaintiffs’ protest, and discouraging Plaintiffs and others from demonstrating, detracts from its importance and provides a false appearance that Denver is not like other cities of all sizes across the country that have mustered sizeable protests at their airports. Denver has held itself out as a “sanctuary city.” Jon Murray, Mayor Hancock says he welcomes “sanctuary city” title if it means Denver supports immigrants and refugees, The DENVER POST (January 30, 2017), http://www.denverpost.com/2017/01/30/mayor-hancock-welcomes-sanctuary-city-title-denver-supports-immigrants-refugees/. For Colorado’s citizens to seemingly show lackluster support in this time of trial would not only irreparable harm Plaintiffs, and others, but it would go against the public interest.
3.6 The balance of the equities weighs in favor of granting a preliminary injunction.
“The balance of equities… generally favors the constitutionally-protected freedom of expression.” Phelps-Roper v. Nixon, 545 F.3d 685, 690 (8th Cir. 2008) overruled on other grounds by Phelps-Roper v. City of Manchester, Mo., 697 F.3d 678 (8th Cir. 2012). Courts have consistently held that when First Amendment freedoms are threatened, the balance of the equities weighs in the Plaintiffs’ favor. See Verlo, 820 F.3d at 1127; Awad, 670 F.3d at 1132. There is no harm to Defendant, who has no significant interest in the enforcement of Regulation 50 since it is likely unconstitutional.
3.7 A preliminary injunction is in the public interest.
“[I]t is always in the public interest to prevent the violation of a party’s constitutional rights.” Awad, 670 F.3d at 1133 (internal quotation marks omitted); accord Verlo, 820 F.3d at 1127; Pac. Frontier v. Pleasant Grove City, 414 F.3d 1221, 1237 (10th Cir. 2005) (“Vindicating First Amendment freedoms is clearly in the public interest.”); Cate v. Oldham, 707 F.2d 1176, 1190 (10th Cir. 1983) (noting “[t]he strong public interest in protecting First Amendment values”).
4. Conclusion
For the reasons stated, Plaintiffs respectfully request that this Court grant their Motion for a Preliminary Injunction, enjoin enforcement of Regulation 50, and prohibit Defendants from arresting Plaintiffs and all others similarly situated when they engage in First Amendment protected activity within Jeppesen Terminal.
Dated this 6th day of February, 2017
KILLMER, LANE & NEWMAN, LLP
s/ Andy McNulty
__________________________David Lane
Andy McNulty
1543 Champa Street, Suite 400 Denver, CO 80202
Counsel for Plaintiffs
The Poor Peoples Potty Project
Pause You Who Read This. In Great Expectations, Dickens writes, “Pause you who read this, and think for a moment of the long chain of iron or gold, of thorns or flowers, that would never have bound you, but for the formation of the first link of one memorable day.”
Again; I ask the reader to pause and think for a moment; think of our human species, that has come so far in many of our improvements under the conditions we inherited here on planet earth; improvements in our sanitation, shelters and food. These improvements were not some idle whimsy idea, they were made because we needed and wanted to survive as a species, we come to understand that shelter, food and sanitation were the ingredients for longevity. We most often take these normal functions of the human body for granted without thinking as we live our daily lives in suburbia, moving with the speed of light from our jobs to our homes. Should you doubt, you have only to try a small experiment; For a few days camp in your back yard, without the use of your kitchen to cook your meals for nourishment, the shelter that provides warmth and a bed to rest after the toil of a long weary day, the toilet that allows you to clean and relieve your natural body functions. These are the basics of every human on planet earth, there are no exceptions to these rules.
So now I’m thinking of the human mind that figured out how to fly a machine to a comet and land there, wow! What an incredible feat, what an incredible cost of money to accomplish this project. It clearly demonstrates the power of the human mind and our ability to solve a problem.
And then I read the second story of humans who have no shelter here on planet earth, no food for nourishment, no toilet to relieve their normal body functions. So I ask myself; When that space ship left planet earth to land on some distant comet, did it leave behind a human race who have lost their way; on compassion and empathy for our fellow travelers of planet earth? Are we moving so fast through this vast wilderness of space that we cannot see with compassion those in need of the most simple function of all humans.
Is there a solution to the problem? I believe there is.
We have a chance to tell our fellow humans, homeless travelers that they are not alone, we need only look into our hearts and rekindle our compassion that was given each of us as a gift.
A simple solution might look like this; we identify where the homeless congregate, we find solutions to zoning for portable toilets, set up in discreet places, arrange for the portable potty to be serviced and maintained.
It is an effort to reclaim our humanity, our compassion, and say that we care about all as we travel this amazing journey called life.
It only takes one person with an idea to change the world, a person who has compassion and empathy; are you one of those humans? All across America I believe there are such people.
I’am asking only, that you look into your heart and ask yourself; as one person, what can I do to help?
If together we can find a solution to one small problem; a place for the homeless to use a toilet; then think of what we might do next. Anything is possible, homeless and hunger.
Is it not time that we pause in our busy life and think of the long chain that tells us, this is the moment we formed a new link and as members of the human species we then can look back at planet earth with pride of what we carry to those distant stars.
Occupy Denver: not as badass as they pretend to be

DENVER, COLORADO- Occupy activists were making their usual cacophony on Friday night when Denver police cruisers began converging into a familiar disproportionate show of force. Experienced skirmishers though Occupiers are, we couldn’t help whispering to each other as we watched more DPD officers accumulate on foot from vehicles yet unseen. The unintended effect of course was that our chanting diminished as the tension rose and Denver onlookers were treated to a literal illustration of the chilling effect of police intimidation. To make matters more embarassing, Occupy was shouting that we would not be silenced! By the time police were trooping upon us there was no sound but DPD boot steps and our “cameras on, everybody, cameras on.”
Our Friday night boycott of the Tattered Cover Bookstore is part of an OD operation to pressure downtown businesses to withdraw their support for the city’s urban camping ban, an ordinance which in effect criminalizes the homeless. The Tattered Cover claims to have asserted neutrality on the city’s decision to forbid sleeping and sheltering in public, but OD stands with Howard Zinn when he claimed “you can’t be neutral on a moving train.” Silence is consent. Injustice prevails when good people say nothing, yada yada. So it’s the Tattered Cover’s turn to step up to what is everyone’s responsibility. OD invited the Tattered Cover to sign a letter rescinding their support for the inhumane ordinance, but the Tattered Cover’s owner held to her obstinence. She was confident that her customers would have sympathy for her business’s precarious balancing act with the community’s unchristian conservatives. If the Tattered Cover wants to put business over doing the right thing, OD concluded that a boycott could provide the commensurate incentive.
A boycott strategy has worked twice before on this campaign. Actually, boycotts and pickets seldom fail. The global have-nots owe everything to street protest. Grown prosperous, middle America has been shorn of this wisdom. Most Americans do not know what protest is about, thus Friday nights in downtown Denver are also a teaching moment for Occupy. Pardon the inconvenience people of Denver, you’re welcome.
To be fair, for the uninitiated, protests are a messy, noisy thing.
As this Friday evening progressed, occupiers suspected the police were going to make an issue of the serenading, it was self-evidently less melodious than the previous weeks. Earlier we noticed officers dispatched in pairs into multiple directions seeking interviewees from among our audience. But we did not expect a DPD delegation to descend upon us at troop strengh. We began shouting down the DPD as their commander shouted “Can everybody hear me?” What authority had officers to interrupt our constitutional right to assemble? It is amply documented that when activists attempt to interrupt the meetings of others, with Occupy’s “mic check” for example, we are escorted from the room with rough haste.
In Occupy’s defense Friday night, we didn’t submit ourselves to being lectured about “what you are free to do etc, etc.” We knew our rights. We also suspected a noise complaint before the hour of 10pm was of dubious legitimacy. We did however accept an abridgement of our free speech, for the sake of, let’s call it, detente. Because it was dark and we were outnumbered.
A few Occupiers were not happy about being made to relinquish megaphones and drums on the trumped-up premise of signed noise complaints. The officers had obviously solicited the complaints; they had not been dispatched in response to any. Some Occupy wild cannons threatened to upset our disarmament truce. Our hushed reproaches become the next inadvertent impediment to regaining a chant momentum.
In debriefing it was agreed that the more impertinent among us are precious resources Occupy should not make a habit of quashing. When demonstrator numbers are enough to effect unarrests, we’ll have occasion to reject civil liberty infringing ultimatums and encourage the pushing of limits beyond the habitual collective consensus comfort level. This security culture indiscretion about protest strategy is tendered here as an encoded call to action.
BUT SERIOUSLY, what do you make of the Denver Police Department’s exagerated show of numbers at the Friday night action? It was the usual DPD MO in the heydays of Occupy, and it’s what they are throwing now at the Anonymous “Every 5th” resurgence, but what about OD’s campaign -to repeal the Urban Camping Ban- could have provoked a law enforcement surge aimed at its decisive truncation?
WHO KNEW a picket of such limited scope could draw such ire. We aren’t threatening Capitalism or banks or energy infrastructure, or DPD’s favorite, FTP.
However hypocritical and exceptionalist the Tattered Cover is behaving, I don’t believe they requested DPD’s move. But I don’t doubt the Downtown Business Partnership is fearful that the famed independent bookstore might cave to protester demands at which point the DBP’s mandate will lose its liberal cover. They know the inevitability of boycott victories, they’re business people.
WWII air veterans of Doolittle Raiders celebrate 71 years of bombing civilians
I read 30 Seconds Over Tokyo when I was still a war-playing kid, before I would understand the mischievous consequences of the Doolittle Raiders B-25 bombers deploying without their bombsights. This was to prevent US war-making advantages falling into enemy hands but it also precluded dropping bombs with accuracy. I’m pretty certain the account for young readers also didn’t explain why over a quarter of the squadron’s bombs were of the incidiary cluster variety. Readers today know what those are for. Doolittle claimed to be targeting military sites in Japan’s capitol, but “invariably” hit civilian areas including four schools and a hospital. Of the American fliers captured, three were tried and executed by the despicable “Japs”, who considered the straffing of civilians to be war crimes. After the war, the US judged the Japanese officers responsible, as if their verdict was a greater injustice against our aviators’ “honest errors”. Today we rationalize our systemic overshoot policy as “collateral damage”.
Every year since WWII, Doolittle’s commandos are feted for their milestone bombing mission. This Veterans Day is to be the last due to their advanced ages. But it is fitting, because isn’t it time Americans faced what we’re celebrating? There’s no denying it took suicidal daring, but the Doolittle Raid inaugurated what became a staple of US warfare, the wholesale terrorizing of civilians from on high, with impunity and indifference. To be fair, the American public has always been kept in the dark. American aircraft have fire-bombed civilians at every diplomatic opportunity since 1942, and a Private Manning sits in the brig for trying to give us a chance to object.
We now know that the Doolittle Raid didn’t turn the tide, nor shake Japanese resolve. It was a retalliation for the attack on Pearl Harbor, intended to boost US morale as if to say, America wasn’t defeated. Kinda like why and how we struck back at Afghanistan after 9/11, just as indiscriminately.
The “Mark Twain” ersatz bombsight
 The Norden bombsight was a closely guarded US secret weapon. An airstrike without it would today be like lobotomizing so-called smart bombs, and deciding to opt for imprecision bombing. The official army record recounts that a subsitute sighting mechanism was improvised for the raid, dubbed the “Mark Twain” and judged to be effective enough. Now a bad joke. Indochina and Wikileaks-wisened, we know the mendacity of that assessment. The vehemently anti-imperialist, anti-racist Twain would not have been honored.
The Norden bombsight was a closely guarded US secret weapon. An airstrike without it would today be like lobotomizing so-called smart bombs, and deciding to opt for imprecision bombing. The official army record recounts that a subsitute sighting mechanism was improvised for the raid, dubbed the “Mark Twain” and judged to be effective enough. Now a bad joke. Indochina and Wikileaks-wisened, we know the mendacity of that assessment. The vehemently anti-imperialist, anti-racist Twain would not have been honored.
Twain satirized Western so-called Enlightenment thus: “good to fire villages with, upon occasion”.
Post-postwar hagiographies of the raid have suggested the improvised bombsight was better suited to low-altitude missions than the Norden model. That conclusion is easily dismissed because the device was used only for the Doolittle run and never after. The sight’s designer, mission aviator C. Ross Greening, offered a explanation for why he named the device after Mark Twain in his pothumously published memoir Not As Briefed. He didn’t.
The bombsight is named the “Mark Twain” in reference to the “lead line” depth finder used on the Mississippi River paddle wheelers in bygone days.
Because its design was so simple, we’re left to suppose. Greening’s bombsight was named for the same “mark” which Samuel Langhorne Clemens adopted as his celebrated pen name. I find it disingeneous to pretend to repurpose an archaic expression whose meaning was already eclipsed by the household name of America’s most outspoken anti-imperialist. Who would believe you named your dog “Napoleon” after a French pastry?
We are given another glimpse into Greening’s sense of humor by how he named his plane, the “Hari-Kari-er” ready to deal death by bomb-induced suicide. Greening’s B-25 is the one pictured above, with the angelic tart holding a bomb aloft. Greening’s plane was another that carried only incendiary ordnance.
Much was made of the sight’s two-piece aluminum construction, reportedly costing 20 cents at the time compared to the $10,000 Norden. This provided the jingoist homefront the smug satisfaction perhaps, combining a frugality born of the Depression with the American tradition of racism, that only pennies were expensed and or risked on Japanese lives.
War Crimes
Targeting civilians, taking insufficient care to avoid civilian casualties, using disproportunate force, acts of wanton retaliation, and the use of collective punishment are all prohibited by international convention. They are war crimes for which the US prosecutes adversaries but with which our own military refuses to abide. Americans make much of terrorism, yet remain blind to state terrorism. Doolittle’s historic raid, judged by the objective against which it is celebrated as a success, was an act of deliberate terrorism.
Forcing the Japanese to deploy more of their military assets to protect the mainland sounds like a legitimate strategy, except not by targeting civilians to illustrate the vulnerability, nor by terrorizing the population, one of Doolittle’s stated aims. He called it a “fear complex”.
It was hoped that the damage done would be both material and psychological. Material damage was to be the destruction of specific targets with ensuing confusion and retardation of production. The psychological results, it was hoped, would be the recalling of combat equipment from other theaters for home defense, the development of a fear complex in Japan, improved relationships with our Allies, and a favorable reaction in the American people.
There is no defending Japan’s imperialist expansion in the Pacific, and certainly not its own inhumanity. The Japanese treated fellow Asians with the same racist disregard with which we dispatched Filipinos. While Americans point in horror at how the Japanese retalliated against the Chinese population for the Doolittle Raid, we ignore that Doolittle purposely obscured from where our bombers were launched, leaving China’s coast as the only probably suspect.
To be fair, most of Doolittle’s team was kept in the dark about the mission until they were already deployed. I hardly want to detract from the courage they showed to undertake a project that seemed virtually suicidal. But how long should all of us remain in the dark about the true character of the Doolittle Raid?
Out of deference for the earlier generation of WWII veterans, those in leadership, certain intelligence secrets were kept until thirty years after the war. Unveiled, they paint a very different picture of what transpired. The fact that the US knew the German and Japanese codes from early on revealed an imbalance not previously admitted, as an example.
About the Doolittle Raid, much is already openly documented, if not widely known. The impetus for the raid was public knowledge, the evidence of its intent in full view.
BY DESIGN
In the aftermath of Pearl Harbor, American newspapers were already touting offers of cash rewards for whoever would be the first to strike back at Japan. President Roosevelt expressed a deliberate interest in hitting the Japanese mainland, in particular Tokyo, to retaliate for the Japanese strike against Pearl Harbor, never mind it had been a solely military target.
Plans were made to exploit the Japanese homeland’s vulnerability to fire, as ninety percent of urban structures were made of paper and wood. Writes historian William Bruce Jenson:
In his “confidential” meeting with reporters back in November, Marshall had declared that the US would have no cavil about burning Japan’s paper cities.
For the Doolittle Raid, a bombing strategy was developed to overwhelm the fire department of his target, the Shiba ward.
A former naval attache in Tokyo told Doolittle: “I know that Tokyp fire department very well. Seven big scattered fires would be too much for it to cope with.”
As lead plane, Doolittle’s role was to literally blaze the way. Fellow pilot Richard Joyce told Nebraska History Magazine in 1995:
The lead airplane, which was going to have Doolittle on board as the airplane commander, was going to be loaded with nothing but incendiaries -2.2 pound thermite incendiaries- in clusters. They drop these big clusters and then the straps break and they spray, so they set a whole bunch of fires. He was to be the pathfinder and set a whole bunch of fires in Tokyo for pathfinding purposes.
Doolittle’s report outlined his objective more formally:
one plane was to take off ahead of the others, arrive over Tokyo at dusk and fire the most inflammable part of the city with incendiary bombs. This minimized the overall hazard and assured that the target would be lighted up for following airplanes.
Greening paints the most vivid picture, of burning the Japanese paper houses to light the way:
Doolittle planned to leave a couple of hours early, and in the dark set fire to Tokyo’s Shiba ward … the mission’s basic tactic had been that Doolittle would proceed alone and bomb a flammable section of Tokyo, creating a beacon in the night to help guide following planes to their targets.
Doolittle’s copilot Lt Richard Cole, told this to interviews in 1957:
Since we had a load of incendiaries, our target was the populated areas of the west and northwest parts of Tokyo.
After the bombers had left on their raid, and before news got back about whether or not they accomplished it, the Navy crew on the carrier USS Hornet already sang this song, which went in part:
Little did Hiro think that night
The skies above Tokyo would be alight
With the fires that Jimmy started in Tokyo’s dives
To guide to their targets the B-25s.
When all of a sudden from out of the skies
Came a basket of eggs for the little slant eyes
Incendiaries

Most of the bombers were loaded with three demolition bombs and an incendiary cluster bomb. Some of the planes carried only incendiaries. According to Doolittle’s official report of the raid, here were some of their stated objectives:
Plane no. 40-2270, piloted by Lt. Robert Gray:
thickly populated small factories district. … Fourth scattered incendiary over the correct areaPlane No. 40-2250, Lt. Richard Joyce:
Incendiary cluster dropped over thickly populated and dense industrial residential sector immediately inshore from primary target. (Shiba Ward)“The third dem. bomb and the incendiary were dropped in the heavy industrial and residential section in the Shiba Ward 1/4 of a mile in shore from the bay and my tat.”
Aircraft 40-2303, Lt Harold Watson:
the congested industrial districts near the railroad station south of the Imperial PalaceAC 40-2283, David Jones:
the congested area Southeast of the Imperial Palace
Even though the planned night raid became a daytime mission, Doolittle did not alter his original role, intended to light the way for the following planes. His target remained the Shiba District of Tokyo. His own plane: “changed course to the southwest and incendiary-bombed highly inflammable section.”
Doolittle’s report included a description of the incendiary bombs:
The Chemical Warfare Service provided special 500 incendiary clusters each containing 128 incendiary bombs. These clusters were developed at the Edgewood Arsenal and test dropped by the Air Corps test group at Aberdeen. Several tests were carried on to assure their proper functioning and to determine the dropping angle and dispersion. Experimental work on and production of these clusters was carried on most efficiently.
As has become an aerial bombardment tradition, crews were let to inscribe messages on the bombs about to be dropped. Accounts made the most of these chestnuts: “You’ll get a BANG out of this.” And “I don’t want to set the world on fire –only Tokyo.”
These details, which reveal the intentions of the raid, were not made known to the public immediately. The Doolittle Raid was planned and executed in secret, with US government and military spokesmen denying knowledge of the operation even in its aftermath. The first word to reach the American public came from the New York Times, citing Japanese sources:
Enemy bombers appeared over Tokyo for the first time in the current war, inflicting damage on schools and hospitals. Invading planes failed to cause and damage on military establishments, although casualties in the schools and hospitals were as yet unknown. This inhuman attack on these cultural establishments and on residential districts is causing widespread indignation among the populace.
This report was dismissed as propaganda. When Japan declared its intention to charge the airman it had taken captive with war crimes, the US protestations redoubled. The accusations were belittled even as our own reports conceded to the possibilities.
Lieutenant Dawson’s Thirty Seconds Over Tokyo was the first published account of the raid. Printed less than a year after the event, wartime-sensitive details such as the phony guns made of broomstick handles poking out the back were left out. Targets were also not specified, but a candor remained, probably intended to be threatening. Lawson described the 500-pound incendiaries as “something like the old Russian Molotov Breadbasket”, and related US naval attache Jurika’s advice:
“If you can start seven good fires in Tokyo, they’ll never put them out,” Jurika promised us. … “I wouldn’t worry too much about setting fires in flimsy-looking sections of Tokyo,” he said. “The Japanese have done an amazing job of spreading out some of their industries, instead of concentrating them in large buildings. There’s probably a small machine shop under half of these fragile-looking roofs.”
“Flimsy” became Lawson’s keyword for the residential areas. Here Lawson described dropping his third and fourth bombs, when he saw their corresponding red light indicators:
The third red light flickered, and, since we were now over a flimsy area in the southern part of the city, the fourth light blinked. That was the incendiary, which I knew would separate as soon as it hit the wind and that dozens of small fire bombs would molt from it.
I was satisfied about the steel-smelter and hoped the other bombs had done as well. There was no way of telling, but I was positive that Tokyo could have been damaged that day with a rock.
Our actual bombing operation, from the time the first one went until the dive, consumed not more than thirty seconds.
Thus: Chance of hitting civilian homes: 50/50.
Charges of Excessive Force could be expected, because
blame the victim for being weaker than: a rock.
Care taken to avoid innocent casualties: 30 seconds.
In a later afterword, Lawson blamed Tokyo for having insufficient bomb shelters.
After the war, US occupation forces recovered Japanese records which documented the losses attributed to the Doolittle Raid: fifty dead, 252 wounded, ninety buildings. Besides military or strategic targets, that number included nine electric power buildings, a garment factory, a food storage warehouse, a gas company, two misc factories, six wards of Nagoya 2nd Temporary Army Hospital, six elementary or secondary schools, and “innumerable nonmilitary residences”.
Strafing
Japan accused the fliers of indescriminate strafing civilians. The US countered that defending fighters were responsible for stray bullets when their gunfire missed the bombers. That’s very likely, except the raiders were candid about their strafing too. Lawson:
I nosed down a railroad track on the outskirts of the city and passed a locomotive close enough to see the surprised face of the engineer. As I went by I could have kicked myself for not giving the locomotive’s boiler a burst of our forward 30-calibre guns, then I remembered that we might have better use for the ammunition.
A big yacht loomed up ahead of us and, figuring it must be armed, I told Thatcher to give it a burst. We went over it, lifted our nose to put the tail down and Thatcher sprayed its deck with our 50-calibre stingers.
Greening’s account of firing on a sailor, raises the moral ambiguity of air warfare with which few airmen grapple. By virtue that technology allows it, combatants become slave to a predetermined outcome:
When we attacked the next patrol boat, a Japanese sailor threw his hands up as if to surrender. I guess he expected us to stop and take him prisoner. We shot him and left this boat smoking too.
The Medals
Friendship Medals exchanged between Japan and the US found themselves requisitioned for Doolittle’s Raid:
Several years prior to the war, medals of friendship and good relationship were awarded to several people of the United States by the Japanese government. In substance these medals were symbolic of the friendship and cooperation between the nations and were to represent the duration of this attitude. It was decided by the Secretary of the Navy, Mr. Frank Knox, that the time was appropriate to have these medals returned. They had been awarded to Mr. Daniel J. Quigley, Mr. John D. Laurey, Mr. H. Vormstein and Lt. Stephen Jurkis.
After arrangements had been made and the medals secured, a ceremony was held on the deck of the Hornet during which the medals were wired to a 500 lb. bomb to be carried by Lt. Ted Lawson and returned to the Japanese government in an appropriate fashion.
Lawson’s plane no 40-2261 dropped that bomb on an “industrial section of Tokyo” omitting to mention that Japan’s industry was still a post-feudal cottage industry.
“The medals were subsequently delivered in small pieces to their donors in Tokyo by Lt. Ted Lawson at about noon, Saturday, April 18, 1942.”
–Mitscher, M.A. Letter Report to Commander Pacific Fleet.
“Through the courtesy of the War Department your Japanese medal and similar medals, turned in for shipment, were returned to His Royal Highness, The Emperor of Japan on April 18, 1942.”
–Knox, F. Letter Report to Mr. H. Vormstein
Occupy Denver hits the Terrible Twos!
LOOK OUT DENVER! There was no birthday cake this year for Occupy Denver, though the second annual #S17 OWS anniversary celebration did not go unmarked. Subgroup offshoots of Denver’s notorietous Occupy deployed themselves with the usual rowdy spirit. Denver Homeless Out Loud, advocates for the homeless where traditional “advocate” kapos leave off, defied the city’s no-sleep no-shelter ordinance by setting up tents on the eve of S17. Police kept the activists awake all night and forbid them to enter the tents, but the encampment hung on until morning for a scheduled solidarity action. At noon Colorado Foreclosure Resistance picketed the offices of Castle Law Group, responsible for 90% of the state’s foreclosures. Occupiers moved on to protest the Westin’s Palm Restaurant (Boycott the Palm) for its stand on criminalizing Denver’s poor. Other Occupiers couldn’t join in because they were in Boulder organizing Occupy Flood Relief. Armed with megaphones, drums, the capability to mobilize at often a moment’s notice, and an attenuation level pegged at disruptive, Occupy Denver acts every bit its age, prepare for it Denver, a year of the terrible twos. Happy Birthday Occupy!
Our collective lockdown mentality, lest a siren call lure us to freedom
 LOCKDOWN. The term has become ubiquitous, though lifted easily out of context, being self-explanatory. Its predecessor “batten down the hatches” used to be too. Before the advent of recreational sailing it came from a work environment synonymous with incarceration, in the days of debtors prison for penury, before which were slave galleys. As an idiom, batten the hatches still means to fasten things down, brace for difficult weather. “Lockdown” was used this week to describe the city of Boston, as its neighborhood of Watertown was swarmed by militarized police, the residents commanded to “shelter in place”, officers barking at them to stay in your houses, under penalty of being shot, by accident we like to suppose, for their own safety is the implication, or be arrested for obstructing justice. We’ve come to know what lock-down means. It’s a prison term for everyone stuck in their cell, until further notice, sometimes indefinitely. Colorado’s Supermax prison operates in a permanent state of lock-down. Of course in this age of school shootings –another self-defining expression, like “going postal”– lock-downs have become an educational tradition, and isn’t likening schools to prisons forcing an interesting slip into Freudian reality?
LOCKDOWN. The term has become ubiquitous, though lifted easily out of context, being self-explanatory. Its predecessor “batten down the hatches” used to be too. Before the advent of recreational sailing it came from a work environment synonymous with incarceration, in the days of debtors prison for penury, before which were slave galleys. As an idiom, batten the hatches still means to fasten things down, brace for difficult weather. “Lockdown” was used this week to describe the city of Boston, as its neighborhood of Watertown was swarmed by militarized police, the residents commanded to “shelter in place”, officers barking at them to stay in your houses, under penalty of being shot, by accident we like to suppose, for their own safety is the implication, or be arrested for obstructing justice. We’ve come to know what lock-down means. It’s a prison term for everyone stuck in their cell, until further notice, sometimes indefinitely. Colorado’s Supermax prison operates in a permanent state of lock-down. Of course in this age of school shootings –another self-defining expression, like “going postal”– lock-downs have become an educational tradition, and isn’t likening schools to prisons forcing an interesting slip into Freudian reality?
Students have always inferred they were inmates. Without looking it up, I’m now certain the expression “matriculation” was abandoned for its unfortunate implication of being compulsory. Before the middle class, vocational training was worse than mandatory, it was an inevitability. If of course a luxury –how far we’ve come. But our labor saving inventions weren’t meant to save our labor, that profit went to the hoarders of what we produced: produce, became grain, now money. With the means of production owned by the land owner, the rest of us are laborers once again. Underemployed, idled, in the lull of post industrialism, we’re put into lockdown.
And we accept it. Now we’re speaking of building walls to control immigration which means a macro lockdown. We’re prisoners of nation states and we’re breeding children in captivity who can never live Born Free outside zoos.
Boston accepted its lockdown. The media is reporting Bostonians are now catching their breath as if the restriction was some collective girdle. How long would the lockdown have seemed justified? I was rather hoping if the lockdown had extended, that Occupy Boston would have rallied to march on Watertown, to reject the premise that a manhunt for a solitary teen of dubious menace would justify unqualified home invasions without search warrants. I’m rather confident, had Watertown been a submunicipality of Denver, that the infamous cop-baiters of Occupy Denver would have flown their colors in the officers’ faces.
The police were hunting a fugitive teen accused of planting a crude bomb at the Boston Marathon. He’d fled a firefight with police after a car chase said to have involved pipe bombs and grenades, but whose? The suspect was armed and dangerous, but was he? The police also warned that he’d be booby-trapping the neighborhood. They searched houses not just to locate the fugitive, but to check that he hadn’t rigged unsuspecting houses. When he was finally caught there was no mention of his being armed. Perhaps that’s why they couldn’t immolate him like the usual felon, because his hiding place was fiberglass and the imaging devices gave away the fact that he was absolutely defenseless. What may have saved Dzhokhar Tsarnaev was perhaps less the virtual Cop Watch of oversight on police scanners broadcast over the internet, but that the young man sought refuge in a boat.
You might quarrel with my nautical analogy, there are perhaps less archaic idioms than “batten down the hatches”, but specifically it means to seal the hull, batten in this case being a verb referring to a tool for reefing the sail, and see, none of this translates anymore. As we lose the middle class, we lose our sailing terms, just as the working class has lost its fisheries. Hatch is still relevant to aircraft and spaceships, which the common urchin might still know virtually, but for how long prison ship Spaceship Earth?
Odysseus had his men lash (See?) him to the mast so he could resist the Sirens’ call that lured sailors to their doom. Literally battening him in lockdown, because beyond here lie dragons, sea monster mermaids who would waylay the course of Western Civilization, which now seems the better idea.
Colorado Extraction Resistance claims responsibility for gas balloon attack on gas frackers

DENVER, COLORADO- Organizers of an annual oil and gas industry conference held at the Grand Hyatt on Monday and Tuesday tried to prevent public interruption of their let’s frack Colorado discussion. They tried to ignore protesters outside. They revoked the admissions passes granted to activists who wanted to attend the open segment of the conference designed for public consumption. They didn’t count on the COLORADO EXTRACTION RESISTANCE to successfully negotiate the heightened security and deliver gas balloons to gas frackers convening in the ballroom.
Attached to the balloons, which swiftly lifted to the ceiling neatly beyond reach, were noisemakers which accentuated the shouts of the Extraction Resisters shouting “Ban Fracking Everywhere!” Most of the interlopers escaped but one was manhandled, his head slammed against the wall, and arrested for wielding balloons. In a dispiriting twist, attendees conspiring to frack the shit out of Colorado were not arrested, though the gases which leak from their wells pose a more eminent public threat than helium.
The successful interruption prompted a spirited protest outside, where conference attendees were heckled and passersby were warned to pay special care as they passed the Grand Hyatt, at that moment sheltering eco-terrorists from citizens arrest.
(UPDATE: Now read their account and full DIY instructions!)
Target of Occupy Denver boycott expects DPD to roll protesters like they’re homeless sleepers
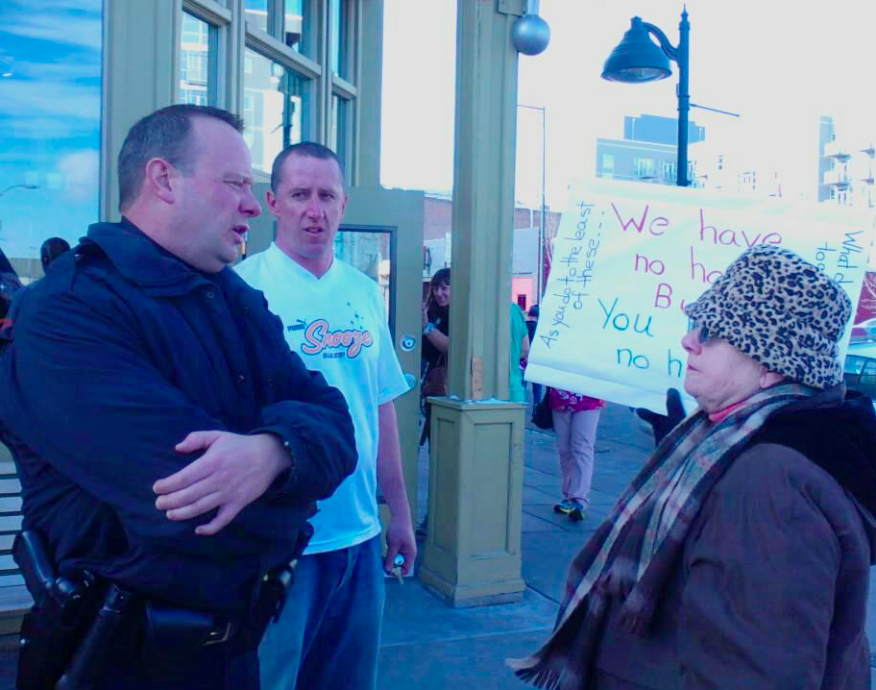

DENVER, COLORADO- Downtown eatery co-owner Jon Schlegel thought the homeless were defenseless when he led an effort to criminalize sleeping or seeking shelter out-of-doors last year. Instead Schlegel incurred the wrath of Occupy Denver, who’ve maintained a now seven-month long Boycott Snooze protest opposite his trendy restaurant. Yes it’s personal, Schlegel opened SNOOZE in a depressed area adjacent to a homeless shelter, now he wants to gentrify his digs by running out the homeless. So every Sunday occupiers bring signs to sway potential customers from supporting Snooze’s war on the homeless, and every Sunday Schlegel calls the police. But there have been no charges, officers remind Occupiers they are within their rights, yet Snoozegoers are treated to the illusion that the boycott’s legality may be borderline. You know, it’s that phony paradox promoted by our corporate media, that free speech means having to tolerate another’s opinion however offensive. (When free speech offends you, you are likely the offender being protested.) The real question is how Denver Police justify juxtaposing their intimidating armed presence against a citizen’s First Amendment rights.
Steve Bass found guilty of camping not occupying, but could jury have ruled otherwise without hearing his defense?

COLORADO SPRINGS, Colo.– You may have underestimated the importance of today’s Camping Ban trial. The local media, social justice community and rights watchdogs missed it. But judging from the police force on hand and the elaborate lock-downs placed on the jury pools, it was evident the City of Colorado Springs thought a lot was at stake. I’ve written already about the draconian motions to prevent defendant Steve Bass from explaining his motives, including a ban of the word “Occupy.” Today the court made audience members remove their “Occupy Colorado Springs” t-shirts, but let the cat out of the bag by the palpable gravitas with which the court officials and police handled jury selection. Except for the absence of TV crews outside, you’d have thought Steve Bass was Hannibal Lector tripped up by an urban camping ordinance at “what happened last year in October at a park downtown.”
 Yeah, even mention of “Acacia Park” was giving away too much, the prosecuting attorney preferred to call it “115 W. Platte Ave.” Every so often a prospective juror would stand up and say “I presume you’re referring to OCCUPY WALL STREET?” like he was solving a riddle, but instead of the door prize that volunteer would be dismissed from the pool for knowing too much.
Yeah, even mention of “Acacia Park” was giving away too much, the prosecuting attorney preferred to call it “115 W. Platte Ave.” Every so often a prospective juror would stand up and say “I presume you’re referring to OCCUPY WALL STREET?” like he was solving a riddle, but instead of the door prize that volunteer would be dismissed from the pool for knowing too much.
After a trial that lasted one third the length of the jury selection, Steve Bass was found guilty. He offered no testimony, his lawyer, the very capable Patty Perelo, made no closing statement, because what defense could be made? Steve and his council elected not to have him testify, because to begin with, he’d have to swear to tell the whole truth, and if he explained he could only tell part of the truth, he’d be slapped with Contempt of Court.
We thought the jurors might have been curious, after seeing the city’s 8×10 glossy pictures with the circles and arrows telling what each one was and hearing not a peep from Bass, but they didn’t express it, and left after giving their verdict. This is Colorado Springs.
One of the prosecution’s witnesses, the arresting officer, nearly spilled the beans when he identified the defendant as someone he couldn’t have confused for someone else, because he’d said he’d encountered Bass many times in the park and shared many conversations.
“Oh?” the defense attorney Perelo perked her ears and asked, “and WHAT did you talk about?”
“Um… homeless policy, mostly.” That’s all HE could say. He couldn’t explain why he’d encountered the defendant so many times, or what the defendant was doing. Attorney Perelo couldn’t push it, because that would be leading him into forbidden territory. His testimony for the prosecutor was delivered straight from his notes.
There were two police witnesses, a map and several photographs, showing the tent and another showing just the poles. Was this necessary for a conviction? Because it necessitated explaining to the jury that said poles were in their “unerected state”. Not to be confused with the tent which was “fully erected”, which the judge pronounced like expressions which tripped off the tongue in cases of serious crime.
A photo of two sleeping bags required the officer to say he found the defendant sleeping “in the bags in the tent in the park” to prove all the elements of a violation of the camping ban.
The prosecuting attorney summarized it thus: “there was a tent, there was a sleeping bag, looks like camping to me.”
Not according to a dictionary definition of course. But that too had been motioned inadmissible. If you look it up, camping is variously defined as to “Live for a time in a camp, tent, or camper, as when on vacation.” Or as when destitute? Dictionaries don’t go there. That’s more like sheltering.
A couple of other examples: Soldiers sleep in tents. They’re not camping. Mountaineers overnighting on the side of a mountain aren’t camping. Refugees of war and natural disasters stay in refuge camps, but aren’t said to be camping. Anyway.
Steve Bass didn’t get his day in court. Everything he wanted to say he couldn’t. His attorney’s strategy today was to prepare for an appeal, on the grounds that the judge deprived Bass of the ability to defend himself.
Did Bass violate the camping ban as the jury decided? The prosecutor explained that nobody, not the judge, nor police officers or herself or the jury was in the position to decide the law. So Steve Bass has to take his case to someone who can.
Jury Selection
Over four hours were spent on choosing a jury, by far the most interesting part of the day. It took three sets of 25 potential jurors to pick six and one alternate. As the process approached lunch hour, the court was eager to buy pizza for seven instead of twenty five, but they didn’t make it.
As I mentioned, usually a juror familiar with “Occupy Wall Street” was dismissed, whether their opinions were favorable or unfavorable. I saw one juror dismissed because delving further would have meant discussing Occupy too much and would expose the other jurors to more occupy talk than the judge or prosecutor wanted.
On the other hand, many jurors had direct relatives in law enforcement, one juror considered a CSPD officer her “knight in shining armor,” so that was another cause for eliminations.
During the second batch, another juror stood up to say he was a former corrections officer, who wasn’t sure if he might have met Steve Bass “in the course of his duties” which poisoned the entire group by suggesting Steve had spent time in prison. That batch was dismissed. In actuality, Steve recognized him, because they both frequented the Dulcimer Shop.
Though Judge Williams maintained a convivial air of impartiality, he betrayed an awful prejudice. Whenever a juror expressed knowing something of what was in the news in October 2011, the judge would asked them if they could refrain from judging Bass based on the misbehavior of others. If jurors who knew about the protests were let to remain in the running, the assumption the judge offered was that “Occupy” was a taint that the defendant hoped they would overcome.
I don’t doubt that this slant extends well beyond Occupy, because municipal courts are notorious for being rubber stamps of a city’s citation process.
For example, in Judge Williams’ instructions to the jury, he read the sample guilty verdict first, in all its solemnity. When he read the not-guilty sample, he broke character to explain that he was not going to repeat the redundant stuff, etc, etc, and then he told the jury they shouldn’t be swayed by the order in which the two samples were read. The dramatic guilty versus the blah blah not-guilty.
Occupy harassment
Knowing about the prohibition against Steve mentioning Occupy, we thought we’d exercise our right not to be gagged. Could it matter? Should it? How preposterous that Steve was being tried and not permitted to say what he was doing. As if some precedent would be set that a defendant might convince a jury that forbidding a person shelter was a bad law.
So we came to court with t-shirts that read OCCUPY COLORADO SPRINGS. Immediately when we sat down, the judge called the lawyers up and decided we’d have to remove our shirts. We were given a chance to explain who we were, but the choice was invert the shirts, put on new ones, or leave. So we walked out.
I had an extra shirt outside with a peace symbol on it. Admittedly a politically-charged shirt, somewhat iconic locally, because it recalled an event in 2007 when peaceful protesters were forcibly removed from a city parade, one of them dragged across the pavement, an elderly woman who subsequently died of complications. So I knew I might be pushing it.
The point being to give Defendant Bass some context. He’s an activist. Alone without a voice he was a perp. With an audience of protestors he becomes a man of mystery. Every accused person in court is sized up in part based on his relations sitting behind him. Why shouldn’t Steve be allowed to show who his friends are?
As I reemerged from my car, already a police supervisor was yelling across the street to tell me I wouldn’t be allowed to wear that shirt. “Are you kidding?” I asked. I had a bag full of them, prepared for this eventuality if other spectators wanted to show solidarity. He was crossing the street to preempt my bringing the confrontation to the steps of the courthouse.
“Eric, you know the judge won’t let you wear that shirt.”
“I know no such thing. He only forbid things that say Occupy.” I knew this to be true, technically.

But they weren’t budging, they claimed a jury pool was already in the courtroom and they didn’t want to take any chances. Oddly, the officer blocking my way, beside the supervisor, was Good Old Officer Paladino who’d brutalized my friends and me in 2007. So he knew the t-shirt too well. Actually Officer Irwin Paladino’s history of abusing protesters goes back to 2003. I decided to dispense with plan B and invert my black t-shirt so I could go back in.
Did the CSPD make the smart call forbidding my t-shirt? I’ll be the first to admit the CSPD have outwitted the local social justice movement at every turn in Colorado Springs. They’re clever and competent, but they’re in the wrong. The CSPD are stepping on our rights, and overstepping their authority to do it. While it may have been superior gamesmanship, it was wrong.
Have I mentioned that they followed us everywhere? As if we were the accused in need of escort. On the officers’ radios we could hear them narrating our movements throughout the building. When Patrick went to the bathroom, an officer followed him inside and made small talk as Patrick peed. Did they think we were going to Mike Check the men’s room?
At one point we were able to see from a window on the second floor hall that CSPD were conferring with a parking enforcement officer around our cars. She was examining the license plates, getting on her phone, standing by the cars, as if waiting for something. The cars were legally parked, the meters fed, and well within the four hour limit. But who wants to argue with an impound lot? I assure you this intimidation tactic worked very well to send us out of the courthouse to rescue our vehicles.
Meanwhile, another friend came into the courthouse and overheard officers discussing whether to deny us entry again, and by what pretext, but I’m getting ahead of myself.
While watching the jury selection, it was the batch that was being dismissed in full, the court bailiff suddenly bolted from behind where we were sitting and told the judge she’d overheard us whispering about inappropriate subjects, specifically using profanity. This accusation was based on a dear Occupier’s habit of muttering colorful asides. Okay this was true, but in his defense, it was after the jury being spoiled, about the jury being spoiled, but inappropriate none-the-less and he apologized. But to tie all together in the misbehavior was a fabrication. The prosecutor tried to have us evicted, and Officer Paladino chimed in about the confrontation I instigated at the door. That’s when my friend told the judge she’d overheard CSPD officers discussing plans to keep us out, so the bailiff’s actions began to appear a little contrived.
This complaint was finally settled with the judge’s warning that one peep out of us would get us 90 days in jail for Contempt of Court. At this point we knew the pieces of duct tape we’d brought in to use to protest Steve’s gagging were definitely OUT.
Just before lunch recess I was able to clarify with Judge Williams whether the peace t-shirt I had wanted to wear was acceptable to the court. Receiving no objection from the prosecutor, the judge told me it would be okay, and then assured me he’d inform CSPD.
Returning from lunch, once again with the peace shirt, the security screeners nearly didn’t let me pass, but I barreled past with the confidence of someone who knows his rights. This time Officer Paladino came upon me at the courtroom door, swaggering right into my face assuring me he was not going to let me pass. FORTUNATELY before he could wrestle my arms behind my back, another supervisor arrived who’d heard the judge, and I was allowed to proceed. Boring story I know. But the pattern was unsettling.
Then Steve was found guilty, you could feel the city’s giddiness as they discussed sentencing. We’re only talking community service, but Colorado Springs has only one contractor for that, the odious Keep Colorado Springs Beautiful, whose hi profile task is to clean up after the CSPD Homeless Outreach Team scoops up the homeless and puts them in shelters very much in the model of correctional facilities. Steve was able to negotiate a less anti-homeless agency, and that’s the story so far.
City Hall of Mirrors
As cities around the US bully Occupy groups around on park verges and college campuses, we here in Colorado Springs have not remained unscathed. Monday morning saw our friendly neighborhood “Homeless Outreach Team,” (HOT), and a much less friendly contingent from the city’s code enforcement office dismantle the previously permitted Occupy site at Acacia Park in downtown Colorado Springs. A surprisingly good-sized group materialized after midnight to vocally express displeasure at the actions of the city as rendered by the police and what appeared to be a rather callous batch of contracted laborers hired to accomplish the actual dismantling. No one got beat up or gassed. The permit surrounding which had developed controversy in our little microcosm is gone and we will now be required to redefine, restructure, and proceed without it. Personally, i feel it to be a good riddance even though we here in Colorado Springs seem to be experiencing a bit of disorientation as a result.
Dan and M.J. of the HOT team, (a redundancy, i know, but common parlance), were present for the dismantling of the tents that had been a fixture at our protest site. Some 50 or so protesters managed to flood the scene, even at the late hour of the event. Despite the relative peace between authorities and Occupiers here, the police present were fully prepared to inflict harm if we protesters had engaged in any form other than the sometimes obnoxious yelling. The whole scene, not unlike other aspects of our unusual local manifestation of the Movement, produced and continues to produce a sense of extreme ambiguity in my own psyche. I like to think of Dan and M.J. as friends, at least in a provisional sense, but i have no choice but to acknowledge that none of my closest friends would ever even think of putting me in jail or beating me up, even if i piss them off.
Tuesday a fairly large group of Occupiers attended a City Council meeting with a previously established agenda, none of which was to address Occupy directly, though it would be difficult to conjure a government meeting with an agenda that pertained to no issue encompassed by Occupy at this juncture. My own experience at the council meeting felt very much like an exercise in futility. A gentleman preceded us Occupiers with a request to restore city funding to his non-profit that helps supply transportation to disabled city residents. As the council and mayor did with our objections next, they seemed to tolerate the man’s speech and then perfunctorily ignore it. No indication of interest or intention to act was in evidence. Aimee Cox, serving as some sort of city liaison, distributed a few sheets describing the city’s appeal process in a few sentences. The remainder of the council meeting involved investment strategy and plans to extract additional money from residents in the form of utility rate hikes.
The minutiae to all this wrangling is just about as pointless to describe as anything i can picture. The clearest vision afforded by the whole scene is still one of a struggle to get things from those that control them on the one hand, while struggling to keep people from getting things on the other. There remains a sense of entitlement held both by those with little, and by those generally smug players with much. I remain convinced that the current state of affairs is fully unsustainable. The global takeover of industry and commerce by factions that appear fully unconcerned by any consideration other than personal enrichment has led to a scenario in which those at the winning end of that paradigm are in as much trouble as anyone else. Sure, if our supply of food, energy, shelter, and so on becomes insufficient those with more clout in hand may well be able to hold out rather longer than those otherwise equipped. A few survivalists will likely outlast inner city dope fiends; but what’s the point? Is the object of human interaction to feel smugger than the next guy? Who gets to feel the smuggest?
Directly attacking the intractable problems of human interaction seems as futile as ever. No amount of negotiation seems effective enough to overcome the entrenched cultural aversion to cooperation and insistence on coming out on top that has produced such a three ring circus of a society. Observe that Colorado Springs’s Mayor Bach is in office after a campaign financed largely by real estate and development interests. Really, now, do we need more buildings around here, or aren’t these activities really just the outcome of individual efforts to scrabble up money? Think about that a moment. How much human activity is nothing more than bullshit make-work designed not to be productive, but to shift money around? How much useless crap does Madison Avenue convince us we need for no better reason than to supply income to its players. I’m suggesting that most of the stupid jobs we Occupiers hear we should get so often are self-destructive bullshit. That the great majority of laws and regulations we have allowed to overwhelm our hard-won liberty, spawning the parasitic legal industry, the real estate industry, the huge regulatory bureaucracies of governments all around, and in fact most of the “work” we humans do is utterly pointless. I’m suggesting that we humans will, in fact, need to rethink our entire interaction with one another if we are to survive our own more ridiculous tendencies.
I’m hardly the first person to posit this notion. Jeremy Rifkin, for one, discussed the ideas i merely hint at above in rather more depth in his 1995 book, The End of Work. Of course, suspicious religious folk have raised an uproar at the mere mention of Rifkin for decades now, claiming him to be a Devil-worshiper, among other things. The sad truth seems to be that fundamentalists in this country and others, of Christian orientation and others, seem content to allow their Creator’s handiwork to burn to ash rather than to work together with anyone else to resolve the problems we humans have cobbled together to our own collective detriment. As little as i relish the sort of fight that generally ensues from arguing about spiritual matters, i’ll be finding it necessary to head in that direction in upcoming posts. Hold on tight, and please feel free to engage….
Occupy Colo. Springs evicted last night, loses permit and shelter, wins standoff.

OCCUPIED COLORADO SPRINGS- At 11pm came a two-hour warning, at 1am the wrecking crew. By 3am Colorado Springs Occupiers had no place to sleep or warm up in the cold, but carried on their protest. Loring Wirbel has the best local OWS op-ed yet.
Here’s video footage from Patrick Jay.
#Occupy Colo. Springs Municipal Court

OCCUPIED COLORADO SPRINGS- Attention local media, if you’re looking for authentic spokespeople for Occupy Colorado Springs, you need look no further than today’s front row. Holding the big sign is first arrestee Steve Bass, to his right: three times arrestee Iraq vet Jack Semple, arrestee Amber Hagen, arrestee Raven Martinez, and arrestee Thomas G.
Also pictured, former Colorado Congressman Dennis Apuan, Occupy founding member Jon Martinez and Socialist activist Patrick Jay. Not pictured, Joel Aigner and Hossein Forouzandeh who were speaking at a UCCS occupy teach-in.
Here’s a video of the Saturday arrests of veteran of Fallujah Timothy “Jack” Semple and Amber Hagen of the 7-11 incident. Worth the watch. ROCKSTARS!
Mark your calendars, upcoming arraignments are scheduled November 21, 29 and 30.
Raven addressed the Colorado Springs City Council today on the unconstitutionality of the no-camping ordinance being enforced to curb the Occupy protest. Here’s what she said:
As a citizen of the United States, one has a given right to life, liberty, & property. These rights are protected by both the 5th & 14th Amendments to the Constitution.
In Bolling v Sharpe, The Supreme Court interpreted the 5th Amendment’s due process clause to include an equal protection element.
The 14th Amendment states:
“No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of the citizens of the United States; nor shall any state deprive any person of LIFE, LIBERTY, or PROPERTY, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.”
Knowing that sleep is a necessity of Life, every American citizen has a right to sleep, regardless of status.
“HOMELESSNESS” is considered a status.
The camping ordinance ultimately denies one the right to sleep, therefore the right to live, based on their status. How many people have been arrested for setting up a canopy, with blankets & food, to take a nap or have a picnic on public property.
Now if a homeless person sets up a canopy, has blankets and food with them, will they be told to take down their canopy under the current camping ordinance? If so, then the ordinance is based on status, therefore unconstitutional.
If not, then it leaves too much discretion in the hands of the individual law enforcement officer, making the ordinance over-broad and unconstitutionally vague.
When one is homeless, where can that person sleep? If they set up to sleep on Public property they would be violating the current city ordinance, they will be told to leave and told of a shelter to go to, being their only alternative. This amounts to incarceration in the shelter without a violation of law having been committed. This also violates ones right to due process in that it allows for arbitrary enforcement.
When you criminalize a non-criminal act of necessity, you greatly increase the possibility of that person committing other crimes, as well as decrease that persons ability to obtain employment.
State v Folks, No. 96-19569 MM found that a city ordinance which punished innocent conduct, such as sleeping/camping on public property, violated the defendant’s right to be free from cruel and unusual punishment, which is protected under the 8th Amendment.
I ask you to look at the constitutionality as well as the long term effects of such an ordinance, it starts a domino effect that negatively impacts an already hurting economy.
How much does it cost in tax payers money to pursue such a case?
We have to have change! If we want a better economy and overall society, then the government, Federal, State, & Local, must change the way they conduct business. Criminalizing acts of necessity is business, not a way to protect our American citizens.
“Definition of Insanity: Doing the same thing over & over again and expecting different results.” -Albert Einstein
Pass a new ordinance to repeal the current one.
Last night Occupy Denver sheltered in igloo until DPD igloo-countermeasure

OCCUPIED DENVER- Forbidden from erecting tents in Lincoln Park, despite cold and snow, intrepid OWS protesters took their lemons, made lemonade, and surprised authorities with a PROTEST IGLOO. So DPD drove a bulldozer over it.
Colorado Springs issues permit to sleep on sidewalk but without tents. Let Them Eat Concrete
 COLO. SPRINGS- I’m not crazy about OCCUPY organizers negotiating with city representatives for a tentative permit to occupy Acacia Park. You don’t need permits for free speech, nor does activism gain by the advice of cops. That said, allowing a protest encampment, even without tents, may grow participation more effectively than outrage over oppressive responses to civil disobedience. So what’s come of this strategy today is the same permission that has been granted to the Wall Street activists in Zuccotti Plaza, sleeping bags but no tents. Doesn’t that seem shamelessly punitive? Shelter is a human right, deprivation of which is a violation of the 14th Amendment. It’s likely the city could be held liable for endangering the health and lives of these activists.
COLO. SPRINGS- I’m not crazy about OCCUPY organizers negotiating with city representatives for a tentative permit to occupy Acacia Park. You don’t need permits for free speech, nor does activism gain by the advice of cops. That said, allowing a protest encampment, even without tents, may grow participation more effectively than outrage over oppressive responses to civil disobedience. So what’s come of this strategy today is the same permission that has been granted to the Wall Street activists in Zuccotti Plaza, sleeping bags but no tents. Doesn’t that seem shamelessly punitive? Shelter is a human right, deprivation of which is a violation of the 14th Amendment. It’s likely the city could be held liable for endangering the health and lives of these activists.
So permits or not? No American citizen needs permission to express himself, and whatever means you have to conspire to shut down Wall Street are not going to be allowed. So should an occupation seek a permit? The physics of military occupation are Might Makes Right, not Simon Says. But military intelligence and diplomats play invaluable roles. Might makes right, but guile and craft save the occupiers manpower and lives. Maybe permits create the beachhead with which the American people get their size 99 shoe in the door.
Holding regular meetups with the police is another dilemma. I know I’m not shrewd enough to go head to head with a police department, its vast intelligence resources, and well practiced dissent-quashing strategies. For me a most significant element of the public demonstration is law enforcement’s incapability of predicting unregulated behavior.
The 14th Amendment forbids the state to “deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law.” So we might well pause to consider another news story which emerged today, that the US citizen assassinated by CIA drones in Yemen, wasn’t riding in a convoy as previously claimed, but at a dinner party with a 16-year-old relative and his friends, all of them killed without trial or even legal charges. At its simplest the 14th Amendment says you can’t punish someone before properly found guilty. Forcing inhumane conditions upon a citizen exercising his rights is punitive, cruel and unusual.
In Denver today a similar delegation met with the mayor, who give his permission for protests to continue, as it was his to give, for his subjects to exercise their 1st Amendment Rights, but abridged to exclude at night, in the cold, or in city park. Specifically the Denver mayor said he’d allow them to sleep on sidewalks provided they’re exposed to the elements. No tents. Let them eat concrete.
The Colorado Springs city attorney gave instruction to formalize the handicap with a permit. They can sleep on sidewalks but no shelter allowed. Want a cold or flu? Have at it.
A provocative thought, however sad: will today’s protesters submitting their bodies to rain, cold and snow, submitting their health and spirits to debilitating hardship, streamed live on the internet, will it have a similar effect as images of water hoses on civil rights marchers?
DPD used riot gear in dead of night to arrest camp singing national anthem

DENVER- When Occupy Denver threatens to make a difference is when authorities have to shut it down. The sweep tonight is a good sign.
I’m not worried about Occupy Denver. I have a tent booked for this weekend, the police attack tonight will just raise occupancy rate is all. Now I’ll have to move up my check-in date to be assured a space. Colorado Police have already lost this engagement. The mere threat of arrest tonight only enlarged the protest, it didn’t frighten it off. Middle of the night arrests and tent-clearing are of little consequence. At height of the crowd strength, the police backed down. Tents will go up everywhere tomorrow. There’s not enough riot gear in the US to occupy the multitude of protest occupations. Denver state capitol here we come!
Gov Hickenlooper’s use of State Troopers to clear the capitol lawn in the middle of night probably preempted actions by other Occupy camps to draw police resources away. Next time how can they distract the popo legally? Follow Occupy Denver’s lead. Apparently peaceful, nonviolent free speech is enough to bring clampdown.
GA earlier in evening reaffirmed that movement is not about having messages heard, to be ignored per usual, but SHUTTING DOWN THE SYSTEM. It’s is not about speaking truth to power. Power already knows the truth. What it doesn’t know is extent of peoples’ determination. Denver GA wasn’t won over by voices content to keep occupation as daily sidewalk protests, lasting into winter, to usual no effect. You want protracted Wall Street protest? Antiwar vigils have been ongoing for 10 years…
Tents ARE key issue for all Occupy protests. What is your right to peaceably assemble if you can’t protect yourself from cold? Does 1st Amendment only apply in summer, during the day, and when authorities aren’t too bothered by your dissent? Thinking this movement is about getting your issues heard is to pretend #OccupyWallStreet means “Voice Off to Wall Street.” Nope. Tents are needed in Denver, Wall Street and everywhere because this movement needs to stop the system, not hector it until we lose energy & body temp.
The Denver Post doesn’t have a live camera from their building which overlooks the capitol and Occupy camp. They’re not press, they’re criminals. What they have is nominal, the view above actually, but a low rez surveillance webcam is poor excuse for a media outlet.
Those who think Occupy Denver should have decamped and gone home, are not thinking of the homeless -the fullest victims of Wall Street. Hopefully Occupy members who were praising the Denver Police so warmly in earlier GAs will stick around on sidelines at least to get lesson in police state. Of course all the members who chose to flee DPD intimidation will be welcomed back tomorrow. But voicing their next 2-cents worth? Not so much.
Police are people too, but they have a job to do. By coincidence it’s to stop you from stopping Wall Street. Yep it’s a dilemma. It’s probably no surprise that pro-fracking, pro-coal, pro-war, anti-immigrant, anti-union gov of Colorado would be against Occupy Denver. Issuing a warning of arrests to be made between 11-5am is extortion, threatening unlawful arrest is police state terrorism. Do we accept police raids tonight on Denver and Seattle camps? Protest is civil right, shelter is human right. Police state is fascist wrong.
Something to thing about: Whole crowds can be subdued by one tyrant with a gun, if they remain nonviolent. Numerical superiority counts where people have courage to act. When people say there’s strength in numbers, it’s not if you’re queued obediently to have your eye put out, or shot, or for rigged elections.
Colo. State Troopers are wearing riot gear to face Denver protesters, because post-curfew peaceful campers equals RIOT in Fascist police state.
Iraq & Afghanistan should have thought to require US to withdraw occupation every night. Military bases must violate some vagrancy law.
Cops sympathetic to 99% could have shown their mettle if they’d occupy their sick leave, occupy off-duty, occupy right to refuse unlawful orders. Otherwise state troopers are dumbasses and do not represent Colorado or 99%. I know by regulation cop IQ has max limit, didn’t know cowardice was also requisite.
Occupy Denver was won Oct 14 at 11:01PM, regardless what happens now. Threat of arrest enlarged crowd, didn’t shrink it. The movement’s momentum is proved.
Mid-night raid won’t matter. Cops wouldn’t face crowd at its largest, the Occupy protests have been emboldened past critical mass.
The 40 minute warning given to the protesters is actually the police giving themselves 40 minutes to shit their pants. The OWS juggernaut is on the move and the popo have chosen to side against 99%. Denver officers, you’re marching against the 99%. Occupy Denver will forgive you and blame your bosses. But you’ve probably heard of Anonymous’ motto.
Riot gear worn by Colorado police concedes conceit that Occupy Denver issue is illegal camping. OWS protest camp is free speech and assembly.
Under cover of night Boston PD raided protest, arrested 50 and razed camp
Under cover of darkness, Boston and Massachusetts State Police raided Camp 2 of the OCCUPY BOSTON protest. A reported fifty activists were arrested, the police brutalized mostly elderly Veterans For Peace members trying to protect the campsite. Even as the paddy wagons were being filled, sanitation department garbage trucks were being filled with all the camp materials, tents, sleeping bags, signs and all. The pretext for the raid was that camping was in violation of city ordinances, the excuse being used on Wall Street and here in Colorado Springs. Constitutionally the enforcement of such laws are violating the protesters’ first amendment right to assemble, a right guaranteed night or day, sunny weather or inclement. The right to shelter is guaranteed by the UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Laws targeted at homelessness are being used exactly as opponents feared, to squelch political dissent. Notable about tonight’s raid, the Boston camp was an expansion camp relative to the original encampment, demonstrating that authorities will tolerate protest so long as it is nominal. They definitely do not want to see it growing.
Occupy Denver recognizes Colo. AIM, mixes metaphor to Unoccupy America!
 This weekend the General Assembly of Occupy Denver recognized that its intended occupation was actually a re-occupation, of lands to which original inhabitants lay claim. On Sunday the GA consensus voiced its solidarity with the American Indian Movement of Colorado who submitted a statement for ratification. It’s reprinted below via The Sole Reader:
This weekend the General Assembly of Occupy Denver recognized that its intended occupation was actually a re-occupation, of lands to which original inhabitants lay claim. On Sunday the GA consensus voiced its solidarity with the American Indian Movement of Colorado who submitted a statement for ratification. It’s reprinted below via The Sole Reader:
COLORADO AIM’S CHALLENGE TO #OCCUPYDENVER
An Indigenous Platform Proposal for “Occupy Denver”
“Now we put our minds together to see what kind of world we can create for the seventh generation yet to come.”
John Mohawk (1944-2006), Seneca Nation
As indigenous peoples, we welcome the awakening of those who are relatively new to our homeland. We are thankful, and rejoice, for the emergence of a movement that is mindful of its place in the environment, that seeks economic and social justice, that strives for an end to oppression in all its forms, that demands an adequate standard of food, employment, shelter and health care for all, and that calls for envisioning a new, respectful and honorable society. We have been waiting for 519 years for such a movement, ever since that fateful day in October, 1492 when a different worldview arrived – one of greed, hierarchy, destruction and genocide.
In observing the “Occupy Together” expansion, we are reminded that the territories of our indigenous nations have been “under occupation” for decades, if not centuries. We remind the occupants of this encampment in Denver that they are on the territories of the Cheyenne, Arapaho and Ute peoples. In the U.S., indigenous nations were the first targets of corporate/government oppression. The landmark case of Johnson v. McIntosh (1823), which institutionalized the “doctrine of discovery” in U.S. law, and which justified the theft of 2 billion acres of indigenous territory, established a framework of corrupt political/legal/corporate collusion that continues throughout indigenous America, to the present.
If this movement is serious about confronting the foundational assumptions of the current U.S. system, then it must begin by addressing the original crimes of the U.S. colonizing system against indigenous nations. Without addressing justice for indigenous peoples, there can never be a genuine movement for justice and equality in the United States. Toward that end, we challenge Occupy Denver to take the lead, and to be the first “Occupy” city to integrate into its philosophy, a set of values that respects the rights of indigenous peoples, and that recognizes the importance of employing indigenous visions and models in restoring environmental, social, cultural, economic and political health to our homeland.
We call on Occupy Denver to adopt, as a starting point, the following:
1. To repudiate the Doctrine of Christian Discovery, to endorse the repeal of the papal bull Inter Caetera (1493) to work for the reversal of the U.S. Supreme Court case of Johnson v. M’Intosh 1823), and call for a repeal of the Columbus Day holiday as a Colorado and United States holiday.
2. To endorse the right of all indigenous peoples to the international right of self-determination, by virtue of which they freely determine their political status, and freely pursue their economic, social and cultural futures.
3. To demand the recognition, observance and enforcement of all treaties and agreements freely entered into `between indigenous nations and the United States. Treaties should be recognized as binding international instruments. Disputes should be recognized as a proper concern of international law, and should be arbitrated by impartial international bodies.
4. To insist that Indigenous people shall never be forcibly relocated from their lands or territories.
5. To acknowledge that Indigenous peoples have the right to practice and teach their spiritual and religious traditions customs and ceremonies, including in institutions of the State, e.g. prisons, jails and hospitals„ and to have access in privacy their religious and cultural sites, and the right to the repatriation of their human remains and funeral objects.
6. To recognize that Indigenous peoples and nations are entitled to the permanent control and enjoyment of their aboriginal-ancestral territories. This includes surface and subsurface rights, inland and coastal waters, renewable and non-renewable resources, and the economies based on these resources. In advancement of this position, to stand in solidarity with the Cree nations, whose territories are located in occupied northern Alberta, Canada, in their opposition to the Tar Sands development, the largest industrial project on earth. Further, to demand that President Barack Obama deny the permit for the Keystone XL Pipeline, proposed to run from the tar sands in Canada into the United States, and that the United States prohibit the use or transportation of Tar Sands oil in the United States.
7. To assert that Indigenous peoples have the right to maintain, control, protect and develop their cultural heritage, traditional knowledge and traditional cultural expressions. They have the right to maintain, control, protect and develop their intellectual property over such cultural heritage, traditional knowledge, and traditional cultural expressions. Further, indigenous peoples have the right to the ownership and protection of their human biological and genetic materials, samples, and stewardship of non-human biological and genetic materials found in indigenous territories.
8. To recognize that the settler state boundaries in the Americas are colonial fabrications that should not limit or restrict the ability of indigenous peoples to travel freely, without inhibition or restriction, throughout the Americas. This is especially true for indigenous nations whose people and territories have been separated by the acts of settler states that established international borders without the free, prior and informed consent of the indigenous peoples affected.
9. To demand that the United States shall take no adverse action regarding the territories, lands, resources or people of indigenous nations without the free, prior and informed consent of the indigenous peoples affected.
10. To demand the immediate release of American Indian political prisoner, Leonard Peltier, U.S. Prisoner #89637-132, from U.S. federal custody.
Finally, we also remind Occupy Denver that indigenous histories, political, cultural, environmental, medical, spiritual and economic traditions provide rich examples for frameworks that can offer concrete models of alternatives to the current crises facing the United States. We request that Occupy Denver actively utilize and integrate indigenous perspectives, teachers, and voices in its deliberations and decision-making processes.
Submitted 8 October 2011
American Indian Movement of Colorado
P.O. Box 292, Sedalia, CO 80135
The system was never broken, it was built this way. #occupywallstreet
 OCCUPIED WALL STREET, NYC– Protests enter their third workweek in Liberty Plaza where the cold has arrived but demonstrators are still prohibited from having shelter. Organized labor is rallying their members to join the occupation on Wednesday, with over a million union workers expected to march in solidarity. If you’re not joining in, are you in the way? Colorado Springs Occupiers in Acacia Park are being joined by Tea Partiers, Ron Paulists, and Zietgeisters. The more the merrier. Remember, target the investment bankers down the block, NOON EVERYDAY. They’re getting cranky.
OCCUPIED WALL STREET, NYC– Protests enter their third workweek in Liberty Plaza where the cold has arrived but demonstrators are still prohibited from having shelter. Organized labor is rallying their members to join the occupation on Wednesday, with over a million union workers expected to march in solidarity. If you’re not joining in, are you in the way? Colorado Springs Occupiers in Acacia Park are being joined by Tea Partiers, Ron Paulists, and Zietgeisters. The more the merrier. Remember, target the investment bankers down the block, NOON EVERYDAY. They’re getting cranky.
Demonic DIA mustang Blucifer may be Bronco Blue, but eyes are Herring Red
 The conspiracy theories deepen about cruel oddities at Denver International Airport, and much of the conjecture is now being scuttled with classic disinformation. Questions are substantive enough about DIA construction anomalies, without worrying about Blucifer the red-eyed stallion, his Egyptian pal Anubis, gargoyle luggage gods, prophetic end-times murals, inward-facing concertina wire, tent canvas of pure Kevlar, and the dastardly Freemasons behind it all.
The conspiracy theories deepen about cruel oddities at Denver International Airport, and much of the conjecture is now being scuttled with classic disinformation. Questions are substantive enough about DIA construction anomalies, without worrying about Blucifer the red-eyed stallion, his Egyptian pal Anubis, gargoyle luggage gods, prophetic end-times murals, inward-facing concertina wire, tent canvas of pure Kevlar, and the dastardly Freemasons behind it all.
It’s supposed.
Conspiracy freaks delight in pretending the Masonic Order cannot help but leave triumphant clues about its omniscience. The eyeball pyramid on US paper currency would seem demonstration enough, but conspiracy sleuths nursed on Dan Brown eat that up. And the confusion disseminaters are pouring it on. Who am I to pooh-pooh any particulars, especially conspiracies, of themselves too often scurrilously maligned, except to suggest that the less symbolism-intensive speculation about DIA is plenty obvious, and operatic enough.
The fact that excavation continues at DIA, years after the facility became operative should raise eyebrows. How much excavation is required to build runways on a near-flat landscape? Has DIA really displaced so much earth it’s become a significant fraction of what was removed to carve the Panama Canal? Apparently satellite pictures reveal a growing mound to suggest the extent of cavernous facilities being dug under and around the DIA. The evocative white tents were always for the nomads, on the plains, white settlers needed dugouts.
Where easier to install secretive accommodations than under the everyday lock-down of a post-9/11 airport?
Would DIA serve as a massive underground concentration camp? Ask yourself if a many mile buffered isolation is necessary for that, on top of being underground, or vice-versa. Area 51 remains a mystery without having to comprise buried facilities. We’ve already seen that Superdomes smack in the middle of urban centers make perfectly inhumane detainment centers. Imagine too, the isolation of DIA, without a railway for incoming. The Nazi camps did not predate flight. There would have been no Auschwitz without a railroad line.
A far more obvious application would be as a shelter from the public outside, behind miles of no-man’s land, the single entrance easily closed off. Far from even prying eyes.
Underground shelters have historically been carved in bedrock, NORAD in Cheyenne Mountain as an example. Could a man-made hole ever surpass a mountain range for protection? But perhaps the New World Order has the atomic threat sewn up. The mushroom cloud may still be evoked to frighten the masses, but I’ll bet that all the nuclear arms across the globe are as secure as Israel’s Security Council veto. This DIA shelter may need only protect against biological agents or fallout from an environmental cataclysm.
Old-fashioned bomb shelters have suffered obsolescence due to ease-of-access. What safe-room will save you if you cannot get to it? NORAD only protected those already inside it. What do you do to protect far-flung clients in the age of Twitter-speed atmospheric percussions?
An oversized airport like DIA certainly answers that requirement. While Coloradans might grouse about the interminable drive to DIA, they might one day rue its impenetrability. Meanwhile the jet set will gain admission by simple default of having wings.
Nothing terribly complicated about that setup. If you belonged to the billionaires club, you’d think of a provision like that too. The A-bomb age already prepped Americans for the contingency that a nuclear war would necessitate saving the more important among us. What’s the objection now?
Freedom Flotilla flagship off to Gaza
 The rechristened MV Rachel Corrie sails today from Dundalk, Ireland, to join the Freedom Flotilla intent on running the blockade of Gaza. Israel is already warning Cyprus against allowing the humanitarian convoy to shelter in its ports, rehearsing plans to intercept, and Turkish supporters are rebuffing Israeli threats to bomb relief ships which attempt to reach Palestine. In other news, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development has accepted Israel’s membership, cementing First World culpability for Israeli growth from conquest. Critics had urged Israel’s disqualification because its capitalization has been owed to the occupation and illegal appropriation of Palestinian resources, but could the OECD ultimately disown the US-European joint colonial venture?
The rechristened MV Rachel Corrie sails today from Dundalk, Ireland, to join the Freedom Flotilla intent on running the blockade of Gaza. Israel is already warning Cyprus against allowing the humanitarian convoy to shelter in its ports, rehearsing plans to intercept, and Turkish supporters are rebuffing Israeli threats to bomb relief ships which attempt to reach Palestine. In other news, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development has accepted Israel’s membership, cementing First World culpability for Israeli growth from conquest. Critics had urged Israel’s disqualification because its capitalization has been owed to the occupation and illegal appropriation of Palestinian resources, but could the OECD ultimately disown the US-European joint colonial venture?
What a coincidence that today’s date in 1949 marked the end of the siege of Berlin, when an international effort was mounted by world governments to fly relief convoys of supplies to the besieged population of Berlin. Today western governments won’t abide the expressed will of their citizens and so the people themselves are having to save the Palestinians abandoned in Gaza.
The MV Rachel Corrie has been repainted with a giant Irish flag on its side, and the words “FREE GAZA” along its top. The cargo ship retains its original IMO 6715281 for communications and tracking. Bloggers and journalists will be charting the flotilla’s progress online.
Among the participants on the Free Gaza project are Ken Fleming, Nobel Peace Prize winner; Mairead Maguire, Nobel Peace Prize winner; Denis Halliday, UN Humanitarian Coordinator in Iraq; Matthias Chang, Perdana Global Peace Organizer; Aengus.O’Snodaigh, Sinn Fein; Chris Andrews; Free Gaza Movement co-founder Greta Berlin, Caoimhe Butterly, Ewa Jasiewicz, Fintan Lane, and Niamh Moloughney.
Would you believe Fortune 500 corps & “Bat Gangs?” Yeah, that’s the ticket.
 From the same mouth that told reporters the ludicrous tale that scouts from two Fortune 500 companies told a local realtor (let’s leave her unnamed, shall we) they rejected locating in Colorado Springs on account of the city’s homeless camps along I-25 –yeah right– comes a really despicable meme she’s now trying to spread of teenage “bat gangs” purportedly terrorizing our homeless.
From the same mouth that told reporters the ludicrous tale that scouts from two Fortune 500 companies told a local realtor (let’s leave her unnamed, shall we) they rejected locating in Colorado Springs on account of the city’s homeless camps along I-25 –yeah right– comes a really despicable meme she’s now trying to spread of teenage “bat gangs” purportedly terrorizing our homeless.
The fabrication serves two purposes: to lend urgency to efforts to get the homeless out of their tents, and to scare the vulnerable would-be victims themselves. A tent isn’t shelter enough if there are gangs of youth ready to bludgeon every homeless they encounter.
I was almost taken in myself when I received this email titled “HOMELESS ATTACKS”, the text of which has also been copy and pasted unto other online forums:
Sitting here with a homeless friend who got beat up by the Bat Gang on Saturday. He said it was 8 kids with baseball bats who attacked him under the Bijou Bridge. He was taken to Memorial Hospital and spent the night. He got stitches around his right eye and his right elbow.
We’re lucky he is alive! Again we need your support to transition the homeless out of the tent camps to shelters.
It turns out a user “Beepbeep” has been peddling this hard on local websites, luckily without much traction. Any ideas about how to intervene if she lands another TV interview? Fear-mongering like this slanders the CSPD and further erodes the image of Colorado Springs.
A search of the Gazette brings up the murder last year of a vagrant on the I-25 pedestrian overpass, killed with a baseball bat. A teen bragged to his a friend about the crime, and now the friend may be implicated as well. This is a development from the recent trial. From this our enterprising Iago has extrapolated a “bat gang” of malevolent teens, to put fear into stories told around homeless campfires.
Her most recent example cannot be corroborated. Even given the benefit of the doubt, our misinformant may have fallen dupe to a homeless cliche, the public drunk’s version of “a dog ate my homework.” I remember from friends cleaning up their act at the Salvation Army, when someone fell off the wagon and returned literally bruised, from a fall or fight they were too inebriated to remember, the blame was cast away from themselves. What happened was often a recurring theme, the bang-up attributed to “teenage tormentors” armed with bats.
Can you think of a more despicable strategy, to haunt the neighborhood with a fictional specter, all for the sake of trying to shoo the homeless out of town. It’s the KKK’s burning cross strategy isn’t it?
Will our city presume to prohibit life for whoever can’t afford to pay their way?
In case you thought City Council’s reprieve earlier this winter reflected a soft spot in their heart for the homeless forced to live in tents, in reality the city attorneys advised any purge of the unsightly camps be delayed until an iron-clad ordinance could be devised. The suggested legal verbiage was reviewed at Monday’s meeting, to be formally adopted today. It reads “9.6.109. Camping on Public Property Prohibited.” The definition of “camping” to include: “Sleeping or making preparation to sleep, including the lying down of bedding for the purpose of sleeping.”
No sleeping. On public property.
By the way, I care not the least about a slippery slope that might infringe on your prerogative to take a nap in the park. This is not about the average man losing his middle class privileges to the creep of authoritarian rule-making. At some point I have to presume we agree that human beings have some inalienable rights. They used to be lofty ideals, protected by fundamental principles. On the issue of sleep, we are discussing the right to an involuntary life function.
The right to defecate is what’s got these homeless camps in trouble, but it stands to reason that to shit is more than a right too, it’s a necessity. All of this is dreadful platitude unless it’s escaped our city administrators. Are they suggesting that because the city cannot provide for the services for its people, that the people must forgo their basic creature needs?
What inhuman folly. And on public ground. Where are they to go? Must man pay rent to exist?
That you can dictate the rights of another on private land is open to debate. By whose authority do you claim dominion to use land for yourself? How dare you refuse a fellow human being, wherever he might need to rest his head? Granting the argument for private property, who are you to force your will upon others on shared common property? Others can’t do what? Where?
Do public lands belong only to property owners? You can legislate the right to take property for yourself, but you can’t hoard all of it. You have the right to private land precisely because the remainder is reserved for the public. The authority to give the deed to you comes from a governing entity empowered by everyone. A government is bound to providing for the land-less in exchange for the privilege to sell premium land to the better-off.
And a city has obligations to service that public land just as much as it serves the private lots. Can local administrators say, sorry, no more money for water, sewer, utilities, or security? Neither can it fail its responsibilities to the poor.
You aren’t obligated to provide eat, drink and shelter to all, but you can’t deny men access to the basic resource of land. Would you have men born into cells until they agree to work for their sustenance? Colorado Springs would deny them heat and sleep too. If we could, would we regulate breath?
On public land you have limited authority to regulate. Where private property owners crow about property rights, so do the public have property rights. Every bit, and perhaps more sacrosanct. The public can consent to regulation, for the safety and health of all etc, but that doesn’t encompass prohibition. You want health and safety, you provide the services. You have no authority to deny the service and then deny man’s basic needs. What an absolute crock.
Below is the text of the city’s proposed ordinance. It describes the creation of a new section, under 9.6.109.
9. Public Offenses, fair enough;
6. Offenses Affecting Property, a functional necessity of course;
109. Camping on Public Property Prohibited. Huh?
NOW, THEREFORE, BE IT ORDAINED BY THE CITY COUNCIL OF THE CITY OF COLORADO SPRINGS:
9.6.109: CAMPING ON PUBLIC PROPERTY PROHIBITED:
A. It is unlawful for any person to camp on any public property, except as may be specifically authorized by the appropriate governmental authority.
B. For the purposes of this section “camp” or “camping” means to use the public area for living accommodation including, but not limited to, the activities and circumstances listed below. These activities and circumstances may be considered in determining whether reasonable grounds for belief have arisen that a person has “camped” or is “camping” in violation of this ordinance.
1. Sleeping or making preparation to sleep, including the lying down of bedding for the purpose of sleeping.
2. Occupying a shelter out-of-doors. “Shelter” shall mean any cover or protection from the elements other than clothing, such as a tent, shack, sleeping bag, or other structure or material.
3. The presence or use of a camp fire, camp stove or other heating source or cooking device.
5. Keeping or storing personal property.
Sleep, a basic animal function. Shelter, a fundamental human need. Fire, the first of mankind’s tools. Before agriculture was fire.
Property. How unbecoming that an ordinance seeking to prohibit the public’s right to public property should also deprive the public of the ability to keep personal property.
Also presented on Monday were recommendations from the city management, detailing the consequences of violating the camping prohibition. They included this paragraph:
FINANCIAL IMPLICATIONS: A violation of these updated ordinances may result in a fine and sentencing to the Criminal Justice Center (CJC). In the past, homeless individuals have been known to ignore summonses to appear in Municipal Court until it is advantageous for them to be placed in CJC (cold weather, need for food and/or shelter, etc.). The preferred method of dealing with these types of violations would be to gain the cooperation of the individuals involved without relying upon the criminal justice system, thus removing them from the circumstance by linking them with the appropriate service agency.
Making the specious argument basically that since homeless persons sometimes get themselves arrested on purpose, authorities are justified in accommodating them full time. How considerate of us.
