Report presented to the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights in September 2001. Authored by Paul Wolf.
COINTELPRO: The Untold American Story
By Paul Wolf with contributions from Robert Boyle, Bob Brown, Tom Burghardt, Noam Chomsky, Ward Churchill, Kathleen Cleaver, Bruce Ellison, Cynthia McKinney, Nkechi Taifa, Laura Whitehorn, Nicholas Wilson, and Howard Zinn.
Presented to U.N. High Commissioner for Human Rights Mary Robinson at the World Conference Against Racism in Durban, South Africa by the members of the Congressional Black Caucus attending the conference: Donna Christianson, John Conyers, Eddie Bernice Johnson, Barbara Lee, Sheila Jackson Lee, Cynthia McKinney, and Diane Watson, September 1, 2001.
Table of Contents
Overview
Victimization
COINTELPRO Techniques
Murder and Assassination
Agents Provocateurs
The Ku Klux Klan
The Secret Army Organization
Snitch Jacketing
The Subversion of the Press
Political Prisoners
Leonard Peltier
Mumia Abu Jamal
Geronimo ji Jaga Pratt
Dhoruba Bin Wahad
Marshall Eddie Conway
Justice Hangs in the Balance
Appendix: The Legacy of COINTELPRO
CISPES
The Judi Bari Bombing
Bibliography
Overview
We’re here to talk about the FBI and U.S. democracy because here we have this peculiar situation that we live in a democratic country – everybody knows that, everybody says it, it’s repeated, it’s dinned into our ears a thousand times, you grow up, you pledge allegiance, you salute the flag, you hail democracy, you look at the totalitarian states, you read the history of tyrannies, and here is the beacon light of democracy. And, of course, there’s some truth to that. There are things you can do in the United States that you can’t do many other places without being put in jail.
But the United States is a very complex system. It’s very hard to describe because, yes, there are elements of democracy; there are things that you’re grateful for, that you’re not in front of the death squads in El Salvador. On the other hand, it’s not quite a democracy. And one of the things that makes it not quite a democracy is the existence of outfits like the FBI and the CIA. Democracy is based on openness, and the existence of a secret policy, secret lists of dissident citizens, violates the spirit of democracy.
Despite its carefully contrived image as the nation’s premier crime fighting agency, the Federal Bureau of Investigation has always functioned primarily as America’s political police. This role includes not only the collection of intelligence on the activities of political dissidents and groups, but often times, counterintelligence operations to thwart those activities. The techniques employed are easily recognized by anyone familiar with military psychological operations. The FBI, through the use of the criminal justice system, the postal system, the telephone system and the Internal Revenue Service, enjoys an operational capability surpassing even that of the CIA, which conducts covert actions in foreign countries without having access to those institutions.
Although covert operations have been employed throughout FBI history, the formal COunter INTELligence PROgrams (COINTELPRO’s) of the period 1956-1971 were the first to be both broadly targeted and centrally directed. According to FBI researcher Brian Glick, “FBI headquarters set policy, assessed progress, charted new directions, demanded increased production, and carefully monitored and controlled day-to-day operations. This arrangement required that national COINTELPRO supervisors and local FBI field offices communicate back and forth, at great length, concerning every operation. They did so quite freely, with little fear of public exposure. This generated a prolific trail of bureaucratic paper. The moment that paper trail began to surface, the FBI discontinued all of its formal domestic counterintelligence programs. It did not, however, cease its covert political activity against U.S. dissidents.” 1
Of roughly 20,000 people investigated by the FBI solely on the basis of their political views between 1956-1971, about 10 to 15% were the targets of active counterintelligence measures per se. Taking counterintelligence in its broadest sense, to include spreading false information, it’s estimated that about two-thirds were COINTELPRO targets. Most targets were never suspected of committing any crime.
The nineteen sixties were a period of social change and unrest. Color television brought home images of jungle combat in Vietnam and protesters and priests burning draft cards and American flags. In the spring and summer months of 1964, 1965, 1966, 1967 and 1968, massive black rebellions swept across almost every major US city in the Northeast, Midwest and California. 2 Presidents Johnson and Nixon, and many others feared violent revolution and denounced the protesters. President Kennedy had felt the opposite: “Those who make peaceful revolution impossible will make violent revolution inevitable.”
The counterculture of the sixties, and the FBI’s reaction to it, were in many ways a product of the 1950s, the so-called “Age of McCarthyism.” John Edgar Hoover, longtime Director of the FBI, was a prominent spokesman of the anti-communist paranoia of the era:
The forces which are most anxious to weaken our internal security are not always easy to identify. Communists have been trained in deceit and secretly work toward the day when they hope to replace our American way of life with a Communist dictatorship. They utilize cleverly camouflaged movements, such as peace groups and civil rights groups to achieve their sinister purposes. While they as individuals are difficult to identify, the Communist party line is clear. Its first concern is the advancement of Soviet Russia and the godless Communist cause. It is important to learn to know the enemies of the American way of life. 3
Throughout the 1960s, Hoover consistently applied this theory to a wide variety of groups, on occasion reprimanding agents unable to find “obvious” communist connections in civil rights and anti-war groups. 4 During the entire COINTELPRO period, no links to Soviet Russia were uncovered in any of the social movements disrupted by the FBI.
The commitment of the FBI to undermine and destroy popular movements departing from political orthodoxy has been extensive, and apparently proportional to the strength and promise of such movements, as one would expect in the case of the secret police organization of any state, though it is doubtful that there is anything comparable to this record among the Western industrial democracies.
In retrospect, the COINTEPRO’s of the 1960s were thoroughly successful in achieving their stated goals, “to expose, disrupt, misdirect, discredit, or otherwise neutralize” the enemies of the State.
Victimization
The most serious of the FBI disruption programs were those directed against “Black Nationalists.” Agents were instructed to undertake actions to discredit these groups both within “the responsible Negro community” and to “Negro radicals,” also “to the white community, both the responsible community and to `liberals’ who have vestiges of sympathy for militant black nationalists simply because they are Negroes…”
A March 4th, 1968 memo from J Edgar Hoover to FBI field offices laid out the goals of the COINTELPRO – Black Nationalist Hate Groups program: “to prevent the coalition of militant black nationalist groups;” “to prevent the rise of a messiah who could unify and electrify the militant black nationalist movement;” “to prevent violence on the part of black nationalist groups;” “to prevent militant black nationalist groups and leaders from gaining respectability;” and “to prevent the long-range growth of militant black nationalist organizations, especially among youth.” Included in the program were a broad spectrum of civil rights and religious groups; targets included Martin Luther King, Malcolm X, Stokely Carmichael, Eldridge Cleaver, and Elijah Muhammad.
A top secret Special Report 5 for President Nixon, dated June 1970 gives some insight into the motivation for the actions undertaken by the government to destroy the Black Panther party. The report describes the party as “the most active and dangerous black extremist group in the United States.” Its “hard-core members” were estimated at about 800, but “a recent poll indicates that approximately 25 per cent of the black population has a great respect for the BPP, incuding 43 per cent of blacks under 21 years of age.” On the basis of such estimates of the potential of the party, counterintelligence operations were carried out to ensure that it did not succeed in organizing as a substantial social or political force.
Another memorandum explains the motivation for the FBI operations against student protesters: “the movement of rebellious youth known as the ‘New Left,’ involving and influencing a substantial number of college students, is having a serious impact on contemporary society with a potential for serious domestic strife.” The New Left has “revolutionary aims” and an “identification with Marxism-Leninism.” It has attempted “to infiltrate and radicalize labor,” and after failing “to subvert and control the mass media” has established “a large network of underground publications which serve the dual purpose of an internal communication network and an external propaganda organ.” Its leaders have “openly stated their sympathy with the international communist revolutionary movements in South Vietnam and Cuba; and have directed others into activities which support these movements.”
The effectiveness of the state disruption programs is not easy to evaluate. Black leaders estimate the significance of the programs as substantial. Dr. James Turner of Cornell University, former president of the African Heritage Studies Association, assessed these programs as having “serious long-term consequences for black Americans,” in that they “had created in blacks a sense of depression and hopelessness.” 6
He states that “the F.B.I. set out to break the momentum developed in black communities in the late fifties and early sixties”; “we needed to put together organizational mechanisms to deliver services,” but instead, “our ability to influence things that happen to us internally and externally was killed.” He concludes that “the lack of confidence and paranoia stimulated among black people by these actions” is just beginning to fade.
The American Indian Movement, arguably the most hopeful vehicle for indigenous pride and self-determination in the late 20th century, was also destroyed. As AIM leader Dennis Banks has observed:
“The FBI’s tactics eventually proved successful in a peculiar sort of way. It’s remarkable under the circumstances – and a real testament to the inner strength of the traditional Oglalas – that the feds were never really able to divide them from us, to have the traditionals denouncing us and working against us. But, in the end, the sort of pressure the FBI put on people on the reservation, particularly the old people, it just wore ’em down. A kind of fatigue set in. With the firefight at Oglala, and all the things that happened after that, it was easy to see we weren’t going to win by direct confrontation. So the traditionals asked us to disengage, to try and take some of the heaviest pressure off. And, out of respect, we had no choice but to honor those wishes. And that was the end of AIM, at least in the way it had been known up till then. The resistance is still there, of course, and the struggle goes on, but the movement itself kind of disappeared.” 7
The same can be said for socialist movements targeted by COINTELPRO. Alone among the parliamentary democracies, the United States has no mass-based socialist party, however mild and reformist, no socialist voice in the media, and virtually no departure from Keynesian economics in American universities and journals. The people of the United States have paid dearly for the enforcement of domestic privilege and the securing of imperial domains. The vast waste of social wealth, miserable urban ghettos, the threat and reality of unemployment, meaningless work in authoritarian institutions, standards of health and social welfare that should be intolerable in a society with such vast productive resources — all of this must be endured and even welcomed as the “price of freedom” if the existing order is to stand without challenge.
COINTELPRO Techniques
From its inception, the FBI has operated on the doctrine that the “preliminary stages of organization and preparation” must be frustrated, well before there is any clear and present danger of “revolutionary radicalism.”
At its most extreme dimension, political dissidents have been eliminated outright or sent to prison for the rest of their lives. There are quite a number of individuals who have been handled in that fashion.
Many more, however, were “neutralized” by intimidation, harassment, discrediting, snitch jacketing, a whole assortment of authoritarian and illegal tactics.
Neutralization, as explained on record by the FBI, doesn’t necessarily pertain to the apprehension of parties in the commission of a crime, the preparation of evidence against them, and securing of a judicial conviction, but rather to simply making them incapable of engaging in political activity by whatever means.
For those not assessed as being in themselves, necessarily a security risk, but engaged in what the Bureau views to be politically objectionable activity, those techniques might consist of disseminating derogatory information to the target’s family, friends and associates, visiting and questioning them, basically, making it clear that the FBI are paying attention to them, to try to intimidate them.
If the subject continues their activities, and particularly if they respond by escalating them, the FBI will escalate its tactics as well. Maybe they’ll be arrested and prosecuted for spurious reasons. Maybe there will be more vicious rumors circulated about them. False information may be planted in the press. The targets’ efforts to speak in public are frustrated, employers may be contacted to try to get them fired. Anonymous letters have been sent by the FBI to targets’ spouses, accusing them of infidelity. Others have contained death threats.
And if the subject persists then there will be a further escalation.
According to FBI memoranda of the 1960s, “Key black activists” were repeatedly arrested “on any excuse” until “they could no longer make bail.” The FBI made use of informants, often quite violent and emotionally disturbed individuals, to present false testimony to the courts, to frame COINTELPRO targets for crimes they knew they did not commit. In some cases the charges were quite serious, including murder.
Another option is “snitch jacketing” – making the target look like a police informant or a CIA agent. This serves the dual purposes of isolating and alienating important leaders, and increasing the general level of fear and factionalism in the group.
“Black bag jobs” are burglaries performed in order to obtain the written materials, mailing lists, position papers, and internal documents of an organization or an individual. At least 10,000 American homes have been subjected to illegal breaking and entering by the FBI, without judicial warrants.
Group membership lists are used to expand the operation. Anonymous mailings of newspaper and magazine articles may be mailed to group members and supporters to convince them of the error of their ways. Anonymous or spurious letters and cartoons are sent to promote factionalism and widen rifts in or between organizations.
According to the FBI’s own records, agents have been directed to use “established local news media contacts” and other “sources available to the Seat of Government” to “disrupt or neutralize” organizations and to “ridicule and discredit” them.
Many counterintelligence techniques involve the use of paid informants. Informants become agents provocateurs by raising controversial issues at meetings to take advantage of ideological divisions, by promoting emnity with other groups, or by inciting the group to violent acts, even to the point of providing them with weapons.
Over the years, FBI provocateurs have repeatedly urged and initiated violent acts, including forceful disruptions of meetings and demonstrations, attacks on police, bombings, and so on, following an old strategy of Tsarist police director TC Zubatov: “We shall provoke you to acts of terror and then crush you.”
A concise description of political warfare is given in a passage from a CIA paper entitled “Nerve War Against Individuals,” referring to the overthrowing of the government of Guatemala in 1954:
The strength of an enemy consists largely of the individuals who occupy key positions in the enemy organization, as leaders, speakers, writers, organizers, cabinet members, senior government officials, army commanders and staff officers, and so forth. Any effort to defeat the enemy must therefore concentrate to a great extent upon these key enemy individuals.
If such an effort is made by means short of physical violence, we call it “psychological warfare.” If it is focussed less upon convincing those individuals by logical reasoning, but primarily upon moving them in the desired direction by means of harassment, by frightening, confusing and misleading them, we speak of a “nerve war”. 8
The COINTELPROs clearly met the above definition of “nerve wars,” and, in the case of the American Indian Movement in Pine Ridge, South Dakota, the FBI conducted a full-fledged counterinsurgency war, complete with death squads, disappearances and assassinations, recalling Guatemala in more recent years.
The full story of COINTELPRO may never be told. The Bureau’s files were never seized by Congress or the courts or sent to the National Archives. Some have been destroyed. Many counterintelligence operations were never committed to writing as such, or involve open investigations, and ex-operatives are legally prohibited from talking about them. Most operations remain secret until long after the damage has been done.
Murder and Assassination
Among the most remarkable of the COINTELPRO revelations are those relating to the FBI’s attempts to incite gang warfare and murderous attacks on Black Panther leaders. For example, a COINTELPRO memo from FBI Headquarters mailed November 25, 1968, informs recipient offices that:
a serious struggle is taking place between the Black Panther Party (BPP) and the US [United Slaves] organization. The struggle has reached such proportions that it is taking on the aura of gang warfare with attendant threats of murder and reprisals.
In order to fully capitalize upon BPP and US differences as well as to exploit all avenues of creating further dissension in the ranks of the BPP, recipient offices are instructed to submit imaginative and hard-hitting counterintelligence measures aimed at crippling the BPP. 9
According to the national chairman of the US organization, who became a professor at San Diego State, the US and the Panthers had been negotiating to avoid bloodshed: “Then the F.B.I. stepped in and the shooting started.”
A series of cartoons were produced in an effort to incite violence between the Black Panther Party and the US; for example, one showing Panther leader David Hilliard hanging dead with a rope around his neck from a tree. The San Diego office reported to the director that:
in view of the recent killing of BPP member SYLVESTER BELL, a new cartoon is being considered in the hopes that it will assist in the continuance of the rift between BPP and US. This cartoon, or series of cartoons, will be similar in nature to those formerly approved by the Bureau and will be forwarded to the Bureau for evaluation and approval immediately upon their completion.
Under the heading “TANGIBLE RESULTS” the memo continues:
Shootings, beatings, and a high degree of unrest continues to prevail in the ghetto area of southeast San Diego. Although no specific counterintelligence action can be credited with contributing to this over-all situation, it is felt that a substantial amount of the unrest is directly attributable to this program.
Between 1968-1971, FBI-initiated terror and disruption resulted in the murder of Black Panthers Arthur Morris, Bobby Hutton, Steven Bartholomew, Robert Lawrence, Tommy Lewis, Welton Armstead, Frank Diggs, Alprentice Carter, John Huggins, Alex Rackley, John Savage, Sylvester Bell, Larry Roberson, Nathaniel Clark, Walter Touré Pope, Spurgeon Winters, Fred Hampton, Mark Clark, Sterling Jones, Eugene Anderson, Babatunde X Omarwali, Carl Hampton, Jonathan Jackson, Fred Bennett, Sandra Lane Pratt, Robert Webb, Samuel Napier, Harold Russell, and George Jackson.
One of the more dramatic incidents occurred on the night of December 4, 1969, when Panther leaders Fred Hampton and Mark Clark were shot to death by Chicago policemen in a predawn raid on their apartment. Hampton, one of the most promising leaders of the Black Panther party, was killed in bed, perhaps drugged. Depositions in a civil suit in Chicago revealed that the chief of Panther security and Hampton’s personal bodyguard, William O’Neal, was an FBI infiltrator. O’Neal gave his FBI contacting agent, Roy Mitchell, a detailed floor plan of the apartment, which Mitchell turned over to the state’s attorney’s office shortly before the attack, along with “information” — of dubious veracity — that there were two illegal shotguns in the apartment. For his services, O’Neal was paid over $10,000 from January 1969 through July 1970, according to Mitchell’s affidavit.
The availability of the floor plan presumably explains why “all the police gunfire went to the inside corners of the apartment, rather than toward the entrances,” and undermines still further the pretense that the barrage was caused by confusion in unfamiliar surroundings that led the police to believe, falsely, that they were being fired upon by the Panthers inside. 10
Agent Mitchell was named by the Chicago Tribune as head of the Chicago COINTELPRO directed against the Black Panthers and other black groups. Whether or not this is true, there is substantial evidence of direct FBI involvement in this Gestapo-style political assassination. O’Neal continued to report to Agent Mitchell after the raid, taking part in meetings with the Hampton family and their discussion with their lawyers.
There has as yet been no systematic investigation of the FBI campaign against the Black Panther Party in Chicago, as part of its nationwide program against the Panthers.
Malcolm X was supposedly murdered by former colleagues in the Nation of Islam (NOI) as a result of the faction-fighting which had led to his splitting away from that movement, and their “natural wrath” at his establishment of a separate mosque, the Muslim Mosque, Inc.
However, the NOl factionalism at issue didn’t just happen. It had been developed by deliberate Bureau actions, through infiltration and the “sparking of acrimonious debates within the organization,” rumor-mongering, and other tactics designed to foster internal disputes. 11 The Chicago Special Agent in Charge, Marlin Johnson, who also oversaw the assassinations of Fred Hampton and Mark Clark, makes it quite obvious that he views the murder of Malcolm X as something of a model for “successful” counterintelligence operations.
“Over the years considerable thought has been given, and action taken with Bureau approval, relating to methods through which the NOI could be discredited in the eyes of the general black populace or through which factionalism among the leadership could be created. Serious consideration has also been given towards developing ways and means of changing NOI philosophy to one whereby the members could be developed into useful citizens and the organization developed into one emphasizing religion – the brotherhood of mankind – and self improvement. Factional disputes have been developed – most notable being Malcolm X Little.” 12
In an internal FBI monograph dated September 1963 found that, given the scope of support it had attracted over the preceding five years, civil rights agitation represented a clear threat to “the established order” of the U.S., and that Martin Luther “King is growing in stature daily as the leader among leaders of the Negro movement … so goes Martin Luther King, and also so goes the Negro movement in the United States.” This accorded well with COINTELPRO specialist William C. Sullivan’s view, committed to writing shortly after King’s landmark “I Have a Dream” speech during the massive civil rights demonstration in Washington, D.C., on August 28 of the same year:
We must mark [King] now, if we have not before, as the most dangerous Negro in the future of this Nation from the standpoint of communism, the Negro, and national security … it may be unrealistic to limit [our actions against King] to legalistic proofs that would stand up in court or before Congressional Committees.
The stated objective of the SCLC, and the nature of its practical activities, was to organize for the securing of black voting rights across the rural South, with an eye toward the ultimate dismantlement of at least the most blatant aspects of the southern U.S. system of segregation. Even this seemingly innocuous agenda was, however, seen as a threat by the FBI. In mid-September of 1957, FBI supervisor J.G. Kelly forwarded a newspaper clipping describing the formation of the SCLC to the Bureau’s Atlanta field office – that city being the location of SCLC headquarters – informing local agents, for reasons which were never specified, the civil rights group was “a likely target for communist infiltration,” and that “in view of the stated purpose of the organization you should remain alert for public source information concerning it in connection with the racial situation.” 13
The Atlanta field office “looked into” the matter and ultimately opened a COMINFIL (communist-inflitrated group) investigation of the SCLC, apparently based on the fact that a single SWP member, Lonnie Cross, had offered his services as a clerk in the organization’s main office. 14 By the end of the first year of FBI scrutiny, in September of 1958, a personal file had been opened on King himself, ostensibly because he had been approached on the steps of a Harlem church in which he’d delivered a guest sermon by black CP member Benjamin J. Davis. 15 By October 1960, as the SCLC call for desegregation and black voting rights in the south gained increasing attention and support across the nation, the Bureau began actively infiltrating organizational meetings and conferences. 16
By July of 1961, FBI intelligence on the group was detailed enough to recount that, while an undergraduate at Atlanta’s Morehouse College in 1948, King had been affiliated with the Progressive Party, and that executive director Wyatt Tee Walker had once subscribed to a CP newspaper, The Worker. 17
Actual counterintelligence operations against King and the SCLC seem to have begun with a January 8, 1962 letter from Hoover to Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy, contending that the civil rights leader enjoyed a “close relationship” with Stanley D. Levison, “a member of the Communist Party, USA,” and that Isadore Wofsy, “a high ranking communist leader,” had written a speech for King. 18
On the night of March 15-16,1962, FBI agents secretly broke into Levison’s New York office and planted a bug; a wiretap of his office phone followed on March 20. 19 Among the other things picked up by the surveillance was information that Jack ODell, who also had an alleged “record of ties to the Communist party,” had been recommended by both King and Levison to serve as an assistant to Wyatt Tee Walker. 20 Although none of these supposed communist affiliations were ever substantiated, it was on this basis that SCLC was targeted within the Bureau’s ongoing COINTELPRO-CP,USA, beginning with the planting of five disinformational “news stories” concerning the organization’s “communist connections” on October 24, 1962. 21 By this point, Martin Luther King’s name had been placed in Section A of the FBI Reserve Index, one step below those individuals registered in the Security Index and scheduled to be rounded up and “preventively detained” in the event of a declared national emergency; Attorney General Kennedy had also authorized round-the-clock surveillance of all SCLC offices, as well as King’s home. 22 Hence, by November 8,1963, comprehensive telephone taps had been installed at all organizational offices, and King’s residence. 23
By 1964, King was not only firmly established as a preeminent civil rights leader, but was beginning to show signs of pursuing a more fundamental structural agenda of social change. Meanwhile, the Bureau continued its efforts to discredit King, maintaining a drumbeat of mass media-distributed propaganda concerning his supposed “communist influences” and sexual proclivities, as well as triggering a spate of harassment by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). 24 When it was announced on October 14 of that year that King would receive a Nobel Peace Prize as a reward for his work in behalf of the rights of American blacks, the Bureau – exhibiting a certain sense of desperation – dramatically escalated its efforts to neutralize him.
Two days after announcement of the impending award, COINTELPRO specialist William Sullivan caused a composite audio tape to be produced, supposedly consisting of “highlights” taken from the taps of King’s phones and bugs placed in his various hotel rooms over the preceding two years.
The result, prepared by FBI audio technician John Matter, purported to demonstrate the civil rights leader had engaged in a series of “orgiastic” trysts with prostitutes and, thus, “the depths of his sexual perversion and depravity.” The finished tape was packaged, along with an accompanying anonymous letter (prepared by Bureau Internal Security Supervisor Seymore F. Phillips on Sullivan’s instruction), informing King that the audio material would be released to the media unless he committed suicide prior to bestowal of the Nobel Prize.
King, look into your heart. You know you are a complete fraud and a great liability to all of us Negroes. White people in this country have enough frauds of their own but I am sure that they don’t have one at this time that is any where near your equal. You are no clergyman and you know it. I repeat you are a colossal fraud and an evil, vicious one at that. …
King, there is only one thing left for you to do. You know what it is. You have just 34 days in which to do (this exact number has been selected for a specific reason, it has definite practical significant. You are done. There is but one way out for you. You better take it before your filthy, abnormal fraudulent self is bared to the nation. [sic]. 25
Sullivan then instructed veteran COINTELPRO operative Lish Whitson to fly to Miami with the package; once there, Whitson was instructed to address the parcel and mail it to the intended victim. 26 When King failed to comply with Sullivan’s anonymous directive that he kill himself, FBI Associate Director Cartha D. “Deke” DeLoach attempted to follow through with the threat to make the contents of the doctored tape public:
The Bureau Crime Records Division, headed by DeLoach, initiated a major campaign to let newsmen know just what the Bureau [claimed to have] on King. DeLoach personally offered a copy of the King surveillance transcript to Newsweek Washington bureau chief Benjamin Bradlee. Bradlee refused it, and mentioned the approach to a Newsday colleague, Jay Iselin. 27
Bradlee’s disclosure of what the FBI was up to served to curtail the effectiveness of DeLoach’s operation, and Bureau propagandists consequently found relatively few takers on this particular story. More, in the face of a planned investigation of electronic surveillance by government agencies announced by Democratic Missouri Senator Edward V. Long, J. Edgar Hoover was forced to order the rapid dismantling of the electronic surveillance coverage of both King and the SCLC, drying up much of the source material upon which Sullivan and his COINTELPRO specialists depended for “authenticity.”
Still, the Bureau’s counterintelligence operations against King continued apace, right up to the moment of the target’s death by sniper fire on a Memphis hotel balcony on April 4, 1968. 28 By 1969, “[FBI] efforts to ‘expose’ Martin Luther King, Jr., had not slackened even though King had been dead for a year.” 29
Those seeking independence for Puerto Rico were similarly attacked. The Bureau considered independentista leader Juan Mari Bras’ near-fatal heart attack during April of 1964 to have been brought on, at least in part, by an anonymous counterintelligence letter:
[deleted] stated that MARI BRAS’ heart attack on April 21, 1964, was obviously brought on by strain and overwork and opinioned that the anonymous letter certainly did nothing to ease his tensions for he felt the effects of the letter deeply. The source pointed out that with MARI BRAS’ illness and effects of the letter on the MPIPR leaders, that the organization’s activities had come to a near halt.
[paragraph deleted]
It is clear from the above that our anonymous letter has seriously disrupted the MPIPR ranks and created a climate of distrust and dissension from which it will take them some time to recover. This particular technique has been outstandingly successful and we shall be on the lookout to further exploit the achievements in this field. The Bureau will be promptly advised of other positive results of this program that may come to our attention. 30
The pattern remained evident more than a decade later when, after reviewing portions of the 75 volumes of documents the FBI had compiled on him, Mari Bras testified before the United Nations Commission on Decolonization:
[The documents] reflect the general activity of the FBI toward the movement. But some of the memos are dated 1976 and 1977; long after COINTELPRO was [supposedly] ended as an FBI activity … At one point, there is a detailed description of the death of my son, in 1976, at the hands of a gun-toting assassin. The bottom of the memo is fully deleted, leaving one to wonder who the assassin was. The main point, however, is that the memo is almost joyful about the impact his death will have upon me in my Gubernatorial campaign, as head of our party, in 1976. 31
When Mari Bras suffered from an attack of severe depression the same year, the San Juan Special Agent in Charge noted in a memo to FBI headquarters that, “It would hardly be idle boasting to say that some of the Bureau’s activities have provoked the situation of Mari Bras.” Given the context established by the Bureau’s own statements vis a vis Mari Bras, it also seems quite likely that one of the means by which the FBI continued to “exploit its achievements” in “provoking the situation” of the independentista leader was to arrange for the firebombing of his home in 1978.
Lethal COINTELPRO operations against the independentistas continued well into the 1980s. As Alfredo Lopez recounted in 1988:
[O]ver the past fifteen years, 170 attacks – beatings, shootings, and bombings of independence organizations and activists – have been documented … there have been countless attacks and beatings of people at rallies and pickets, to say nothing of independentistas walking the streets. The 1975 bombing of a rally at Mayaguez that killed two restaurant workers was more dramatic, but like the other 170 attacks remains unsolved. Although many right-wing organizations claimed credit for these attacks, not one person has been arrested or brought to trial. 32
A clear instance of direct FBI involvement in anti-independentista violence is the “Cerro Maravilla Episode” of July 25,1978. On that date, two young activists, Arnaldo Dario Rosado and Carlos Soto Arrivi, accompanied a provocateur named Alejandro Gonzalez Malave, were lured into a trap and shot to death by police near the mountain village. Official reports claimed the pair had been on the way to blow up a television tower near Cerro Maravilla, and had fired first when officers attempted to arrest them. A taxi driver who was also on the scene, however, adamantly insisted that this was untrue, that neither independentista had offered resistance when captured, and that the police themselves had fired two volleys of shots in order to make it sound from a distance as if they’d been fired upon. “It was a planned murder,” the witness said, “and it was carried out like that.” What had actually happened became even more obvious when a police officer named Julio Cesar Andrades came forward and asserted that the assassination had been planned “from on high” and in collaboration with the Bureau. This led to confirmation of Gonzalez Molave’s role as an infiltrator reporting to both the local police and the FBI, a situation which prompted him to admit “having planned and urged the bombing” in order to set the two young victim up for execution. In the end, it was shown that:
Dario and Soto [had] surrendered. Police forced the men to their knees, handcuffed their arms behind their backs, and as the two independentistas pleaded for justice, the police tortured and murdered them. 33
None of the police and other officials involved were ever convicted of the murders and crimes directly involved in this affair. However, despite several years of systematic coverup by the FBI and U.S. Justice Department, working in direct collaboration with the guilty officers, ten of the latter were finally convicted on multiple counts of perjury and sentenced to prison terms ranging from six to 30 years apiece. Having evaded legal responsibility for his actions altogether, provocateur Gonzalez Molave was shot to death in front of his home on April 29,1986, by “party or parties unknown.” This was followed, on February 28,1987, by the government’s payment of $575,000 settlements to both victims’ families, a total of $1,150,000 in acknowledgment of the official misconduct attending their deaths and the subsequent investigation(s).
Despite tens of thousands of pages of documentary evidence, the idea that the Bureau would utilize private right-wing operatives and terrorists is a chilling, alien concept to most Americans. Nevertheless, the FBI has financed, organized, and supplied arms to right-wing groups that carried out fire-bombings, burglaries, and shootings. 34
This was the case during the FBI’s COINTELPRO in South Dakota in the 1970’s against the Oglala Sioux Nation and the American Indian Movement. Right-wing vigilantes were used to disrupt the American Indian Movement (AIM) and selectively terrorize and murder the Oglala Sioux people 35, in what could only be described as a counter-insurgency campaign. During the 36 months roughly beginning with the 1973 seige of Wounded Knee and continuing through the first of May 1976, more than sixty AIM members and supporters died violently on or in locations immediately adjacent to the Pine Ridge Reservation. A minimum of 342 others suffered violent physical assaults. As Roberto Maestas and Bruce Johansen have observed:
Using only these documented political deaths, the yearly murder rate on Pine Ridge Reservation between March 1, 1973, and March 1, 1976, was 170 per 100,000. By comparison, Detroit, the reputed “murder capital of the United States,” had a rate of 20.2 in 1974. … The political murder rate at Pine Ridge between March 1, 1973, and March 1, 1976, was almost equivalent to that in Chile during the three years after the military coup supported by the United States deposed and killed President Salvador Allende. 36
To commemorate the 1890 massacre of Wounded Knee, in which 300 Minnecojou Lakota were slaughtered by the U.S. Seventh Cavalry, hundreds of Native Americans from reservations across the West gathered in Wounded Knee, on the Pine Ridge Reservation in South Dakota, during the winter of 1972-73. 37
This situation was already tense due to a series of unsolved murders on the reservation, and a struggle between the administration of the Oglala Sioux tribal president, Dick Wilson, and opposition organizations on the reservation, including AIM. Wilson had been bestowed with a $62,000 Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) grant for purposes of establishing a “tribal ranger group” – an entity which designated itself as “Guardians Of the OgIala Nation” (GOONs). Wilson’s “goon squads” patrolled the reservation, unleashing a reign of terror against Wilson’s enemies. When victims attempted to seek the protection of the BIA police, they quickly discovered that perhaps a third of its roster – including its head, Delmar Eastman (Crow), and his second-in-command, Duane Brewer (OgIala) – were doubling as GOON leaders or members. For their part, BIA officials – who had set the whole thing up – consistently turned aside requests for assistance from the traditionals as being “purely internal tribal matters,” beyond the scope of BIA authority.
On Feb 28th, 1973, residents of Wounded Knee, South Dakota found the roads to the hamlet blockaded by GOONs, later reinforced by marshals service Special Operations Group (SOG) teams and FBI personnel. By 10 p.m., Minneapolis SAC Joseph Trimbach had flown in to assume personal command of the GOONs and BIA police, while Wayne Colburn, director of the U.S. Marshals Service, had arrived to assume control over his now reinforced SOG unit. Colonel Volney Warner of the 82nd Airborne Division and 6th Army Colonel Jack Potter – operating directly under General Alexander Haig, military liaison in the Nixon White House – had also been dispatched from the Pentagon as “advisors” coordinating a flow of military personnel, weapons and equipment to those besieging Wounded Knee. As Rex Weyler has noted:
Documents later subpoenaed from the Pentagon revealed that Colonel Potter directed the employment of 17 APCs [armored personnel carriers], 130,000 rounds of M-16 ammunition, 41,000 rounds of M-40 high explosive, as well as helicopters, Phantom jets, and personnel. Military officers, supply sergeants, maintenance technicians, chemical officers, and medical teams remained on duty throughout the 71 day siege, all working in civilian clothes [to conceal their unconstitutional involvement in this “civil disorder”]. 38
On March 5, Dick Wilson – with federal officials present – held a press conference to declare “open season” on AIM members on Pine Ridge, declaring “AIM will die at Wounded Knee.” For their part, those inside the hamlet announced their intention to remain where they were until such time as Wilson was removed from office, the GOONs disbanded, and the massive federal presence withdrawn.
Beginning on March 13, federal forces directed fire from heavy .50 caliber machineguns into the AIM positions. The following month was characterized by alternating periods of negotiation, favored by the army and the marshals – which the FBI and GOONs did their best to subvert – and raging gun battles when the latter held sway. Several defenders were severely wounded in a firefight on March 17, and on March 23 some 20,000 more rounds were fired into Wounded Knee in a 24-hour period.
The FBI’s “turf battle” with the “soft” elements of the federal government rapidly came to a head. On April 23, Chief U.S. Marshal Colburn and federal negotiator Kent Frizzell were detained at a GOON roadblock and a gun pointed at Frizzell’s head. By his own account, Frizzell was saved only after Colburn leveled a weapon at the GOON and said, “Go ahead and shoot Frizzell, but when you do, you’re dead.” The pair were then released. Later the same day, a furious Colburn returned with several of his men, disarmed and arrested eleven GOONs, and dismantled the roadblock. However, “that same night… some of Wilson’s people put it up again. The FBI, still supporting the vigilantes, had [obtained the release of those arrested and] supplied them with automatic weapons.” The GOONs were being armed by the FBI with fully automatic M-16 assault rifles, apparently limitless quantifies of ammunition, and state-of-the-art radio communications gear. When Colburn again attempted to dismantle the roadblock:
FBI [operations consultant] Richard [G.] Held arrived by helicopter to inform the marshals that word had come from a high Washington source to let the roadblock stand … As a result the marshals were forced to allow several of Wilson’s people to be stationed at the roadblock and to participate in … patrols around the village. 39
On the evening of April 26, the marshals reported that they were taking automatic weapons fire from behind their position, undoubtedly from GOON patrols. The same “party or parties unknown” was also pumping bullets into the AIM/ION positions in front of the marshals, a matter which caused return fire from AIM. The marshals were thus caught in a crossfire. At dawn on the 27th, the marshals, unnerved at being fired on all night from both sides, fired tear gas cannisters from M-79 grenade launchers into the AIM/ION bunkers. They followed up with some 20,000 rounds of small arms ammunition. AIM member Buddy Lamont (Oglala), driven from a bunker by the gas, was hit by automatic weapons fire and bled to death before medics, pinned down by the barrage, could reach him.
When the siege finally ended through a negotiated settlement on May 7, 1973, the AIM casualty count stood at two dead and fourteen seriously wounded. An additional eight-to-twelve individuals had been “disappeared” by the GOONs. They were in all likelihood murdered and – like an untold number of black civil rights workers in the swamps of Mississippi and Louisiana – their bodies secretly buried somewhere in the remote vastness of the reservation.
Of the 60-plus murders occurring in an area in which the FBI held “preeminent jurisdiction,” not one was solved by the Bureau. In most instances, no active investigation was ever opened, despite eye-witnesses identifying members of the Wilson GOON squad as killers.
U.S. Court of Appeals Judge Gerald Heaney, after reviewing numerous court transcripts and FBI documents, concluded that the United States Government overreacted at Wounded Knee. Instead of carefully considering the legitimate grievances of Native Americans, the response was essentially a military one.
While Judge Heaney believed that the “Native Americans” had some culpability in the firefight that day, he concluded the United States must share the responsibility. It never has. The FBI has never been held accountable or even publicly investigated for what one Federal petit jury and Judge Heaney concluded was complicity in the creation of a climate of fear and terror on the Pine Ridge Reservation.
Other AIM casualties include Richard Oaks, leader of the 1970 occupation of Alcatraz Island by “Indians of All Tribes,” who was gunned down in California the following year. Larray Cacuse, a Navajo AIM leader, was shot to death in Arizona in 1972. In 1979, AIM leader John Trudell, preparing to make a speech in Washington, was told by FBI personnel that, if he gave the speech, there would be “consequences.” Trudell not only made his speech, calling for the U.S. to get out of North America and detailing the nature of federal repression in Indian country, he burned a U.S. flag as well. That night, his wife, mother-in-law, and three children were “mysteriously” burned to death at their home on the Duck Valley Reservation in Nevada.
Agents Provocateurs
Many details are now available concerning these extensive campaigns of terror and disruption, in part through right-wing paramilitary groups organized and financed by the national government, but primarily through the much more effective means of infiltration and provocation of existing groups. In particular, much of the violence that occurred on college campuses can be attributed to government provocateurs.
The Alabama branch of the ACLU argued in court that in May 1970 an FBI agent “committed arson and other violence that police used as a reason for declaring that university students were unlawfully assembled” — 150 students were arrested. The court ruled that the agent’s role was irrelevant unless the defense could establish that he was instructed to commit the violent acts, but this was impossible, according to defense counsel, since the FBI and police thwarted his efforts to locate the agent who had admitted the acts to him. 40
William Frapolly, who surfaced as a government informer in the Chicago Eight conspiracy trial, an active member of student and off-campus peace groups in Chicago, “during an antiwar rally at his college, … grabbed the microphone from the college president and wrestled him off the stage” and “worked out a scheme for wrecking the toilets in the college dorms…as an act of antiwar protest.” 41
One FBI provocateur resigned when he was asked to arrange the bombing of a bridge in such a way that the person who placed the booby-trapped bomb would be killed. This was in Seattle, where it was revealed that FBI infiltrators had been engaged in a campaign of arson, terrorism, and bombings of university and civic buildings, and where the FBI arranged a robbery, entrapping a young black man who was paid $75 for the job and killed in a police ambush. 42
In another case, an undercover operative who had formed and headed a pro-Communist Chinese organization “at the direction of the bureau” reports that at the Miami Republican convention he incited “people to turn over one of the buses and then told them that if they really wanted to blow the bus up, to stick a rag in the gas tank and light it.” They were unable to overturn the vehicle. 43
The Ku Klux Klan
During the 1960’s, the FBI’s role was not to protect civil rights workers, but rather, through the use of informants, the Bureau actively assisted the Ku Klux Klan in their campaign of racist murder and terror.
Church Committee hearings and internal FBI documents revealed that more than one quarter of all active Klan members during the period were FBI agents or informants. 44 However, Bureau intelligence “assets” were neither neutral observers nor objective investigators, but active participants in beatings, bombings and murders that claimed the lives of some 50 civil rights activists by 1964. 44
Bureau spies were elected to top leadership posts in at least half of all Klan units. 45 Needless to say, the informants gained positions of organizational trust on the basis of promoting the Klan’s fascist agenda. Incitement to violence and participation in terrorist acts would only confirm the infiltrator’s loyalty and commitment.
Unlike slick Hollywood popularizations of the period, such as Alan Parker’s film, “Mississippi Burning,” the FBI was instrumental in building the Ku Klux Klan in the South,
“…setting up dozens of Klaverns, sometimes being leaders and public spokespersons. Gary Rowe, an FBI informant, was involved in the Klan killing of Viola Liuzzo, a civil rights worker. He claimed that he had to fire shots at her rather than ‘blow his cover.’ One FBI agent, speaking at a rally organized by the Klavern he led, proclaimed to his followers, ‘We will restore white rights if we have to kill every negro to do it.'” 46
Throughout its history, the Klan has had a contradictory relationship with the national government: as a defender of white privilege and the patriarchal status quo, and as an implicit threat, however provisional, to federal power. Depending on political conditions in society as a whole, vigilante terror can be supplemental to official violence, or kept on the proverbial shortleash. 47 As a surrogate army in the field of terror against official enemies, the Klan enjoys wide latitude. But when it moves into an oppositional mode and attacks key institutions of national power, Klan paramilitarism – but not its overt white supremacist ideology – is treated as an imminent threat to the social order, suppressed, but never destroyed, unlike other COINTELPRO target groups.
These roles are not mutually exclusive. As anti-racist researcher Michael Novick warns: “The KKK and its successor and fraternal organizations are deeply rooted in the actual white supremacist power relations of US society. They exist as a supplement to the armed power of the state, available to be used when the rulers and the state find it necessary.” 48
The Klan’s “supplemental” role, particularly as a private armed force sporadically deployed to arrest the development of movements for Black freedom, is best considered by comparison to other Bureau operations. Unlike other COINTELPROs, the “Klan – White Hate Groups” program was of a different order entirely. Senior FBI management and a majority of agents in the field endorsed the Klan’s values, if not the vigilante character of their tactics; from militaristic anti-communism to extreme racial hatred; from ultra-nationalism to misogynist puritanism. 49
This was evident during the civil rights struggles of the sixties, when Freedom Riders and local community activists directly confronted hostile police forces – many of whom were openly allied with the Klan. Despite clear jurisdictional authority to enforce federal law, the FBI consistently refused to protect civil rights workers under attack across the South. More than once, the Bureau refused to warn those under imminent threat of violence.
FBI inaction in the area of civil rights enforcement wasn’t simply a matter of what the Pike Committee of the House of Representatives dubbed “FBI racism.” Rather, FBI bureaucratic lethargy, when it came to protecting Black lives, underscored its mission against subversion for constituents whose privileges and power were threatened by a militant movement for Black rights. 50
Strikingly different from anti-communist COINTELPROs that enmeshed broad social sectors in a web of entanglements, FBI monitoring of the Klan was strictly confined to the organization itself. No serious efforts were made to explore the supplemental role of White Citizens’ Councils, many of which were active Klan fronts, let alone investigate the obvious and widespread police complicity in racist violence. 51 Bureau surveillance of the Klan was purely passive, hardly the directed aggression reserved for left-wing targets.
In May, 1961, as civil rights activists turned up the heat, the FBI passed information to the Klan about Freedom Rider buses on their way to Birmingham, Alabama. A police sergeant, Thomas Cook, attached to the Birmingham police intelligence branch was plied with reports by Bureau informants. A Klan member himself, Cook furnished this information to Robert Shelton’s Alabama Knights and arranged several meetings to discuss “matters of interest.” Cook supplied Klan leaders with the names of “inter-racial organizations,” the location of meetings, and the membership lists of civil rights groups for circulation in Klan publications. FBI informant Gary Thomas Rowe wrote a confidential memo to the Birmingham Special Agent in Charge (SAC) stating that Cook had handed over inter-office intelligence memos on civil rights activists during a Klan meeting. Rowe insisted that Cook not only gave him relevant information that police had in their files, but urged Rowe to “help himself to any material he thought he would need for the Klan.” 52
According to documents obtained by the American Civil Liberties Union, the Birmingham SAC called Cook and informed him of the progress that Freedom Rider buses had made and when they were scheduled to arrive in the city. According to Rowe, Cook and Birmingham’s public safety director, arch-segregationist Eugene “Bull” Connor conspired with Klan leaders and directly organized physical attacks on Freedom Riders when the buses reached their destination. According to one FBI memo, Connor declared: “By God, if you are going to do this thing, do it right.” 53
In consultation with Shelton’s group, Birmingham police agreed not to show up for 15 or 20 minutes after the buses pulled in, to give Klansmen sufficient time to carry out their attack. Assailants were promised lenient treatment if through some fluke, they managed to get arrested. During a planning meeting that finalized logistical details, Grand Titan Hubert Page advised Klansmen that Imperial Wizard Shelton had spoken with Detective Cook, and was informed that Freedom Rider buses were scheduled to arrive at 11:00 am.
Earlier that day, the KKK intercepted another bus on its way to Birmingham, beating the passengers and setting the vehicle ablaze. As agreed during consultations with Klan leadership, when the buses arrived no police were present at either of Birmingham’s bus terminals, but 60 Klansmen – including Rowe – were waiting. Klansmen attacked civil rights workers, reporters and photographers, viciously beating anyone within reach with chains, pipes and baseball bats.
According to ACLU attorney Howard Simon, “We found that the FBI knew that the Birmingham Police Department was infiltrated by the Klan, that many members of the police department were Klan members, that they knew a person in intelligence was passing information directly to leaders of the Klan, and they also knew their undercover agent had worked out an agreement with the police department to stay away from the terminals. They knew all that and still continued their relationship with the police department.” 54
Though the Bureau claimed that its “Klan – White Hate Groups” COINTELPRO was launched in order to stifle white supremacist activities, the historical record proves otherwise. The more well known, but by no means only examples of Klan terror during the period – the 1963 bombing of the Sixteenth Street Baptist Church that killed four black children; the 1964 murders of civil rights workers Goodman, Chaney and Schwerner in Mississippi: and the 1965 assassination of Viola Liuzzo and her companion near Selma, Alabama, point to knowledge of the crimes, and complicity in subsequent cover-ups by FBI officials.
Bureau informant Gary Thomas Rowe was a central figure in some of the most publicized crimes of the period, indulging in freelance acts of racist terror. He was suspected of involvement in firebombing the home of a wealthy Black Birmingham resident, the detonation of shrapnel bombs in Black neighborhoods and the murder of a Black man during a 1963 demonstration. He became a prime suspect in the Birmingham church bombing after he failed two polygraph tests. His answers were described by investigators as “deceptive” when he denied having been with the Klan group that planted the bomb. 55
Despite enough evidence to open a preliminary investigation, the FBI refused, covering-up for Rowe even when another informant, John Wesley Hall, named him as a member of a three-man Klan security committee holding veto power over all proposed acts of violence. Years later, an independent inquiry uncovered evidence that Hall became a Bureau informant two months after the bombing and despite the fact that a polygraph test convinced the Alabama FBI that he was probably involved in the attack himself, Hall admitted to having moved dynamite for the plot’s ringleader, Robert E. Chambliss, a Klan member since 1924. Even though court testimony and a wealth of evidence linked Hall, Rowe and other members of the Alabama Knight’s to the bombing, the suspects were convicted on a misdemeanor charge – “possession of an explosive without a permit.” It took more than a decade and three bungled investigations to finally convict Chambliss of the crime. 56
In July 1997, almost 35 years after the Sixteenth Street Baptist Church bombing, the FBI re-opened its investigation based on “new information.” However, mainstream news accounts failed to report the pivotal role played by Bureau informants. The Rev. Fred Shuttlesworth, a target of a 1963 Klan assassination plot, believes he knows why only one man was convicted for the bombing. “It is well known,” the 75-year old civil rights leader said, “there was collusion all along between the FBI, local law enforcement and the Klan.” Rev. Shuttlesworth should know: Bureau informant John Wesley Hall was the man who proposed killing the minister. 57
New light was shed on Rowe’s privileged position as an FBI provocateur tasked to “disrupt and neutralize” the civil rights struggle. During a subsequent investigation into the murder of Viola Liuzzo, evidence surfaced that it was Rowe who actually fired the fatal shots that took her life. But instead of prosecuting Rowe, the Bureau placed him in a federal witness protection program. 58
In 1978, Rowe was indicted by an Alabama grand jury as Liuzzo’s killer. But complicity in shielding Rowe and the Bureau from exposure came to light when the contents of a J. Edgar Hoover memo to President Lyndon Johnson became public. Hours after the killings Hoover wrote: “A Negro man was with Mrs. Liuzzo and reportedly was sitting close to her.” In a subsequent memo to aides, Hoover said he informed the President that “she was sitting very, very close to the Negro in the car, that it had the appearance of a necking party.” 59 While providing a glimpse into the pathological nature of Hoover’s racism and misogyny, the Director fails to enlighten us as to the mechanics of a “necking party” during a 100 mph car chase in the dead of night, a “party” by terrorized individuals fleeing armed Klan thugs intent on killing them in cold blood. However twisted, Hoover’s slander was calculated to establish a motive; one that would “justify” Mrs. Liuzzo’s murder on grounds of breaking one of nativism’s primal laws: the prohibition against sex between the races.
On November 3, 1979, a posse organized by Klansmen and neo-Nazis murdered five members of the Communist Workers Party (CWP) in broad daylight. The CWP had organized a “Smash the Klan” demonstration in Greensboro, North Carolina among the city’s mostly black and working class mill workers. CWP members included union organizers and activists who had upset “the fundamental order of things.” 60
An essential component for the operation, organized by night-riding Klansmen, was U.S. Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (BATF) agent, Bernard Butkovich. The BATF agent, a Vietnam veteran and demolitions expert undercover in the local branch of the American Nazi Party, helped the Klan obtain automatic weapons, and also in making their escape. 61
The posse had been organized and led by an FBI infiltrator, Edward Dawson. Dawson was also a paid informant for the Greensboro Police Department. 62 Dawson reported to his handlers that eighty-five Klansmen meeting in nearby Lincolnton had expressed their intent to counter-demonstrate on November 3. 63
The night-riders had stated they intended to arm themselves for their counter-demonstration and that Klan leader, Grand Dragon Virgil Griffin, was actively calling out Klansmen from other states to participate. It was also rumored that neo-Nazis from the Winston-Salem area had obtained a machine gun and other weapons. Dawson reported to Greensboro detective Jerry Cooper that Klansmen and neo-Nazis were assembling at the home of a local Klan member and that they were armed. 64
The police/FBI informant had received a copy of the parade route the day before the CWP-initiated march; a map had been supplied by Detective Cooper. Dawson had driven over the parade route three hours earlier with a contingent of out-of-town Klansmen. Dawson also alerted Cooper that the Klansmen and neo- Nazis possessed three handguns and nine long-barrelled rifles, including automatic weapons supplied by BATF agent Bernard Butkovich. 65
Prior to the beginning of the CWP’s march and demonstration, Cooper and other police officials drove by the house where the Klansmen and neo-Nazis were assembling. They jotted down license plate numbers and then declared a lunch break — at approximately 10 a.m. 66 Less than an hour later, Cooper, trailing behind the Klan caravan reported, “shots fired” and then “heavy gunfire.” The tactical squad assigned to monitor the march were still out to lunch. 67
Two other officers, responding to a domestic disturbance call, noted the absence of patrol cars usually assigned to the area. They arrived at the Morningside projects, the site of the CWP march. Officer Wise later reported having received a most unusual call from the police communications center. The officers were asked how long they anticipated being at their call; they were subsequently advised to “clear the area as soon as possible.” 68
Moments later, five demonstrators lay dead, murdered in broad daylight by members of the Ku Klux Klan and the American Nazi Party. 69 According to Michael Novick, the Greensboro massacre “set the tone for neo-Nazi organizing by the KKK and other white supremacists in the ensuing decade.” 70
A subsequent civil suit brought against the neo-Nazis, the Klan and the Greensboro police resulted in a partial award to the surviving family members. FBI and BATF agents walked away scott-free.
The Secret Army Organization
Convinced that the United States was under threat of an imminent communist takeover, Robert DePugh, a disenchanted member of the John Birch Society, founded the Minutemen in the early sixties. Forged as a “last line of defense against communism,” DePugh’s secret warriors were dedicated to building an underground army to fight against “the enemy within.” 71
However absurd this paranoia may appear on the surface, it had serious and deadly consequences for anyone caught in the cross-hairs. Before their undoing in 1969, the result not of a sinister plot by “communist infiltrators in the government,” but because DePugh and others were prepared to rob banks to finance the organization, the Minutemen had built a formidable national network, with thousands of members stockpiling secret arsenals with more than enough firepower to match their feverish rhetoric. In 1966, 19 New York Minutemen were arrested and accused of plotting to bomb three summer camps allegedly used by “Communist, left wing and liberal” groups “for indoctrination purposes.” Subsequent raids uncovered a huge arms cache that included military assault rifles, bombs, mortars, machine guns, grenade launchers and a bazooka.
In February 1970, six Minutemen from four states led by Jerry Lynn Davis held a clandestine summit in northern Arizona. Surveying the ruins, they were convinced that “communist elements” in the Justice Department had destroyed the group. Undeterred by recent events, they formed the nucleus of the Secret Army Organization (SAO).
As conceived by Davis and the others, the SAO would be armed but low-key: a propaganda group with a potential for waging guerrilla war against leftists, should the need arise. Emphasizing regional autonomy and a decentralized structure, they believed they had inoculated themselves against unwanted attention from “communist-controlled” government agencies. Shortly after the meeting, chapters were established in San Diego, Las Vegas, Phoenix and Seattle with promising contacts made in Portland, El Paso, Los Angeles and Oklahoma. 72
A review of events in San Diego, submitted to the Church Committee in June 1975 and based on “pubic admissions of the officers and agents involved, including sworn testimony at various criminal trials and statements given to news reporters and investigators,” 73 describes how the FBI played a central role in the creation of the Secret Army Organization, placing informant Howard Berry Godfrey in a leadership position.
Godfrey, a San Diego fireman, devout Mormon, and self-styled commando, was an FBI informant for more than five years. According to ex-members, it was Godfrey who was the real force behind the SAO. While employed by the FBI, Godfrey selected the organization’s name and defrayed its start-up costs, including expenditures for printing and mailing literature. By September 1971, there were four active cells in San Diego. Little did they know they were under the direction of the FBI, the State’s ultimate “secret army organization.”
San Diego was the center of a thriving activist community committed to a multitude of projects anathema to the nativist right. With 200,000 active-duty soldiers stationed at nearby bases, the Movement for a Democratic Military (MDM) was the outgrowth of antiwar efforts to influence soldiers bound for Vietnam. MDM organizing had made small, but promising chinks in the military’s armor. Campus organizing by the Students for a Democratic Society (SDS), and the emergence of militant Chicano organizations in the area were viewed as serious threats to the successful prosecution of the war. A thriving underground press, in the form of the San Diego Street Journal, was in stark contrast to the conservative and establishment-oriented media. But when the Journal ran a series of exposes on the shady financial empire of Nixon crony, C. Arnholt Smith, the response from the right was swift. It would soon turn violent. 74
Between November 1969 and January 1970, remnants of the Minutemen launched attacks against the Journal. Bullets were fired into the office, paint splashed over furniture, equipment smashed, records and subscription lists stolen, staff cars firebombed, Journal vending machines vandalized. When the newspaper attempted to relocate to new offices, their prospective landlord was arrested by the San Diego police on a fabricated murder charge. Released after an hour, he told the Journal they’d have to look elsewhere. As the SAO gradually came online as a Bureau surrogate, attacks against the newspaper and its staff intensified. 75
Another SAO target was Dr. Peter Bohmer, a radical economics professor at San Diego State University who was popular with students and an articulate spokesperson against the war. Harassed by conservative university bureaucrats who objected to his antiwar activism, Bohmer was fired after a protracted struggle. Predictably, his much-publicized battle with the university drew SAO scrutiny. Beginning in 1971, a vicious campaign was launched against the professor. In April, tear gas crystals were dumped in a car parked in front of his home. On May 4, a muffled voice warned over the phone “the cross hairs are on you.”
In the summer of 1971, San Diego was chosen as the site for the 1972 Republican convention. Harassment against Bohmer increased, punctuated by assaults targeting the antiwar and Chicano movements. 76 Among these acts were destruction of newspaper offices and book stores, firebombing of cars, and the distribution of leaflets giving the address of the collective where anti-war activist Peter Bohmer lived “for any of our readers who may care to look up this Red Scum, and say hello.”
On January 6, 1972 the SAO dramatically upped the ante. Earlier that day SAO cross-hair stickers were plastered on the door of Bohmer’s office; that evening a caller threatened, “This time we left a sticker, next time we may leave a grenade. This is the SAO!”
A few hours later, in a car parked outside Bohmer’s home, SAO soldier George Mitchell Hoover fiddled with a gun. Sitting next to him was Godfrey, the FBI’s informant. Aiming a 9mm Polish Radom pistol, Hoover fired two shots into the house; he would have fired a third but the weapon jammed. The first bullet struck San Diego Street Journal reporter Paula Tharp, shattering her elbow. The second shot narrowly missed Shari Whitehead and lodged in a window frame above her head. Two shell-casings matching the slug removed from Tharp’s arm were retrieved from the street.
The next day Godfrey turned over the gun to his FBI control agent, Steve Christiansen, a devout Mormon and dedicated anti-communist himself. The Special Agent hid the weapon under his couch for more than six months while the San Diego police conducted a half-hearted investigation. Though guilty of covering-up a criminal act, Christiansen insisted that Bureau superiors knew he was hiding the gun and fully approved of his actions to protect “confidential sources.” 77
Although the Tharp shooting generated considerable publicity, and even some pressure to make arrests, the San Diego police responded with the absurd story that Bohmer carried out the attack himself in an effort “to attract sympathy for his cause.” 78
Relentless harassment continued throughout the spring of 1972; more firebombings, threatening phone calls, more cross-hair stickers, just another day at the office for right-wing counterguerrillas. But then the group made a fatal mistake, one that would cost them dearly.
On June 19, 1972, William Yakopec entered the Guild Theater, a local porno house; concealed under his jacket was a bomb. After he pried a cover loose from a vent at the rear of the building, he hurriedly left the premises. Moments later a powerful explosion ripped through the theater, destroying the screen, blowing debris 60 feet into the air and showering the terrified audience with concrete shards and two-by-fours. Unfortunately for Yakopec and the SAO, a deputy district attorney and a San Diego cop were in the audience, conducting an “investigation” to determine whether I am Curious (Yellow) met pertinent criteria to be banned as pornography. 79
Though city fathers had no problem when right-wing militias directed their wrath at suitable targets, taking out a cop and a district attorney was too much even in San Diego. Rubien D. Brandon, the officer who narrowly escaped being blown to kingdom come, angrily phoned the FBI and demanded the name of their informer. A week later, seven members of the SAO were behind bars. Yakopec was charged with the Guild Theater bombing, George Hoover with the Tharp shooting and the group’s nominal leader, Jerry Lynn Davis, with receiving stolen property and possession of illegal explosives. Reluctantly, the Bureau realized the time had come to shut the project down.
During the investigation of the Guild Theater bombing, the Yakopec home and those of other SAO members were raided by police. Investigators recovered two half pound blocks of C-4 plastique, HDP primers, blasting caps, 30-40 feet of fuses, SAO literature, stacks of cross-hair stickers ready to go and a small arsenal of weapons, including an unopened case of M-16’s valued at more than $60,000. During a simultaneous raid on the home of Genevieve and Richard Fleury, police seized ammunition, dozens of revolvers, lugers and eight bandoliers containing more than a thousand rounds of 30-caliber bullets. It was later revealed that some of these munitions had been transferred to the SAO from the Marine base at Camp Pendelton by a right-wing physician, Dr. Harold Young. Ex-Minuteman Dino Martinelli claimed he had been involved in the transfer and that the SDPD and FBI were aware of the thefts but did nothing. 80
American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) attorney Frederick Hetter discovered during a subsequent investigation “that [FBI infiltrator] Godfrey supplied 75% of the money for the SAO” in order for the terrorist army to acquire the weapons. 81
What were the results of exposing the extensive links between federal authorities and the Secret Army Organization? While Yakopec, Hoover and Davis went to prison, Godfrey, the FBI’s point-man, was rewarded with a job in the state fire marshal’s office. Agent Christiansen left the Bureau shortly after his role in the affair came to light. Refusing to talk, Christiansen would only tell reporters that “The FBI is taking good care of us.” 82 The FBI then continued with other illegal intelligence and terror programs directed against Bohmer and associates, including several assassination plots. Not one FBI agent or informer has been prosecuted.
Snitch Jacketing
Under the guidance of the FBI, informants were often able to work their way into positions of power, such as was the case with Chicago-BPP Chief of Security William O’Neal, or American Indian Movement bodyguard Douglas Durham. Such individuals were often considered valuable due to the (FBI-supplied) information they were able to provide. Besides misleading and provoking the infiltrated groups, another technique used by informants was to “snitch jacket” genuine activists, to make them appear to be the informants. One such person was Kwame Toure, formerly Stokely Carmichael.
Utilizing the services of an infiltrator who had worked his way into a position as the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee leader’s bodyguard, the Bureau deliberately created the false appearance that Stokely Carmichael was himself an operative. 83 In a memo dated July 10, 1968, the SAC, New York, proposed to Hoover that:
… consideration be given to convey the impression that CARMICHAEL is a CIA informer. One method of accomplishing [this] would be to have a carbon copy of an informant report supposedly written by CARMICHAEL to the CIA carefully deposited in the automobile of a close Black Nationalist friend … It is hoped that when the informant report is read it will help promote distrust between CARMICHAEL and the Black Community … It is also suggested that we inform a certain percentage of reliable criminal and racial informants that “we have it from reliable sources that CARMICHAEL is a CIA agent. It is hoped that the informants would spread the rumor in various large Negro communities across the land. 84
Pursuant to a May 19,1969 Airtel from the SAC, San Francisco, to Hoover, the Bureau then proceeded to “assist” the BPP in “expelling” Carmichael through the forgery of letters on party letterhead. The gambit worked, as is evidenced in the September 5, 1970 assertion by BPP head Huey P. Newton: “We … charge that Stokely Carmichael is operating as an agent of the CIA.” 85
Snitch jacketing has even resulted in the target’s death. This appears to have occurred in 1975 in the case of Anna Mae Pictou Aquash, a young Micmac woman working with the American Indian Movement on the Pine Ridge Reservation. According to attorney Bruce Ellison,
“I represented a young mother and AIM member named Anna Mae Pictou on weapons charges. She told me after her arrest that the FBI threatened to see her dead within a year unless she cooperated against members of AIM. In an operation [similar to those] previously used against members of the Black Panther Party, the FBI, through an informant named Doug Durham who had infiltrated AIM leadership, began a rumor that she was an informant.
“Six months later her body was found on the Pine Ridge Reservation. The FBI said she died of exposure. They cut off her hands, claiming that this was necessary to identify her, and buried her under the name of Jane Doe.
“We were able to get her body exhumed, and a second, independent autopsy revealed that rather than dying of exposure, that someone had placed a pistol to the back of her head and pulled the trigger. When I asked for her hands after the second autopsy, because she was originally not buried with her hands, an FBI agent went to his car and came back and handed me a box, and with a big smile on his face he said, ‘You want her hands? Here.'” 86
The FBI agents involved then used the morgue photos of Aquash to frighten another victim, Myrtle Poor Bear, a woman with a history of deep psychological disorder, for which she had undergone extensive treatment, explaining to their captive that she’d end up “the same way” unless she did exactly what they wanted. Poor Bear quoted Agent Wood as informing her, in specific reference to Aquash, that “they [Price and Wood] could get away with killing because they were agents.” Poor Bear was coerced into giving false testimony which led to the extradition of Leonard Peltier, who remains a political prisoner to this day. [See “Political Prisoners” section].
The Subversion of the Press
In 1960, the FBI implemented a formal COINTELPRO with the expressed intent of destroying pro-independence groups in Puerto Rico. In doing so, the Bureau engaged in the same kind of political warfare that was used by the United States in Chile and elsewhere in Latin America. In an August 4, 1960 memorandum to the Special Agent in Charge, San Juan, Director Hoover wrote:
“In considering this matter, you should bear in mind the Bureau desires to disrupt the activities of these organizations and is not interested in mere harrassment.” 87
San Juan complied, at least on the level of planting disinformation in the island press. Agents systematically planted articles and editorials, often containing malicious gossip concerning independentista leaders’ alleged sexual or financial affairs, in “friendly” newspapers, and dispensed “private” warnings to the owners of island radio stations that their FCC licenses might be revoked if pro independence material were aired.
There is clear evidence that agents “talked to” the owners of radio stations WLEO in Ponce, WKFE in Yauco and WJRS in San German about their licensing as early as 1963. One result was cancellation of the one hour daily time-block allotted to “Radio Bandera,” a program produced by the APU. Such tactics to deny a media voice to independentistas accord well with other, more directly physical methods employed during the 1970s, after COINTELPRO supposedly ended:
[There was] the bombing of Claridad [daily paper first of the MPIPR and then the PSP] printing presses which has occurred at least five times in the present decade. Although the MPI [now PSP] usually furnished the police with detailed information as to the perpetrators of these acts, not even one trial has ever been held on this island in connection with these bombings, nor even one arrest made. The same holds true for a 1973 bombing of the National Committee of the [PIP]. 88
In the same memo, Hoover recommended gearing up the COINTELPRO, using existing infiltrators within “groups seeking independence for Puerto Rico” as agents provocateurs. The director felt that “carefully selected informants” might be able to raise “controversial issues” within independentista formations. Further, he pointed out that such individuals might be utilized effectively to create situations in which “nationalist elements could be pitted against the communist elements to disrupt some of the organizations, particularly the MPIPR and … FUPI.”
Hoover also instructed that “the San Juan Office should be constantly alert for articles extolling the virtues of Puerto Rico’s relationship to the United States as opposed to complete separation from the United States, for use in anonymous mailings to selected subjects in the independence movement who may be psychologically affected by such information.”
The Bureau engaged in intensive investigation of independentista leaders both on the island and in New York in order to ascertain their “weaknesses” in terms of “morals, criminal records, spouses, children, family life, educational qualifications and personal activities other than independence activities.” The findings, however flimsy or contrived, were pumped into the media, disseminated as bogus cartoons or “political broadsides,” and/or surfaced within organizational contexts by provocateurs, all with the express intent of setting the leaders one against the other and at odds with their respective organizational memberships.
When evidence to support such redbaiting contentions could not be discovered, the FBI’s COINTELPRO specialists simply made it up:
MPIPR leaders, cognizant of the basic antipathy of Puerto Ricans, predominantly Roman Catholic, to communism, have consistently avoided, at times through public statements, any direct, overt linkage of the MPIPR to communism … The [San Juan office] feels that the above situation can be exploited by means of a counterintelligence letter, purportedly by an anonymous veteran MPIPR member. This letter would alert MPIPR members to a probable Communist takeover of the organization. 89
Not only did the Bureau’s systematic denial of media access to, spreading of disinformation about, and fostering of factionalism within the independentista movement have the effect of negating much of the movement’s electoral potential within the island arena itself, such tactics also subverted other initiatives to resolve the issue of Puerto Rico’s colonial status in a peaceful fashion. This concerns in particular a plebescite called for July 23, 1967. During the ten months prior to the scheduled referendum to determine the desires of the Puertorriqueno public with regard to the political status of their island, the Bureau went far out of its way to spread confusion. The COINTELPRO methods used included creation of two fictitious organizations Grupo pro-Uso Voto del MPI (roughly, “Group within the MPIPR in Favor of Voting to Achieve Independence”) and the “Committee Against Foreign Domination of the Fight for Independence” – as the medium through which to misrepresent independentista positions “from the inside .” One outcome was that Puertorriqueno voters increasingly shied away from the apparently jumbled and bewildering independentista agenda and “accepted” continuation of a “commonwealth” status under U.S. domination.
A 1967 Airtel from SAC, San Juan to J. Edgar Hoover describes a portion of the COINTELPRO methods to be used in subverting the 1967 United Nations plebescite to determine the political status of Puerto Rico:
[deleted] of the MPIPR Youth, has a personal following, and the San Juan Office feels that if [deleted] can be split from the MPIPR at this time, enough of the MPIPR Youth members would be sufficiently confused and disgruntled to effectively neutralize the MPIPR during the critical period just prior to the plebescite scheduled for July 23, 1967. 90
With this accomplished, the Bureau set about seeing to it the independentistas remained artificially discredited (and the overall Puertorriqueño option to mount a coherent effort to protest or reconvene the plebescite truncated) by shifting responsibility for the disaster onto its foremost victims:
It might be desirable to blame the communist bloc and particularly Cuba for the failure of the United Nations and to criticize Mari Bras and others for isolating the Puerto Rican independence forces from the democratic countries. 91
The other COINTELPRO’s also made use the news media. One tragic story concerns Jean Seberg, a well known actress and white supporter of the Black Panther Party. According to former FBI agent M. Wesley Swearingen, who worked in Los Angeles at the time, a culture of racism had so permeated the Bureau and its field offices that the agents seethed with hatred toward the Panthers and the white women who associated with them.
“In the view of the Bureau,” Swearingen reported, “Jean was giving aid and comfort to the enemy, the BPP … The giving of her white body to a black man was an unbearable thought for many of the white agents. An agent [allegedly Richard W. Held] was overheard to say, a few days after I arrived in Los Angeles from New York, ‘I wonder how she’d like to gobble my dick while I shove my .38 up that black bastard’s ass [a reference to BPP theorist Raymond “Masai” Hewitt, with whom Seberg was reputedly having an affair].” 92
On May 27, 1970, when Seberg was in her fifth month of pregnancy, Held sent a telegram to headquarters requesting approval to plant a story with Hollywood gossip columnists to the effect that Seberg was pregnant, not by her husband, Romaine Gary, but by a Panther. Held’s idea was approved, although implementation was to be postponed “approximately two additional months,” to protect the secrecy of a wiretap the Bureau had installed in the LA and San Francisco BPP headquarters, and until the victim’s “pregnancy would be more visible to everyone.” Hoover felt that Seberg should be “neutralized” because she’d been a financial supporter of the Black Panther Party.
The schedule was apparently accelerated, because on June 6, Held sent Hoover a letter and attached newspaper clipping demonstrating the “success” of his COINTELPRO action: a column by Joyce Haber, which had run in the Los Angeles Times on May 19. Known by the FBI to have been emotionally unstable and in the care of a psychiatrist before the operation began, Seberg responded to the “disclosure” by attempting suicide with an overdose of sleeping pills. This in turn precipitated the premature delivery of her fetus; it died two days later. Seberg held a press conference, and brought the fetus in a glass jar, to prove that it was white.
Henceforth, a shattered Jean Seberg was to regularly attempt suicide on or near the anniversary of her child’s death. In 1979, she was successful. Romaine Gary, her ex-husband, who all along maintained he was the father of the child, followed suit shortly thereafter. There is no indication that this was ever considered to be anything other than an extremely successful COINTELPRO operation.
The FBI actively promoted the idea that the Panthers and other black nationalists were anti-Semitic, in order to weaken their support “among liberal and naive elements.” In one indicent, the New York Office sent anonymous letters to Rabbi Meir Kahane of the right-wing Jewish Defense League to try to provoke a response against the BPP. In reference to a July 25, 1969 FBI report entitled, “JEWISH DEFENSE LEAGUE, RACIAL MATTERS” the New York Field Office proposed:
Referenced report has been reviewed by the NYO in an effort to target one individual within the Jewish Defense League (JEDEL) who would be the suitable recipient of information furnished on an anonymous basis that the Bureau wishes to disseminate and/or use for future counterintelligence purposes.
NY is of the opinion that the individual within JEDEL who would most suitably serve the above stated purposed would be Rabbi MEIR KAHANE, a Director of JEDEL. It is noted that Rabbi KAHANE’s background as a writer for the NY newspaper “Jewish Press” would enable him to give widespread coverage of anti-Semetic [sic] statements made by the BPP and other Black Nationalist hate groups not only to members of JEDEL but to other individuals who would take cognizance of such statements. …
In view of the above comments the following is submitted as the suggested communication to be used to establish rapport between the anonymous source and the selected individual associated with JEDEL:
Dear Rabbi Kahane:
I am a negro man who is 48 years old and served his country in the U.S. Army in WW2 and worked as a truck driver with “the famous red-ball express” in Gen. Eisenhour’s Army in France and Natzi Germany. One day I had a crash with the truck I was driving, a 2 1/2 ton truck, and was injured real bad. I was treated and helped by a Jewish Army Dr. named “Rothstein” who helped me get better again.
Also I was encouraged to remain in high school for two years by my favorite teacher, Mr. Katz. I have always thought Jewish people are good and they have helped me all my life. That is why I became so upset about my oldest son who is a Black Panther and very much against Jewish people. My oldest son just returned from Algiers in Africa where he met a bunch of other Black Panthers from all over the world. He said to me that they all agree that the Jewish people are against all the colored people and that the only friends the colored people have are the Arabs.
I told my child that the Jewish people are the friends of the colored people but he calls me a Tom and says I’ll never be anything better than a Jew boy’s slave.
Last night my boy had a meeting at my house with six of his Black Panther friends. From the way they talked it sounded like they had a plan to force Jewish store owners to give them money or they would drop a bomb on the Jewish store. Some of the money they will get will be sent to the Arabs in Africa.
They left books and pictures around with Arab writing on them and pictures of Jewish soldiers killing Arab babys. I think they are going to give these away at Negro Christian Churchs.
I thought you might be able to stop this. I think I can get some of the pictures and books without getting myself in trouble. I will send them to you if you are interested.
I would like not to use my real name at this time.
A friend”
It is further suggested that a second communication be sent to Rabbi KAHANE approximately one week after the above described letter which will follow the same foremat [sic], but will contain as enclosures some BPP artifacts such as pictures of BOBBY SEALE, ELDRIDGE CLEAVER, a copy of a BPP newspaper, etc. It is felt that a progression of letters should then follow which would further establish rapport with the JEDEL and eventually culminate in the anonymous letter writer requesting some response from the JEDEL recipient of these letters. 93
Political Prisoners
When the government can select a person for criminal persecution because of their political activity, when they can fabricate evidence against that person and suppress evidence proving that fabrication, and prosecute a person and put them in prison for any amount of time, let alone for life, then you have a political prisoner.
There are numerous people in American jails who’ve dedicated their lives to the transformation of their country, who put the benefit of their communities ahead of themselves, who believed that transformation was not only possible but they were willing to die for it. They were willing to die to end brutality, racism, economic discrimination, imperialism, war.
In the case of AIM, this has meant the wholesale jailing of the movement’s leadership. Virtually every known AIM leader in the United States has been incarcerated in either state or federal prisons since (or even before) the organization’s formal emergence in 1968, some repeatedly. After the 1973 siege of Wounded Knee the FBI caused 542 separate charges to be filed against those it identified as “key AIM leaders.” This resulted in 15 convictions, all on such petty or contrived offenses as “interfering with a federal officer in the performance of his duty.” Russell Means was faced with 37 felony and three misdemeanor charges, none of which held up in court. Organization members often languished in jail for months as the cumulative bail required to free them outstripped resource capabilities of AIM and supporting groups.
Another example was the “Panther 21” case, which in 1969 was the longest criminal trial in New York history. It took the jury just ninety minutes to reach “not guilty” verdicts in all of the 156 of the charges against the thirteen defendants who ultimately stood trial.
A fair accounting of American political prisoners is beyond the scope of this report, which seeks only to draw attention to the problem of political repression and the tactics used, making note of a few illustrative cases.
Leonard Peltier
U.S. Court of Appeals Judge Gerald Heaney, after reviewing numerous court transcripts and FBI documents, concluded that the United States Government overreacted at Wounded Knee. Instead of carefully considering the legitimate grievances of Native Americans, the response was essentially a military one which culminated in a deadly firefight on June 26, 1975, between Native Americans and FBI agents and U.S. Marshals.
While Judge Heaney believed that the “Native Americans” had some culpability in the firefight that day, he concluded the United States must share the responsibility. It never has. The FBI has never been held accountable or even publicly investigated for what one Federal petit jury and Judge Heaney concluded was complicity in the creation of a climate of fear and terror on the Pine Ridge Reservation.
The resulting firefight near Oglala was preceded by FBI documents internally declaring AIM to be one of the most dangerous organizations in the country and a threat to national security. It followed by two months the issuing of a position paper entitled “FBI Paramilitary Operations in Indian Country,” a how-to plan for dealing with AIM in the battlefield. It used such terms as “neutralization,” which in the document was defined as “shooting to kill.” It included the role of the then-Nixon White House in handling complaints as to such military tactics being utilized domestically.
It followed by one month the build-up of FBI personnel on the Pine Ridge Reservation with mostly SWAT team members from various divisions of the FBI. It followed by three weeks an inspection tour of the reservation by senior FBI officials and the reporting of concern by those officials for the widespread support enjoyed by AIM in the outlying communities on the Pine Ridge Reservation, such as Oglala.
The FBI headquarters document further referred to an area near Oglala which reportedly contained bunkers and would require the use of paramilitary forces to assault. Three weeks later a firefight broke out on the ranch of elders Cecelia and Harry Jumping Bull which lasted for nearly nine hours. FBI documents describe as many as 47 people being involved in the battle with SWAT teams of the FBI, the Bureau of Indian Affairs, and State police agencies.
Three young men lost their lives that day, each shot in the head, two FBI agents and one AIM member. Members of the American Indian Movement, before they escaped, sat and prayed for the three men who died that day. The FBI has always only considered that only two men died that day, their own agents.
One of the agents had in his briefcase a map of the reservation. It had the Jumping Bull ranch circled with the word “bunkers” written next to it. The bunkers turned out to be aged and crumbling root cellars.
Leonard Peltier and other AIM members from outside the reservation had come into the Jumping Bull area to join other local AIM members because the climate of violence on the reservation had gotten so intense that people felt the need to gain assistance from the outside, so men and women came in, including Leonard Peltier, and they brought with them their single-shot 22’s and their rusted shotguns and a few hunting rifles that they were able to get, and they were in a camp on the Jumping Bull ranch.
The government used the incident to increase its campaign of disruption and destruction of the American Indian Movement. FBI agents, dressed and equipped like combat soldiers, searched homes and questioned Pine Ridge residents at gunpoint. Armored vehicles patrolled the reservation, as did SWAT teams and National Guard helicopters.
This was accompanied by a public disinformation campaign by the FBI, designed to make Oglala residents and their guests appear to be the aggressors and, in fact, terrorists. The U.S. Commission on Civil Rights would soon report, “It is patently clear that many of the statements released to the media regarding the incident are either false, unsubstantiated, or directly misleading.”
Noting Leonard Peltier’s regular presence and involvement in AIM activities throughout the country, the FBI targeted him for prosecution from the desks of its agents. According to FBI documents, about two and a half weeks after the firefight, the Bureau was going to, in its own words, “develop information to lock Peltier into the case,” and it set out to do so.
The FBI eventually charged four AIM members, including Peltier, with the killing of the agents. No one has ever been prosecuted for the killing of AIM member Joe Stuntz that day.
After hearing testimony of numerous eyewitnesses to the violence directed at AIM members by the goon squad and the Federal Bureau of Investigation, two of Leonard Peltier’s codefendants were acquitted on self-defense grounds by an all-white jury in the conservative town of Cedar Rapids, Iowa — truly a remarkable thing, but people who were willing to keep their eyes and their ears open and listen to the truth, and were able, by a judge who had the courage and willingness to learn himself, to allow this evidence to be presented.
However, after those acquittals, the FBI analyzed why these two men, these two long-haired indian militant men could be acquitted by an all-white jury, and decided a new judge was needed. FBI documents show that in a meeting in Washington, D.C. at FBI headquarters, there was a decision made to “put the full prosecutive weight of the Federal Government” against Leonard Peltier.
Evidence shows the government used now admittedly false eyewitness affidavits to extradite Peltier from Canada. This would catch the attention of Amnesty International and the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals, but only a little bit.
The Court of Appeals would call such conduct “a clear abuse of the investigative process by the FBI” and give credence to the claims of indian people that if the government is willing to fabricate evidence to extradite a person in this country, it is willing to fabricate evidence to convict those branded as the enemy. Well, absolutely true, but Leonard Peltier remains in prison.
At Peltier’s trial the government presented evidence and argued to the jury that he personally shot and killed the agents. To do this, the government presented ballistics evidence purportedly connecting a shell casing found near the agents’ bodies with a rifle said to be possessed by Peltier on that day, and the coerced and fabricated eyewitness account of a terrified teenager, claiming that the agents followed Peltier in a van, precipitating the firefight in Oglala.
Documents obtained under the Freedom of Information Act show that the ballistics evidence was a fraud; that the rifle could not have fired the expended casing found near the body. Further, the FBI had suppressed evidence showing the agents followed a pickup, not a van, into the compound, and thought someone else, not Peltier, was in that vehicle.
Citing the case of Leonard Peltier as an example, Amnesty International has called for an independent inquiry into the use of our criminal justice system for political purposes by the FBI and other intelligence agencies in this country. Amnesty cited similar concerns for other members of AIM and other victims of the COINTELPRO-type operations by the FBI.
Upon disclosure of these documents, a renewed effort in a new trial was sought from the courts. While concluding that the suppressed evidence “casts a strong doubt” on the government’s case, the appellate courts denied relief. The U.S. Attorney’s office has now admitted in court that it had no credible evidence Leonard Peltier killed the agents, and speciously claimed it never tried to prove it did. Under our system, if there is a reasonable doubt, then Leonard Peltier is not guilty, yet he has been in prison for nearly 25 years for a crime he did not commit.
The FBI still withholds thousands of pages of documents in this case, claiming in many instances that disclosure would compromise the national security. In the absence of such disclosure, no further efforts in a new trial are possible. And Leonard Peltier is not alone in his imprisonment for his political activities.
Mumia Abu Jamal
In the case of Mumia Abu-Jamal, neutralization occurred by falsely creating the appearance that he was in commission of a crime he did not commit, to put him in prison. The cost of political activism can include judicial railroading into the electric chair, or the gas chamber or lethal injection.
It is unquestionable that from a very early age, Mumia Abu-Jamal was specifically targeted for neutralization by the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the Philadelphia Police, and that the pattern of police activity evident in that targeting, was continued, as it was in a number of comparable cases, so long as he maintained political activism, and this creates the basis to believe that he was in fact framed for the crime.
Mumia was deprived a fair trial, in which key witnesses were not allowed to testify, exculpatory evidence was excluded, and a key witness had been arrested numerous times for prostitution, opening the possibility that her testimony was paid or coerced. Although no motive was ever shown for why Mumia would have killed a police officer, there was a certainly a motive to neutralize and frame him.
Geronimo ji Jaga Pratt
Elmer Gerard (“Geronimo” or “G” ji Jaga) Pratt was an active member of the Los Angeles Black Panther Party (LA-BPP) Chapter during the counterintelligence campaign which resulted in the “shooting war” described earlier, between the US organization and the Panthers.
When Bunchy Carter and Ed Huggins were assassinated by US gunmen on January 17, 1969, it was discovered that Carter had prepared an audio tape for such an eventuality, designating Pratt his successor as head of the LA-BPP. Pratt was also named by Carter to succeed himself and Huggins as chapter representative on the national Panther Central Committee. 94 It was at precisely this point that he appears to have been personally targeted for “neutralization” through the application of COINTELPRO techniques.
Pratt was designated a “Key Black Extremist” by the L.A. Bureau office and placed in the National Security Index. 95 As a consequence, he was targeted not only for neutralization by the FBI, but, as former Panther infiltrator Louis Tackwood had pointed out, this automatically placed him “on the wall’ of the Los Angeles Police Department’s (LAPD) Criminal Conspiracy Section (CCS) “glass-house” (headquarters) as an individual to be eliminated by local police action. As the informant explained the CCS operation:
The room is broken up into divisions, see my point? Black, white, chicano and subversives. Everybody’s there. And every last one of the walls has pictures of them. This one black, the middle all white, and the chicanos all on this side. Most of the files are on the walls, you see? … They got everybody. Panthers, SDS, Weathermen. Let me explain to you. They got a national hookup. You see my point? And because of this national power, they are the only organization in the police department that has a liaison man, that works for the FBI, and the FBI has a liaison man who works with the CCS.” 96
The inevitable consequence of this was that the new LA-BPP was placed under intensely close surveillance by the FBI 97 and subjected to a series of unfounded but serious arrests by the Bureau’s local police affiliates at CCS.
A conspiracy investigation of Pratt was opened with regard to the robbery of a Bank of America facility already known by the Bureau to have been carried out by US members. 98 Pratt was also made the subject of a personalized series of COINTELPRO cartoons designed to make him a target for the attentions of US.
This was followed very closely by a Bureau effort to ensnarl both Pratt and Roger Lewis in a violation of the 1940 Smith Act and plotting of “insurrection.” 99
Four days after a similar raid on a Panther apartment in Chicago (the raid which left Mark Clark and Fred Hampton dead), forty men of the Special Weapons and Tactics (SWAT) squad, with more than a hundred regular police as backup, raided the Los Angeles Panther headquarters at 5:30 in the morning … (No suggestion has been made that the two raids were linked. But it’s interesting to note that Fred Hampton had been in Los Angeles one or two days before his death, meeting with Geronimo Pratt, whom Tackwood says was the main target of the second raid.) The Panthers chose to defend themselves, and for four hours they fought off police, refusing to surrender until press and public were on the scene. Six of them were wounded. Thirteen were arrested. Miraculously, none of them were killed. 100
The similarities between the Chicago and Los Angeles raids are undeniable, with a special local police unit closely linked to the FBI involved in both assaults, spurious warrants seeking “illegal weapons” utilized on both occasions, predawn timing of both raids to catch the Panthers asleep and a reliance upon overwhelming police firepower to the exclusion of all other methods. Both raids occurred in the context of an ongoing and highly energetic anti-BPP COINTELPRO, and – as in the Hampton assassination – bullets were fired directly into Pratt’s bed. Unlike the Chicago leader, however, Pratt was sleeping on the floor, the result of spinal injuries sustained in Vietnam. 101
Pratt was explicitly singled out for neutralization by the head of the Bureau’s LA-COINTELPRO section, Richard Wallace Held – the son of Richard G. Held, who orchestrated the coverup of FBI involvement in the Hampton-Clark assassinations. 102
In both instances, the FBI had managed to place an infiltrator/provocateur very high within the local BPP chapter – O’Neal in Chicago, in Los Angeles it was Melvin “Cotton” Smith, number three man in the LA-BPP, who provided detailed floorplans, including sleeping arrangements of the Panther facility, prior to the raid. 103 And, in both cases, surviving Panthers were immediately arrested for their “assault upon the police.” 104
When the resultant case against the L.A. Panthers was finally prosecuted in July, 1971:
… there was a “surprise” development. Melvin “Cotton” Smith turned up as a star witness for the prosecution. According to Deputy District Attorney Ronald H. Carroll, Smith had turned State’s evidence to escape prosecution … [However] on November 22, 1971, Tackwood testified … he had started working for [CCS Sergeant R.G.] Farwell in the fall of 1969, before the December 8 raid, and had been told by Farwell that [FBI infiltrator] Cotton Smith was to be Tackwood’s contact. Since Smith’s testimony was crucial to the State’s case, Tackwood’s exposure of Smith’s real role was a devastating blow to the prosecution. 105
One consequence of this revelation was that, after eleven days of deliberation, the jury returned acquittals or failed to reach any verdict whatsoever relative to charges of conspiring to assault and murder police officers brought against all thirteen Panther defendants. Oddly, nine of the defendants, including Pratt, were convicted of the relatively minor and technical charge of conspiring to possess illegal weapons. 106 In addition:
In order for the armed police assault on the Panther headquarters to have been justified, the police contention that the Panthers had fired on them first would have had to have been true, in which case at least some of the Panthers would have been guilty of conspiracy to commit murder and assault charges … The failure of the jury to return guilty verdicts on these charges represented a total repudiation of the CCS [and FBI] “conspiracy” theory that led to the raids on December 8. 107
On December 18, 1968, two black men robbed and shot a white couple, Caroline and Kenneth Olsen, on a Santa Monica, California tennis court. Caroline Olsen died one week later.
Pratt was accused of “the tennis court murder” in a letter dated August 10, 1969, addressed to LAPD Sergeant Duwayne Rice by an “underworld informant” and marked “Do Not Open Except In Case of My Death.” Although the informant had not died, Rice opened and read the accusation, and turned it over to CCS detective Ray Callahan for presentation to a grand jury which secretly indicted Pratt.
The informant would later testify at trial that Pratt, in direct personal conversation with him, had “bragged” of the crime. He further testified that a .45 calibre Colt automatic seized by the LAPD, belonging to Pratt but not ballistically matching the tennis court murder weapon, was actually the gun in question, Pratt having “changed the barrel” in order to alter its ballistic pattern. A second informant, who did not testify, corroborated this testimony. 108
The supposed informant corroboration testimony, it was later revealed, was obtained from Cotton Smith, already unmasked as an infiltrator/provocateur during the 1971 shootout trial and thus unable to credibly take the stand in the Olsen murder case. In 1985, Smith totally recanted his allegations against Pratt, stating unequivocally that the former Panther leader had been “framed,” but by “the FBI rather than local police”; he specifically named LA FBI COINTELPRO operative George Aiken as having been instrumental in the affair. 109
Kenneth Olsen, the surviving victim, identified Pratt as the murderer in open court, as did Barbara Reed, a shopkeeper who had seen the gunmen prior to the shooting. Mitchell Lachman, who had been near the tennis court on the evening of the murder, testified the gunmen fled in a vehicle matching the description of Pratt’s white over red GTO convertible.
However, both Olsen and the District Attorney omitted mention of the fact that he had positively identified another man – Ronald Perkins – in a police lineup very shortly after the fact, on December 24, 1968; they had similarly neglected to mention that LAPD personnel had “worked with” Olsen from photo spreads for some months prior to the trial, with an eye toward obtaining the necessary ID of Pratt. 110 Again, both the prosecutors and Mrs. Reed, the other witness who offered a positive ID on Pratt, “forgot” comparable police coaching, and all parties to the State’s case somehow managed to overlook the fact that both Olsen and Reed had repeatedly described both gunmen as “clean shaven,” while Pratt was known to have worn a mustache and goatee for the entirety of his adult life. 111 This leaves Lachman’s testimony that the assailants fled the scene in a white-over-red convertible “like” (but not necessarily) Pratt’s; even if it were the same car, it was well established – and never contested by the State – that virtually the whole LA-BPP had use of the vehicle during the period in question. 112
Pratt’s defense was that he was in Oakland, some 400 miles north of Santa Monica, attending a BPP national leadership meeting on the evening in question. Presentation of this alibi was, however, severely hampered by the refusal of many of those also in attendance – such as David, June, and Pat Hilliard, Bobby and John Seale, Nathan Hare, Rosemary Gross and Brenda Presley (all of the Newton faction) – to testify on his behalf. 113 Kathleen Cleaver, also in attendance at the meeting, did testify that Pratt was in Oakland from December 13-25, 1968, but even her efforts to do so had been hampered by COINTELPRO letters to her husband “explaining” that it was “too dangerous” for her to return to the United States during the trial. 114 With the weight of testimony heavily on the side of the prosecution, Pratt was convicted of first degree murder on July 28, 1972 and sentenced to seven years to life. 115
There were other problems with the case which went beyond Pratt’s inability to assemble defense witnesses. For instance, it did occur to the defense that if the FBI were tapping the phones of the BPP national offices in Oakland during December of 1968 – as seems likely – the Bureau itself might well be able to substantiate Pratt’s whereabouts on the crucial night. The FBI, however, submitted at trial that no such taps or bugs existed, an assertion which was later shown to be untrue. 116
The Bureau then refused to release its logs from the wiretaps, on “national security” grounds, until forced to do so by an FOIA suit brought by attorneys Jonathan Lubell, Mary O’Melveny and William H. O’Brien. 117 At that point (1981), the transcripts were delivered, minus precisely the records covering the period of time which might serve to establish Pratt’s innocence; “The FBI has indicated that the transcripts of the conversations recorded by these telephone taps have been lost or destroyed,” wrote the frustrated judge. 118
The State’s star witness, who first accused Pratt of the tennis court murder in his letter to Rice, testified to Pratt’s “confession” of the crime (i.e., “bragging”) and finally reconciled the prosecution’s ballistics difficulties, was none other than the infiltrator/provocateur, expelled from the BPP by Pratt, Julius C. (aka Julio) Butler. At the trial, the prosecution went considerably out of its way to bolster Butler’s credibility before the jury by “establishing” that the witness was not a paid FBI informant:
Q: And when you were working for the Black Panther Party, were you also working for law enforcement at the same time?
A: No.
Q: You had severed any ties you had with law enforcement?
A: That’s correct.
Q: Have you at any time since leaving the Sheriffs Department worked for the FBI or the CIA?
A: No.
Q: Are you now working for the FBI or CIA?
A: No.
This testimony was entered despite the fact that Los Angeles FBI Field Office informant reports concerning one Julius Carl Butler show he performed exactly this function, at least during the period beginning in August of 1969 (the time when he ostensibly made his initial accusation against Pratt) until January 20, 1970 (after Pratt was jailed without bond on the Olsen murder charge). During the whole of 1970, he filed monthly reports with the Bureau, he was “evaluated” by the FBI as an informant during that year, and his informant file was not closed until May of 1972 – immediately prior to his going on the witness stand. 119
Louis Tackwood has consistently contended that Butler was an FBI infiltrator of the BPP from the day he joined the Party in early 1968 and that he actively worked with CCS detectives Ray Callahan and Daniel P. Mahoney to eliminate Pratt. 120
At the trial, the Bureau also submitted that Pratt was not the target of COINTELPRO activity; several hundred documents subsequently released under the FOIA demonstrate this to have been categorically untrue. Further:
On 18 December 1979, eight years after Pratt’s trial, the California Attorney-General’s office filed a declaration in court that his defense camp had been infiltrated by one FBI informant. The Deputy Attorney-General wrote to the court and defense counsel on 28 July 1980, enclosing a copy of a letter of the same date from the Executive Assistant Director of the FBI. This letter revealed that two had been in a position to obtain information about Elmer Pratt’s defense strategy. 121
One reason for the seemingly blanket recalcitrance of the authorities – federal, state and local – in extending even the most elementary pretense of justice in the Pratt case may revolve around his quiet refusal to abandon the political principles which caused him to become a COINTELPRO target in the first place. Whatever the particulars of official motivation in the handling of the Pratt case, it must be assessed within the overall COINTELPRO-BPP context, especially a counterintelligence-related instructional memo, dated October 24, 1968, and sent by Bureau headquarters to all field offices. It reads in part:
Successful prosecution is the best deterrent to such unlawful activities [as dissident political organizing]. Intensive investigations of key activists … are logically expected to result in prosecutions under substantive violation within the Bureau’s jurisdiction. 122
To this, the Church Committee’s rejoinder in its investigation of the Bureau’s COINTELPRO illegalities still seems quite appropriate: “While the FBI considered Federal prosecution a ‘logical’ result, it should be noted that key activists were chosen not because they were suspected of having committed or planning [sic] to commit any specific Federal crime.” 123 After 27 years in prison and five habeus corpus motions, the conviction for the tennis court murder was finally vacated and Geronimo ji Jaga was released.
Dhoruba Bin Wahad
In 1966, the New York City Police Department commenced its own investigation of the Black Panther Party. Detective Ralph White of the New York City Police Department was directed to infiltrate the Black Panther Party and submit daily reports on the Party and its members. The NYPD regularly communicated with police departments throughout the country, sharing information on the BPP, its members and activities.
The NYPD was also working with the FBI on a daily basis. On August 29, 1968 FBI Special Agent Henry Naehle reported on his meeting with a member of an NYPD “Special Unit” investigating the BPP. SA Naehle acknowledged that the FBI?s New York Field Office (NYO) “has been working closely with BSS in exchanging information of mutual interest and to our mutual advantage.”
An FBI “Inspector?s Review” for the first quarter of 1969 shows that the NYPD, in conjunction with the FBI, had an “interview” and “arrest” program as part of their campaign to neutralize and disrupt the BPP. The NYPD advised the FBI that these programs have severely hampered and disrupted the BPP, particularly in Brooklyn, New York, where, for a while, BPP operations were at a complete standstill and in fact have never recovered sufficiently to operate effectively.
A series of FBI documents reveal a joint FBI/NYPD plan to gather information on BPP members and their supporters in late 1968. During an unprovoked attack by off-duty members of the NYPD on BPP members attending a court appearance in Brooklyn, the briefcase of BPP leader David Brothers was stolen by the NYPD and its contents photocopied and given to the FBI. Rather than seeking to prosecute the police officers for this theft, the FBI ordered “a review of these names and telephone numbers [so that] appropriate action will be taken.”
That “appropriate action” included an effort to label Brothers and two other BPP leaders, Jorge Aponte and Robert Collier, as police informants. On December 12, 1968, the FBI?s New York Office proposed circulating flyers warning the community of the “DANGER” posed by Brothers, Collier and Aponte. The NYO proposed that the flyers “be left in restaurants where Negroes are known to frequent (Chock Full of Nuts, etc.)” BSS later told the FBI that its proposal was successful in that David Brothers had come under suspicion by the BPP. An FBI memorandum dated December 2, 1968 captioned “Counterintelligence Program” lists several operations during the previous two-week period. It closes by stating that “every effort is being made in the NYO to misdirect the operations of the BPP on a daily basis.”
In August 1968, Dhoruba Bin Wahad, then known as Richard Dhoruba Moore, joined the BPP, and within a few months was promoted to a position of leadership. He was soon identified by the Bureau and by the NYPD as a “key agitator” and placed in the FBI’s “Security Index”, “Agitator Index,” and “Black Nationalist Photograph Album.” FBI supervisors instructed the NYO to “develop better liaison and closer working relationship with the NYCPD” in their investigation of Dhoruba Bin Wahad.
On April 2, 1969 Bin Wahad and 20 other members of the Black Panther Party were indicted on charges of conspiracy in the so-called “Panther 21” case. A NYPD memorandum notes that the Panther 21 arrests were considered a “summation” of the overt and covert investigation commenced in 1966. In a bi-weekly report to FBI Headquarters listing several counterintelligence operations the FBI reported that
To date, the NYO has conducted over 500 interviews with BPP members and sympathizers. Additionally, arrests of BPP members have been made by Bureau Agents and the NYCPD. These interviews and arrests have helped disrupt and cripple the activities of the BPP in the NYC area. Every effort will be made to continue pressure on the BPP…
In July 1969, the NYPD sent officers to Oakland, California to monitor the Black Panther Party’s nationwide conference calling for community control of police departments. An NYPD memorandum candidly acknowledged that community control of the police, “may not be in the interests of the department.”
Through its warrantless wiretaps of BPP telephones, the FBI learned that the BPP was trying to raise the $100,000 bail that had been set for Bin Wahad, whose release was considered by the BPP to be a priority over the other 20 defendants, due to his leadership role in the organization. Fundraising efforts were impeded by FBI/NYPD counterintelligence operations. For example, following a fund raiser at the home of conductor Leonard Bernstein, the FBI sent falsified letters to those in attendance in order to “thwart the aims and efforts of the BPP in their attempt to solicit money from socially prominent groups…” Unable to raise bail, Dhoruba Bin Wahad spent the next year incarcerated.
The FBI continued to target BPP community programs. For example, the FBI pressured several churches not to institute the BPP’s Free Breakfast for Children Program at their parishes. In September, 1969, an NYPD BSS representative told the FBI that the BPP was disintegrating in New York.
By March of 1970, the BPP had raised enough money to post bail for the most articulate leaders and chose Mr. Bin Wahad for release. The FBI ordered that he be immediately and continuously surveilled and that donors of bail money be identified. Director Hoover reminded his New York Office that the activities of Panther 21 defendants were of “vital interest” to the “Seat of Government”.
Through their warrantless wiretaps of BPP offices and residences, the FBI became aware in May 1970 of dissatisfaction among New York BPP members, including Bin Wahad, with West Coast BPP members. A COINTELPRO operation prepared by the New Haven Field Office and submitted to the FBI’s New York Office consisted of an FBI-fabricated note wherein Bin Wahad accused BPP leader Robert Bay of being an informant.
This successful operation resulted in Dhoruba Bin Wahad’s demotion within the BPP. Aware of his disillusionment, the FBI disseminated information regarding BPP strife to the media and participated in a plan to either recruit Bin Wahad as an informant or have BPP members believe he was an agent for the FBI.
In August 1970, BPP leader Huey P. Newton was released from prison. A plethora of counterintelligence actions followed which sought to make Newton suspicious of fellow BPP members, particularly those, like the Bin Wahad, who were on the East Coast.
By early 1971, the plan bore fruit. On January 28, 1971, FBI Director Hoover reported that Newton had become increasingly paranoid and had expelled several loyal BPP members:
Newton responds violently…The Bureau feels that this near hysterical reaction by the egotistical Newton is triggered by any criticism of his activities, policies or leadership qualities and some of this criticism undoubtedly is result of our counterintelligence projects now in operation.
This operation was enormously successful, resulting in a split within the BPP with violent repercussions. In early January 1971, Fred Bennett, a BPP member affiliated with the New York chapter, was shot and killed, allegedly by Newton supporters. Newton came to believe that Bin Wahad was plotting to kill him. Bin Wahad, in turn, was told by Connie Matthews, Newton?s secretary, that Newton was planning to have Bin Wahad and Panther 21 co-defendants Edward Joseph and Michael Tabor killed during Newton?s upcoming East Coast speaking tour. As a result of the split and fearing for his life, Bin Wahad, along with Tabor and Joseph, were forced to flee during the Panther 21 trial.
On May 13, 1971, the Panther 21, including Dhoruba Bin Wahad, were acquitted of all charges in the less than one hour of jury deliberations, following what was at that time the longest trial in New York City history. BSS Detective Edwin Cooper begrudgingly reported to defendant Michael Codd that the case “was not proven to the jury?s satisfaction.” Alarmed and embarrassed by the acquittal, Director Hoover ordered an “intensification” of the investigations of acquitted Panther 21 members with special emphasis on those, like Bin Wahad, who were fugitives.
On May 19, 1971, NYPD Officers Thomas Curry and Nicholas Binetti were shot on Riverside Drive in Manhattan. Two nights later, two other officers, Waverly Jones and Joseph Piagentini, were shot and killed in Harlem. In separate communiques delivered to the media, the Black Liberation Army claimed responsibility for both attacks.
Immediately after these shootings, the FBI made the investigation of these incidents, called “Newkill,” a part of their long-standing program against the BPP. Before any evidence had been collected, BPP members, in particular those acquitted in the Panther 21 case, were targeted as suspects. Hoover instructed the New York Office to consider [the] possibility that both attacks may be result of revenge taken against NYC police by the Black Panther Party (BPP) as a result of its arrest of BPP members in April, 1969 [i.e. the Panther 21 case].
On May 26, 1971, J. Edgar Hoover met with then President Richard Nixon who told Hoover that he wanted to make sure that the FBI did not “pull any punches in going all out in gathering information…on the situation in New York.” Hoover informed his subordinates that Nixon’s interest and the FBI’s involvement were to be kept strictly confidential.
“Newkill” was a joint FBI/NYPD operation involving total cooperation and sharing of information. The FBI made all its facilities and resources, including its laboratory, available to the NYPD. In turn, NYPD Chief of Detectives Albert Seedman, who coordinated the NYPD’s investigation, ordered his subordinates to give the FBI “all available information developed to date, as well as in future investigations.”
On June 5, 1971, Bin Wahad was arrested during a robbery of a Bronx after hours “social club”, a hangout for local drug merchants. Seized from inside the social club was a .45 caliber machine gun. Although the initial ballistics test on the weapon failed to link it with the Curry-Binetti shooting, the NYPD publicly declared they had seized the weapon used in May 19. The NYPD now had in custody a well-known and vocal Black Panther leader and the alleged weapon linked to a police shooting. His prosecution and conviction would both neutralize an effective leader and justify the failed Panther 21 case. But there was no direct evidence linking Bin Wahad to the shooting.
Pauline Joseph, a diagnosed paranoid schizophrenic, became the prosecution?s star witness. Ms. Joseph first surfaced when she made a phone call to the NYPD on June 12, 1971, supplying her name and address and stating that Bin Wahad and Edward Joseph (a Panther 21 defendant who jumped bail with Bin Wahad) were innocent of the Curry-Binetti shooting. She told the police that Bin Wahad “did not do it, either the Riverside Drive [Curry-Binetti] shooting or the 32nd precinct [Piagentini-Jones] shooting…”
The first person to arrive at Ms. Joseph?s apartment was NYPD Lieutenant Kenneth Sauer, the head of the 24th precinct detective squad. Contrary to her testimony at trial, Ms. Joseph continued to maintain that Bin Wahad was innocent of the Curry-Binetti shooting. Later that day she was interviewed by BSS Detective Edwin Cooper. Joseph repeated that Bin Wahad was innocent.
Ms. Joseph was arrested, and committed as a material witness. For nearly two years she remained in the exclusive custody of the New York County District Attorney?s Office. She was repeatedly interviewed by state and federal authorities.
Ms. Joseph, while in the custody of the District Attorney, was recruited as a “racial informant” for the FBI. She was paid for her services and housed first in a hotel and then in a furnished apartment, paid for by the District Attorney. Pauline Joseph, a diagnosed paranoid schizophrenic, became the prosecution?s star witness in the case.
Dhoruba Bin Wahad was indicted for the attempted murder of Officers Curry and Binetti on July 30, 1971. Although the NYPD and FBI continuously interviewed Ms. Joseph, and prepared written memoranda of those interviews, the Assistant District Attorney represented that, except for a one paragraph statement made on the night of her commitment and her grand jury testimony, there were no prior statements. The text of Ms. Joseph?s initial phone call was withheld by the prosecution through two trials. No notes of memoranda of the initial, exculpatory interviews by Lieutenant Sauer and Detective Cooper were ever provided to Bin Wahad. Neither were reports of subsequent interiews during the two years she was in custody. After three trials, Dhoruba Bin Wahad was convicted of attempted murder and sentenced by Justice Martinisto to the maximum penalty, 25 years to life.
In December 1975, after learning of Congressional hearings which disclosed the FBI’s covert operations against the BPP, Dhoruba Bin Wahad filed a lawsuit in Federal District Court, charging that he had been the victim of numerous illegal and unconstitutional actions designed to “neutralize” him, including the frame-up in the Curry-Binetti case.
In 1980, the FBI and NYPD were ordered by the Court to produce their massive files on Mr. Bin Wahad and the BPP, that they had claimed did not exist. The FBI and NYPD documents revealed that Mr. Bin Wahad was indeed a target of FBI/NYPD covert operations and, for the first time, depicted the FBI’s intimate involvement in the Curry-Binetti investigation. The “Newkill” file, which was finally produced in unredacted form in 1987, after 12 years of litigation, contains numerous reports which should have been provided to Dhoruba Bin Wahad during his trial.
In a decision announced December 20, 1992, Justice Bruce Allen of the New York State Supreme Court ordered a new trial. The court exhaustively analyzed the prosecution?s circumstantial case, particularly the testimony of Pauline Joseph. The court found that the inconsistencies and omissions in the prior statements contradicted testimony “crucial to establishing the People?s theory of the case”. The inconsistencies, said the Court “went beyond mere details” and involve “what one would expect to have been the most memorable aspects of [the night of the shooting]”. On January 19, 1995, the District Attorney moved to dismiss the indictment, acknowledging that they could not prove their case. The indictment was dismissed. After more than 20 years in prison, Mr. Bin Wahad is at liberty today, residing in Accra, Ghana.
The COINTELPRO off-shoot “Newkill” and later “Chesrob” (an FBI acronym named after Assata Shakur, aka Joanne Chesimard) had other targets as well. Members of the Black Panther Party forced underground by Cointelpro-instigated violence were hunted down by local and federal law enforcement officials. In the three years after the 1971 BPP split, BPP members, Harold Russsel, Woody Green, Twyman Meyers and Zayd Shakur were killed during confrontations with law enforcement. Others were captured and charged with crimes. All were tried at a time when the public (and juries) knew nothing of COINTELPRO. During these trials, as in the trials of Dhoruba Bin Wahad and Geronimo Pratt, exculpatory evidence was withheld and other violations of the United States Constitution were committed. However, post-conviction motions on behalf of these former BPP members were unsuccessful and they remain in prison today. They include Anthony Jalil Bottom, Herman Bell, Robert Seth Hayes, Sundiata Acoli, Abdul Majid and Bashir Hameed. Two of these former BPP members died while in prison: Albert Nuh Washington in 2000 and Teddy Jah Heath in 2001. Both spent over 25 years in prison but were denied compassionate release even in their last days.
Marshall Eddie Conway
In 1970, Marshall Eddie Conway was Minister of Defense of the Baltimore chapter of the Black Panther Party. He was also employed by the United States Postal Service. Unbeknownst to Conway, some of the founding members of the Baltimore chapter were undercover officers with the Baltimore Police Department, who reported daily on his activities in the chapter. At the same time, the Federal Bureau of Investigation began its own investigation of Conway, recording his whereabouts, contacting his employers at the Post Office and maintaining “liaison” with the Baltimore Police Department.
On April 23, 1970, a Baltimore Police officer was shot and killed. Later that night, another officer named Nolan was fired upon by an unapprehended Black male. Two men arrested at the scene of the first shooting were allegedly associates of members of the Baltimore BPP chapter. Because of this, the police attributed both incidents to the BPP. Not surprisingly, Nolan then claimed that a picture of Conway, a well-known BPP member, resembled the unapprehended shooter. The next day, Conway was arrested while working at the Post office. He was charged with both the homicide and the attempted homicide of Nolan. Conway was held without bail.
Conway petitioned the court to have either Charles Garry or William Kunstler, two attorneys who consistently represented party members, represent him at his trial. Although both offered their services free of charge, the court denied Conway?s request. Instead, a lawyer was appointed who performed no pre-trial investigation and never met with Conway. Deprived of his rights, Conway chose to absent himself from much of his January, 1971 trial.
But the state’s case, relying solely upon Nolan?s equivocal and highly suspect photo identification, was shaky. To buttress their case, the state called one Charles Reynolds, a known jailhouse informant. He ultimately testified that while he shared a cell with Conway pre-trial, Conway made admissions to him. In fact, as was verified by the court transcript, Conway loudly objected when Reynolds was placed in his cell because everyone knew he was an informant. Reynolds, who was a fugitive from Michigan, was promised release if he testified. When the trial was over, he got his wish.
Represented by inadequate counsel and tried at a time when the existence of COINTELPRO was not known, Conway was convicted and sentenced to life imprisonment. All appeals have been denied and he has been denied parole, as are all “lifers” in the State if Maryland. He has now been incarcerated for over 31 years and is probably the longest held political prisoner in the United States, if not the world.
Justice Hangs in the Balance
Although COINTELPRO was first exposed during the Watergate period, and incomparably more serious than anything charged against Nixon, it was virtually ignored by the national press and journals of opinion. A review of these programs demonstrates the relative insignificance of the charges raised against Nixon and his associates, specifically, the charges presented in the Congressional Articles of Impeachment. 124
In the early 1970s, there occurred a seemingly endless series of revelations about governmental transgressions. A “credibility gap” was engendered by the federal executive branch having been caught lying too many times, too red-handedly and over too many years in its efforts to dupe the public into supporting the U.S. war in Southeast Asia. This had reached epic proportions when Daniel Ellsberg leaked the “Pentagon Papers,” a highly secret government documentary history of official duplicity by which America had become embroiled in Indochina, and caused particularly sensitive excerpts to be published in the New York Times. 125
Then on March 8, 1971, a group calling itself the Citizen’s Commission to Investigate the FBI, broke into an FBI office in a small town called Media, Pennsylvania. They subjected the FBI to what the FBI has been habitually subjecting political dissidents to throughout the course of its history. That is, in Bureau parlance, a black bag job. The information they obtained was widely distributed through left and peace movement channels, and summarized the following week in the Washington Post. 126
An analysis of the documents in this FBI office revealed that 1 percent were devoted to organized crime, mostly gambling; 30 percent were “manuals, routine forms, and similar procedural matter”; 40 percent were devoted to political surveillance and the like, including two cases involving right-wing groups, ten concerning immigrants, and over 200 on left or liberal groups. Another 14 percent of the documents concerned draft resistance and “leaving the military without government permission.” The remainder – only 15% – concerned bank robberies, murder, rape, and interstate theft. 127
“Among the 34 cases [of infiltration] for which some information is available, 11 involved white campus groups, 11, predominantly white peace groups and/or economic groups; 10, black and Chicano groups; and two right-wing groups.” Furthermore, “in two-thirds of the 34 cases considered here, the specious activists appear to have gone beyond passive information gathering to active provocation.” 128
One year later, the political scandal known as Watergate began to unravel, when five men were arrested for breaking into the headquarters of the Democratic National Committee, located in the Watergate apartment and office complex in Washington, D.C. It was soon discovered that one of the men was employed by the Committee to Re-elect the President (CRP or CREEP) and that the break-in had been planned by two others with close ties to the White House.
In this peculiar and potentially volatile set of circumstances, a government-wide effort was undertaken to convince the public that its institutions were fundamentally sound, albeit in need of fine-tuning and a bit of housecleaning. It was immediately announced that U.S. ground forces would be withdrawn from Vietnam as rapidly as possible. Televised congressional hearings were staged to “get to the bottom of Watergate,” a spectacle which soon led to the resignations of a number of Nixon officials, the brief imprisonment of a few of them, and the eventual resignation of the president himself.
The ousting of Richard Nixon for his misdeeds on August 9, 1974 was described in the nation’s press as “a stunning vindication of our constitutional system.” 129 Yet the Watergate affair — allegedly the media’s finest hour — merely demonstrated their continued subservience to power and official ideology. Until the dust had settled over Watergate, there was virtually no mention of the government programs of violence and disruption or comment concerning them, and even after the Watergate affair was successfully concluded, there has been only occasional discussion.
Beginning in 1974, the Senate held hearings to investigate COINTELPRO and other intelligence agency abuses. No other congressional investigation into these types of matters has been so extensive, either before or since.
The Senate Select Committee to Study Governmental Operations with Respect to Intelligence Activities, commonly known as the Church committee, after Chairman Frank Church, produced a extensive series of reports entitled, “Intelligence Activities and the Rights of Americans,” encompassing not only COINTELPRO, but also a wide variety of other subjects, including electronic surveillance by the National Security Agency, domestic CIA mail opening programs, the misuse of the IRS, the assassination of President Kennedy, covert actions abroad, assassination plots involving foreign leaders, and various topics related to military intelligence.
The Church committee found that COINTELPRO, presumably set up to protect national security and prevent violence, actually engaged in other actions “which had no conceivable rational relationship to either national security or violent activity. The unexpressed major premise of much of COINTELPRO is that the Bureau has a role in maintaining the existing social order, and that its efforts should be aimed toward combating those who threaten that order.”
This meant that the Bureau would take actions against individuals and organizations simply because they were critical of government policy. The Church committee report gives examples of such actions, violations of the right of free speech and association, where the FBI targeted people because they opposed U.S. foreign policy, or criticized the Chicago police actions at the 1968 Democratic National Convention. The documents assembled by the Church committee “compel the conclusion that Federal law enforcement officers looked upon themselves as guardians of the status quo” and cite the surveillance and harassment of Martin Luther King Jr. as an example of this.
With regard to COINTELPRO, the Church committee’s report was based, it says, on a staff study of more than 20,000 pages of Bureau documents, and included depositions of many of the Bureau agents involved in the programs. The FBI eventually acknowledged having conducted 2,218 separate COINTELPRO actions from mid-1956 through mid-1974. These, the bureau conceded, were undertaken in conjunction with other significant illegalities: 2,305 warrantless telephone taps, 697 buggings, and the opening of 57,846 pieces of mail. 130 This itemization, although an indicator of the magnitude and extent of FBI criminality, was far from complete. The counterintelligence campaign against the Puerto Rican independence movement was not mentioned at all, while whole categories of operational techniques – assassinations, for example, and obtaining false convictions against key activists – were not divulged with respect to the rest. There is solid evidence that other sorts of illegality were downplayed as well.
The FBI’s quid pro quo for cooperating in this charade seems to have been that none of its agents would actually see the inside of a prison as a result of the “excesses” thereby revealed. 131 The result was that
“The Justice Department has decided not to prosecute anyone in connection with the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s 15-year campaign to disrupt the activities of suspected subversive organizations.” 132
J. Stanley Pottinger, head of the Civil Rights Division, reported to the attorney general that he had found “no basis for criminal charges against any particular individuals involving particular incidents.” The director of the FBI also made clear that he saw nothing particularly serious in the revelations of the Church and Pike Committees. There is as yet no public record or evidence of any systematic investigation of these practices. The press paid little heed to the record that was being exposed during the Watergate period and even since has generally ignored the more serious cases and failed to present anything remotely resembling an accurate picture of the full record and what it implies.
The object of all this muscle-flexing was, of course, to create a perception that congress had finally gotten tough, placing itself in a position to administer appropriate oversight of the FBI. It followed that citizens had no further reason to worry over what the Bureau was doing at that very moment, or what it might do in the future.
In 1975 the Senate Select Committee concluded that in order to complete its (re)building of the required public impression, it might be necessary to risk going beyond exploration of the Bureau’s past counterintelligence practices and explore ongoing (i.e.: ostensibly post-COINTELPRO) FBI conduct vis a vis political activists. Specifically at issue in this connection was what was even then being done to the American Indian Movement, and hearings were scheduled to begin in July. But this is where the Bureau, which had been reluctantly going along up to that point, drew the line. The hearings never happened. Instead, they were “indefinitely postponed” in late June of 1975, at the direct request of the FBI. 133
The Church committee cites the testimony of FBI director Clarence M. Kelley as indication that even after the official end of COINTELPRO, “faced with sufficient threat, covert disruption is justified.” 134
The Legacy of COINTELPRO
The repression of dissident groups can be traced far back into US history, at least to the passage of the Alien and Sedition Acts, by which “the Federalists sought to suppress political opposition and to stamp out lingering sympathy for the principles of the French Revolution,” or to the judicial murder of four anarchists for “having advocated doctrines” which allegedly lay behind the explosion of a bomb in Chicago’s Haymarket Square after a striker had been killed by police in May 1886. 135 The Pinkerton Detective Agency, a private investigating agency of the ninteenth century, made extensive use of informants, strike-breakers and provocateurs.
During the first World War, when the long-time, powerful head of the FBI, J. Edgar Hoover led the Bureau of Investigation, there was a “mass deprivation of rights incident to the deserter and selective service violator raids in New York and New Jersey in 1918…” 136 What happened is that 35 Bureau Agents assisted by police and military personnel and a “citizens auxiliary” of the Bureau, “rounded up some 50,000 men without warrants of sufficient probable cause for arrest.”
In 1920 the Bureau, along with Immigration Bureau agents, carried on the “Palmer Raids” (authorized by Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer), which, in 33 cities rounded up 10,000 persons. The Church Committee report 137 talks of “the abuses of due process of law incident to the raids,” quoting a scholarly study 138 that these raids involved “indiscriminate arrests of the innocent with the guilty, unlawful seizures by federal detectives…” and other violations of constitutional rights.
The Church Committee cites a report of distinguished legal scholars 139 made after the Palmer Raids, and says the scholars “found federal agents guilty of using third-degree tortures, making illegal searches and arrests, using agents provocateurs….”
Attorney General Palmer justified his actions “to clean up the country almost unaided by any virile legislation” on grounds of the failure of Congress “to stamp out these seditious societies in their open defiance of law by various forms of propaganda”:
Upon these two basic certainties, first that the “Reds” were criminal aliens, and secondly that the American Government must prevent crime, it was decided that there could be no nice distinctions drawn between the theoretical ideals of the radicals and their actual violations of our national laws. Palmer’s “information showed that communism in this country was an organization of thousands of aliens, who were direct allies of Trotzky.” Thus “the Government is now sweeping the nation clean of such alien filth,” with the overwhelming support of the press, until they perceived that their own interests were threatened. 140
Elsewhere he described the prisoners as follows:
Out of the sly and crafty eyes of many of them leap cupidity, cruelty, insanity, and crime; from their lopsided faces, sloping brows, and misshapen features may be recognized the unmistakable criminal type.
Palmer’s declared purpose was “to tear out the radical seeds that have entangled American ideas in their poisonous theories.” 141
One early FBI target was Marcus Garvey, founder of the Universal Negro Improvement Association. Under his leadership, UNIA, which to this day remains the largest organization of African Americans ever assembled, devoted itself mainly to the realization of various “bootstrapping” strategies (i.e., undertaking business ventures as a means of attaining its twin goals of black pride and self-sufficiency).
Nonetheless, despite UNIAs explicitly capitalist orientation, or maybe because of it, Hoover launched an inquiry into Garvey’s activities in August 1919. When this initial probe revealed no illegalities, Hoover, railing against Garvey’s “pro-Negroism,” ordered that the investigation be not only continued but intensified. UNIA was quickly infiltrated by operatives recruited specifically for the purpose, and a number of informants developed within it. Still, it was another two years before the General Intelligence Division was able to find a pretext – Garvey’s technical violation of the laws governing offerings of corporate stock – upon which to bring charges of “mail fraud.” Convicted in July 1923 by an all-white jury, the UNIA leader was first incarcerated in the federal prison at Atlanta, then deported as an undesirable alien in 1927. By then, the organization he’d founded had disintegrated. Hoover, in the interim, had vowed to prevent anyone from ever again assuming the standing of what he called a “Negro Moses.”
World War II brought a return of the FBI to counterintelligence operations as President Franklin D. Roosevelt issued a series of instructions establishing the basic domestic intelligence structure for the federal government. Roosevelt was advised by Hoover to proceed with the utmost degree of secrecy:
In considering the steps to be taken for the expansion of the present structure of intelligence work, it is believed imperative that it proceed with the utmost degree of secrecy in order to avoid criticism or objections which might be raised to such an expansion by either ill-informed persons or individuals having some ulterior motive … Consequently, it would seem undesirable to seek any special legislation which would draw attention to the fact that it was proposed to develop a special counterespionage drive of any great magnitude. 142
According to William C. Sullivan, Hoover’s assistant for many years:
Such a very great man as Franklin D. Roosevelt saw nothing wrong in asking the FBI to investigate those opposing his lend-lease policy — a purely political request. He also had us look into the activities of others who opposed our entrance into World War II, just as later Administrations had the FBI look into those opposing the conflict in Vietnam. It was a political request also when he [Roosevelt] instructed us to put a telephone tap, a microphone, and a physical surveillance on an internationally known leader in his Administration. It was done. The results he wanted were secured and given to him. Certain records of this kind … were not then or later put into the regular FBI filing system. Rather, they were deliberately kept out of it. 143
The passage in 1940 of the Smith Act, made “sedition” a peacetime as well as a wartime offense. The doctrine was laid out clearly by Supreme Court Justice Robert H. Jackson in his opinion upholding of the Smith Act on the grounds “that it was no violation of free speech to convict Communists for conspiring to teach or advocate the forcible overthrow of the government, even if no clear and present danger could be proved.” For if the clear and present danger test were applied, Jackson argued, “it means that Communist plotting is protected during its period of incubation; its preliminary stages of organization and preparation are immune from the law, the Government can move only after imminent action is manifest, when it would, of course, be too late.” Thus there must be “some legal formula that will secure an existing order against revolutionary radicalism…. There is no constitutional right to `gang up’ on the Government.” Opposition tendencies, however minuscule, must be nipped in the bud prior to “imminent action.”
Hoover claimed that in 1940, “advocates of foreign isms” had succeeded in boring into every phase of American life, masquerading behind front organizations. 144 In 1939, Hoover told the House Appropriations Committee that his General Intelligence Division had compiled extensive indices of individuals, groups, and organizations engaged in subversive activities, in espionage activities, or any activities that are possibly detrimental to the internal security of the United States.. . . Their backgrounds and activities are known to the Bureau. These indexes will be extremely important and valuable in a grave emergency. 145
After World War II, the FBI’s attention turned from fascism to communism. This was the beginning of the Cold War. In March of 1946, Hoover informed Attorney General Tom Clark that the FBI had found it necessary to intensify its investigation of Communist party activities and Soviet espionage cases and it was taking steps to list all members of the Communist party and any others who might be dangerous in the event of a break with the Soviet Union, or other serious crisis involving the United States and the USSR.. . . It might be necessary in a crisis to immediately detain a large number of American citizens. 146
As for the Communist party, “ordinary conspiracy principles” sufficed to charge any individual associated with it “with responsibility for and participation in all that makes up the Party’s program” and “even an individual,” acting alone and apart from any “conspiracy,” “cannot claim that the Constitution protects him in advocating or teaching overthrow of government by force or violence.” 147
In 1948, the Mundt-Nixon bill, calling for the registration of the Communist party, was reported out of Nixon’s House Committee on Un-American Activities. Senate liberals objected, and after a Truman veto they proposed as a substitute “the ultimate weapon of repression: concentration camps to intern potential troublemakers on the occasion of some loosely defined future ‘Internal Security Emergency’,” 148 including, as one case, “insurrection within the United States in aid of a foreign enemy.” 149
This substitute was advocated by Benton, Douglas, Graham, Kefauver, Kilgore, Lehman, and Humphrey, then a freshman senator. Humphrey later voted against the bill, though he did not retreat from his concentration camp proposal. In fact, he was concerned that the conference committee had brought back “a weaker bill, not a bill to strike stronger blows at the Communist menace, but weaker blows.” The problem with the new bill was that those interned in the detention centers would have “the right of habeas corpus so they can be released and go on to do their dirty business.” 150
In 1949 the attorney general’s list was established, excluding members of “communist front organizations” from federal employment, since their influence on government policies would be such that those policies will either favor the foreign country of their ideological choice or will weaken the United States government domestically or abroad to the ultimate advantage of the … foreign power. Consequently, [Mr. Hoover] urged that attention be given to the association of government employees with front organizations. These included not only established fronts but also temporary organizations, spontaneous campaigns, and pressure movements so frequently used by subversive groups. If a disloyal employee was affiliated with such fronts, he could be expected to influence government policy in the direction taken by the group. 151
The first formal COINTELPRO, aimed at the U.S. Communist Party, commenced on August 28, 1956. Although this was the first instance in which the Internal Security Branch was instructed to employ the full range of extralegal techniques developed by the bureau’s counterintelligence specialists against a domestic target in a centrally coordinated and programmatic way, the FBI had conducted such operations against the CP and to a lesser extent the Socialist Workers Party (SWP) on an ad hoc basis at least as early as 1941.
Instructively, Hoover began at the same time to include a section on “Negro Organizations” in reports otherwise dedicated to “Communist Organizations” and “Axis Fifth Columnists.” In 1954 there was also the Communist Control Act, a statute outlawing the CP and prohibiting its members from holding certain types of employment.
Viewed against this backdrop, it is commonly believed that, however misguided, COINTELPRO-CPUSA was in some ways well intended, undertaken out of a genuine concern that the CP was engaged in spying for the Soviet Union. Declassified FBI documents, however, reveal quite the opposite. While espionage and sabotage “potentials” are mentioned almost as afterthoughts in the predicating memoranda, unabashedly political motives take center stage. The objective of the COINTELPRO was, as Internal Security Branch chief Alan Belmont put it at the time, to block the CP’s “penetration of specific channels of American life where public opinion is molded” and to prevent thereby its attaining “influence over the masses.”
From the outset, considerable emphasis was placed on intensifying the bureau’s long-standing campaign to promote factional disputes within the Party. To this end, the CP was infiltrated more heavily than ever before. It has been estimated that by 1965 approximately one-third of the CP’s nominal membership consisted of FBI infiltrators and paid informants, while bona fide activists were systematically snitch jacketed. A formal “Mass Media Program” was also created, “wherein derogatory information on prominent radicals was leaked to the news media.”
The programs directed against the Communist party continued through the 1960s, with such interesting innovations as Operation Hoodwink from 1966 through mid-1968, designed to incite organized crime against the Communist party through documents fabricated by the FBI, evidently in the hope that criminal elements would carry on the work of repression and disruption in their own manner. 152
In October 1961, the “SWP Disruption Program” was put into operation against the Socialist Workers Party. The grounds offered, in a secret FBI memorandum, were the following: the party had been “openly espousing its line on a local and national basis through running candidates for public office and strongly directing and/or supporting such causes as Castro’s Cuba and integration problems…in the South.” The SWP Disruption Program, put into operation during the Kennedy administration, reveals very clearly the FBI’s understanding of its function: to block legal political activity that departs from orthodoxy, to disrupt opposition to state policy, to undermine the civil rights movement.
CISPES
The FBI has continued to violate the constitutional rights of citizens through the 1980’s, up to 1990, as revealed by Ross Gelbspan in his book Break-Ins, Death Threats And The FBI. Utilizing thousands of pages of FBI documents secured through the Freedom of Information Act, Gelbspan found that activists who opposed U.S. policy in Central America “experienced nearly 200 incidents of harassment and intimidation, many involving…break-ins and thefts or rifling of files.” Gelbspan?s intent was to “add a small document to the depressingly persistent history of the FBI as a national political police force.”
During the 1980’s as the FBI waged an “active measures” campaign against the Committee In Solidarity with the People of El Salvador (CISPES), a former FBI informant, Frank Varelli, became disillusioned with the Bureau’s attempt to destroy CISPES. Acting on disinformation supplied by the murderous Salvadoran National Guard, false information was forwarded by the FBI to the Defense Intelligence Agency.
The National Guard claimed that one FMLN coalition member, the Armed Revolutionary Group (GAR), “were to promote in North America a strong and violent campaign of agitation and propaganda on behalf of FMLN-FDR, having obtained immediate support from different sectors of North American society. Among the groups providing support were labor unions, Gay Power groups, Pro- Abortion groups, groups involved in the women’s liberation movement, and organizations that are opposed to the strengthening of the military forces of the US.” 153
Although not a shred of evidence existed linking these North American organizations to the GAR, the groups were included in the National Guard communique — at the direct request of the FBI.
According to Varelli, “Can you imagine if gay rights groups, abortion rights groups, the Equal Rights Amendment groups were known to support a group that had killed more than 20 police and soldiers in a year?” The informant added, “Once the FBI had this data in their files, they could proceed to investigate all these other groups. What is even worse, the FBI knew that this material from the National Guard was strictly disinformation. But they passed the same material along to the Secret Service, the Defense Intelligence Agency and other agencies in the intelligence community without alerting them to the fact that it was completely fabricated.” 154
The FBI found it “imperative to formulate some plan of attack against CISPES,” not because of its suspected involvement in terrorism or any other criminal activity, but because of its association with “individuals [deleted] who defiantly display their contempt for the U.S. government by making speeches and propagandizing their cause.” In plain English, CISPES was politically objectionable to the Bureau – no more, or less – and was therefore deliberately targeted for repression. 155
The investigation was ultimately expanded to include not only CISPES itself, but nearly 2000 organizations and individuals with which CISPES had some sort of interactive relations. This included pastors of local churches who were sympathetic to the Salvadorean peasantry, and Duke University, which provided meeting space.
The Bureau admits it paid Varelli from 1981 to 1984 to infiltrate CISPES. Varelli has testified that the FBI’s stated objective was to “break” CISPES. He recounts a modus operandi straight out of the annals COINTELPRO – from break-ins, bogus publications and disruption of public events to planting guns on CISPES members and seducing CISPES leaders in order to get blackmail photos for the FBI. 156
Alerted by Varelli’s disclosures, the Center for Constitutional Rights obtained a small portion of the Bureau’s CISPES files and released them to the press. The files show the U.S. government targeting a very broad range of religious, labor and community groups opposed to its Central America policies. They confirm that the FBI’s objective was to attack and “neutralize” these groups. 157 Mainstream media coverage of these revelations elicited a flurry of congressional investigations and hearings. Publicly exposed, the FBI tried to scapegoat the whistle blower. Its in-house investigation found Varelli “unreliable” and held that his reports of CISPES terrorism were false. The Bureau denied any violation of the constitutional rights of U.S. citizens or involvement in the hundreds of break-ins reported by Central America activists. A grand total of six agents received “formal censure” and three were suspended for 14 days. FBI Director William Sessions declared the case closed, a mere “aberration” due to “failure in FBI management.” 158
The Judi Bari Bombing
There is no better example than the Judi Bari “boom and bust” case to show that the FBI kept on well into the 1990s using covert action tactics against political movements and activists which they perceived as threats to the established order. One can make a case that the FBI is still using such tactics in the Bari case in 2001.
The car bombing of Judi Bari and Darryl Cherney on May 24, 1990 made headlines across the nation. At the FBI’s instigation, Oakland California police immediately arrested the two nonviolent environmental leaders and told the media that they were terrorists blown up by their own bomb. For the next two months, the FBI and police held a series of press conferences where they dribbled out false evidence of the pair’s guilt to feed a drumbeat of sensational media coverage.
But there was clear evidence that Bari was targeted because of her leftist environmental and labor organizing. Someone wanted to stop the two Northern California Earth First! leaders, the organizers of Redwood Summer, the largest ever campaign of nonviolent protests against corporate liquidation logging of the redwoods.
After two months, the Alameda County District Attorney declined to file any charges, citing lack of evidence against the pair. There is evidence, though, from the FBI’s own files, that agents falsified evidence, suppressed exonerating evidence, and conspired with Oakland police to frame the two bombing victims. Moreover, the records show that the FBI stubbornly refused to do a genuine investigation of the bombing, and failed to pursue real evidence and leads turned over to them, such as fingerprints or death threats Bari received.
Bari, the mother of two young daughters, was nearly killed when the powerful motion-triggered pipe bomb wrapped with nails for shrapnel effect blew up directly under her driver’s seat. The bomb caused horrifying maiming and crippling injuries, leaving her with a paralyzed right foot and unending pain for the rest of her life.
Bari and Cherney were on an organizing tour for their campaign, which at first they called Mississippi Summer in the Redwoods in homage to the civil rights movement that inspired it. The idea was to have mass nonviolent civil disobedience to delay the cutting of redwoods long enough to let voters decide the issue in November 1990, when two statewide timber reform initiatives would be on the ballot. The call went out to college students across America: Come to Northern California and save the redwoods.
In the June 10, 1990 San Francisco Examiner, writer Jane Kay raised the issue of law enforcement interest:
“Environmental activism is the new target of political suspicion and surveillance, and law enforcement agencies are stepping up action against those who demand radical change. Calling them agitators, outsiders, the mafia and extremists, local, state and federal investigators and prosecutors say they suspect them of violent acts — or the potential for them. They have responded in the last year with arrests, searches, seizures and questioning.”
FBI files contained evidence of Bari and Cherney’s innocence, but not until three years after the bombing did the FBI begin (grudgingly) to disclose that evidence, and then only under court order and Congressional pressure. A year after the bombing, with no progress in the official investigation, and with the FBI still telling the media that there were no other suspects but Bari and Cherney, the pair filed a federal civil rights suit against the FBI and Oakland Police, charging them with conspiring “to suppress, chill and ‘neutralize’ their constitutionally protected activities in defense of the environment.”
Now Bari and Cherney could investigate the bombing themselves, using civil discovery and subpoena power to compel the FBI and police to turn over files and evidence and to submit to questioning under oath. Ten years later, their charges are supported by over 20,000 pages of evidence, including FBI files and the testimony of over 70 FBI agents and police officers. The evidence of police misconduct is strong enough that the suit has survived repeated motions by the FBI and Oakland to dismiss it.
Bari and Cherney discovered that police crime scene photos clearly showed that the bomb ripped a two foot by four foot hole in the floorboard centered directly under the driver’s seat. FBI files revealed that a top explosives expert, agent David R. Williams, inspected the bombed car three weeks after the explosion and showed the local agents that the bomb had been completely hidden under the driver’s seat. He told them the bomb was detonated by a motion trigger, and had functioned as designed rather than exploding accidentally.
That put the lie to FBI statements that the bomb was on the back seat floorboard where they would have seen it — the principal claim used to justify arresting Bari and Cherney for possession and transportation of an explosive device. Knowing full well from their own expert’s testimony that Bari and Cherney were innocent victims, the FBI and Oakland police continued to lie to the media for another five weeks, saying they had plenty of evidence they were the bombers.
Bari’s last work in her life was to oversee a crucial phase of her lawsuit so that her legal team could take the case to trial on behalf of her children, to clear her name, and to secure the rights of all activists to be free from FBI interference with their constitutional rights. Although she died of cancer on March 2, 1997, the suit is continued by Bari’s estate and Cherney.
Bari felt sure as soon as it happened that timber interests were behind the bombing. She told investigating officers in the hospital that she began receiving death threats soon after she had announced plans for Redwood Summer. Police found copies of written threats in her bombed car.
Perhaps the key incident that made her the target of the bomb attack was her demand for government seizure of timber corporation property. Bari appeared in a coalition with Louisiana Pacific workers before an April 3, 1990 meeting of Mendocino County’s Board of Supervisors. LP had closed several sawmills as the trees were used up, leaving many of their workers jobless. Bari demanded that the county use eminent domain powers to seize LP corporate timberlands and turn them over to the workers.
Her property seizure demand and her coalition with disgruntled timber workers certainly focused negative timber industry attention on Bari, and probably the FBI’s too. A local paper published a large front page photo of Bari from the board meeting. A copy of that photo with the circle and cross hairs of a rifle scope drawn over her face was the most frightening death threat Bari received, she said. The photo was smeared with excrement and stapled to the door of the Mendocino Environmental Center along with a yellow ribbon, the symbol of timber industry support groups opposed to Redwood Summer and Proposition 130, the “Forests Forever” initiative on the November ballot.
If the “Forests Forever” initiative, Prop. 130, had passed in the fall 1990 election, the three big logging corporations of the redwood region — Georgia Pacific, Louisiana Pacific and Pacific Lumber — would have lost billions of dollars. It would have put an end to unsustainable liquidation logging and clearcutting, and ended industry control over the board that wrote timber regulations.
With an enormous financial motive to defeat the initiative, the corporations hired the giant public relations firm Hill & Knowlton to manage a PR campaign to turn public opinion against the initiative. An important part of the campaign was to derail Redwood Summer. It was drawing media attention to the overlogging, which would work in favor of Prop.130.
There were many signs of an orchestrated COINTELPRO-like campaign of harassment and intimidation against Bari and other environmentalists in the weeks before the bombing. Someone cooked up counterfeit EF! flyers and press releases calling for violence and sabotage during Redwood Summer, and Pacific Lumber and Louisiana Pacific knowingly distributed the fakes to workers, community members and media in a move calculated to deceive people about EF!’s nonviolent intentions and create an atmosphere of hatred and violence toward environmentalists.
As the FBI and police smeared Bari, Cherney and Earth First! as terrorists after the bombing, the PR company quickly put out propaganda falsely labeling Prop. 130 “the Earth First! initiative,” and calling it “too extreme.” By some reports, they spent up to $20 million by the time voters defeated the initiative by a narrow margin.
FBI records obtained through the Freedom of Information Act show that the FBI infiltrated and spied on Earth First! almost from its beginning in 1980, with the earliest known FBI report on it dated 1981. Heavily censored FBI documents obtained through Bari’s suit indicate weekly meetings in spring 1990 between an FBI agent and a secret informant in Northern California. Deposition testimony by Oakland Police Department officers and FBI agents states the FBI had an informant on EF! leaders, and the FBI told OPD that Cherney and Bari were already “the subjects of an investigation in the terrorist field” when they were bombed. They could have been under surveillance when the bomb was placed.
Just before the Bari bombing, the FBI was wrapping up “Operation Thermcon” in Arizona, a 3-year covert operation employing over 50 FBI agents designed to entrap and discredit EF! and its co-founder Dave Foreman as explosive-using terrorists. The FBI infiltrated a tiny Arizona EF! group with an undercover agent provocateur, won their trust over a couple of years, and tried to persuade them to use thermite, an explosive incendiary, to take down a power line. The activists refused the FBI infiltrator’s offer to provide explosives, and he settled for providing them with a cutting torch instead. The FBI provocateur provided the equipment, trained the activists in its use, chose the target, drove them to the site, and joined an FBI strike team in busting them in the act on May 31, 1989, almost a year to the day before the Bari bombing. Foreman was not directly involved, but was charged with conspiracy for providing $100 to the group. The resulting “Arizona Five” trial ended in plea bargains in August, 1991, with prison sentences for two of the activists, and with probation and fines for the others, including Foreman. Note that the Bari bombing came midway between the arrest and the trial in the Thermcon case.
Thermcon was the FBI’s code name meaning “thermite conspiracy,” but there was no thermite involved except in the FBI scheme to tie EF! to explosives despite the fact they have never advocated or used explosives in their entire history. The FBI had a public relations goal in Thermcon, to deceive the public into believing EF! were violent extremists so as to neutralize their effectiveness and isolate them from public support. It was a classic COINTELPRO against Earth First!
The true goal of Thermcon was revealed when Michael Fain, the FBI’s undercover agent provocateur in the case, accidentally left his body wire running and recorded his conversation with other agents. On the tape, Fain is heard to say, “I don’t really look for them to be doing a lot of hurting people. (Foreman) isn’t really the guy we need to pop — I mean in terms of an actual perpetrator. This is the guy we need to pop to send a message. And that’s all we’re really doing. . . . Uh-oh! We don’t need that on tape! Hoo boy!” The FBI’s true goal was to “send a message” to the public that Earth First! was a terrorist group.
Bari and Cherney’s investigation turned up several connections between the timber industry and the FBI, including a chummy “Dear Bill” letter sent to FBI Director William Sessions by a board member of Maxxam, which owns Pacific Lumber.
Louisiana Pacific had an FBI connection that directly involved bombs. One month before the Bari bombing, the FBI conducted a bomb investigator school in Humboldt County. FBI terrorist squad bomb expert Frank Doyle blew up cars with pipe bombs on a Louisiana Pacific logging site, then his students practiced investigating. Louisiana Pacific was the company whose timberlands Bari asked the government to seize, after which she immediately began receiving death threats.
There is the mystery of another bomb at an LP sawmill in Cloverdale, California, about an hour’s drive south of Bari’s home. Two weeks after the FBI bomb school (and two weeks before Bari’s car exploded), a partly-exploded firebomb was found. That bomb, a pipe bomb next to a can of gasoline, failed to fully explode or to ignite the gasoline. A cardboard sign near the firebomb bore the words, “LP screws millworkers,” a message that could be associated with Bari. A cardboard sign next to a firebomb makes no sense, unless it was designed to fail and to leave evidence that could be used to help to frame Bari for the Oakland bomb two weeks later.
The FBI lab found that the Cloverdale and Oakland bombs matched exactly in components and construction method, and were built by the same person(s). This same type of bomb was studied at the FBI bomb school two weeks earlier, according to testimony of an Oakland officer who was there. Investigators found a usable fingerprint on the cardboard sign, but there is no record that the FBI ever tried to match the print to Bari or Cherney, or to anyone else.
Less than an hour after the Oakland explosion, none other than Special Agent Frank Doyle, the bomb school instructor, took charge of the bomb scene investigation. There were at least five of his bomb school students at the scene, and they were overheard on a videotape joking about the scene being the “final exam.” Since he was the FBI’s terrorist squad bomb expert and their instructor the other FBI and Oakland bomb investigators who were at the scene first deferred to his pronouncements about the evidence.
It was Doyle who overruled the Oakland sergeant who got there first and said the bomb was under the driver’s seat and that he could see the pavement under the car through the hole in the seat bottom. It was Doyle who falsely said the bomb was on the floor behind the driver’s seat where it would have been easily seen. It was also Doyle who falsely claimed that two bags of nails found in the back of Bari’s car matched nails taped to the bomb for shrapnel effect, when in fact they were not even the same type, and were clearly different to the naked eye. (Bari worked as a carpenter, and always had tools and nails in the car.)
Other officers on the scene testified that Doyle argued with them, and quoted him saying, “I’ve been looking at bomb scenes for 20 years, and I’m looking at this one, and I’m telling you you can rely on it. This bomb was visible to the people who loaded the back seat of this car.”
Exactly three weeks later, when Supervisory Special Agent David R. Williams — the FBI crime laboratory’s top explosives expert — inspected the bombed car, he pointed out to Doyle that impact marks left by the pipe bomb’s end caps on the transmission tunnel and driver’s door, combined with the location of the hole in the floorboard and the damage to the seat cushion, clearly proved the bomb was under the driver’s seat, not in the back where Doyle had said.
Despite this early clear evidence that Bari was the target of attempted murder, the FBI and Oakland PD continued telling the media and the court that Bari and Cherney were their only suspects, and fabricating other stories about nails from the bomb matching nails found in Bari’s house. Repetition is a fundamental of the “Big Lie” propaganda technique, maintaining a drumbeat of false information until it is accepted by the media and the public as the truth. There can be no doubt that the FBI was knowingly lying about the evidence.
M. Wesley Swearingen, a retired career FBI agent with first-hand inside knowledge of COINTELPRO wrote in his book “FBI Secrets — An Agent’s Expose:
“(COINTELPRO) is still in operation today, but under a different code name. The operation is no longer placed on paper where it can be discovered through the release of documents under the Freedom of Information Act. ? A clear example of the FBI’s continued COINTELPRO is in the FBI’s alleged involvement in the 1990 bombing of the vehicle occupied by Judi Bari and Darryl Cherney … which was an effort to neutralize Judi Bari.”
There could hardly have been a more ideal location than Oakland for an FBI covert operation against Bari. The media coverage of the Oakland bombing was far more extensive, and was far more easily manipulated by the FBI, than if it had happened in Mendocino or Humboldt Counties where Bari lived and spent nearly all of her time. Oakland was the home of the Black Panther Party for Self Defense, which bore the brunt of the most extreme COINTELPRO of all, including multiple assassinations and frame-ups of its leaders. The Oakland Police Department has a long history of cooperating with the Bureau in targeting progressive and radical groups.
In deposition in the Bari case, OPD intelligence division chief Kevin Griswold admitted that his department keeps files on over 300 political groups and individuals in the Bay Area. Griswold said the Oakland Police have spied on EF! since 1984, and had their own informant inside EF! who reported back to Griswold on plans for upcoming demonstrations. This even though EF! is not based in Oakland and was not active there prior to the Bari bombing. Griswold said he shares information from his spies with the FBI. Encouraging and tapping into political spying operations run by local police like Oakland’s was one of the key ways the FBI got around the Attorney General’s guidelines that barred the bureau from purely political spying.
The special agent in charge of the FBI’s San Francisco office at the time of the bombing was Richard W. Held, a 26-year veteran of the FBI’s COINTELPRO “dirty tricks” campaigns against the Black Panthers, American Indian Movement and Puerto Rican independence activists.
Under deposition under oath in the Bari case, Held claimed he was unaware of the details of the Bari-Cherney case, and implied that it was not important enough to merit his attention. But files in the San Francisco FBI office contained a memo from Washington ordering his office to provide weekly reports on the Bari case so that headquarters could respond to the “numerous inquiries” they were getting from the media. Held’s testimony was also contradicted by FBI agents under his command who said in their depositions that they briefed him daily on the case.
The unraveling of the frame-up of Bari and Cherney may have brought an early end to Held’s 25-year FBI career. It is a strong tradition in the FBI not to embarrass the bureau. Held announced his early resignation from the FBI in May of 1993, the day before Bari held a press conference with the newly released Oakland Police crime scene photos exposing the FBI lies about the location of the bomb. Held told reporters he resigned because he expected reassignment to a new post and didn’t want to move his family. His father, Richard G. Held, had risen to the high post of Deputy Director of the FBI, and Held’s career track was headed for the top as well. He told reporters his mother cried when he told her he was resigning, so clearly Held’s FBI career was very important to him and his family, and it seems unlikely he would end it early just to avoid a relocation.
Other cases have come to light where the FBI allegedly used bombs to frame radicals twenty years before the Bari bombing. FBI agent provocateur David Sannes was used to get radicals in Seattle to use bombs so that they could be arrested and discredited. When he learned that the FBI wanted him to set up one bomber to die in a booby-trapped explosion, he refused to go along and went public.
Sannes said in an interview on WBAI radio “My own knowledge is that the FBI along with other Federal law enforcement agencies has been involved in a campaign of bombing, arson and terrorism in order to create in the mass public mind a connection between political dissidence of whatever stripe and revolutionaries of whatever violent tendencies.”
Though the Seattle cases happened in the early 1970s, just before the supposed termination of COINTELPRO, the goal of the FBI’s Operation Thermcon at the time of the Bari bombing 20 years later was to connect well-known Earth First! leaders with the use of explosives in the public mind, the same FBI strategy Sannes exposed in the Seattle cases.
Until the Bari-Cherney suit finally has its day in court, beginning October 1, 2001, many questions will lie unanswered. But it seems more rational than paranoid to believe there was an FBI and corporate timber connection to the bombing. Both timber and the FBI had ample motives, history, means and opportunity to bomb Bari. There are also FBI connections to both Maxxam/Pacific Lumber and Louisiana Pacific — even involving bombs, in LP’s case.
Big Timber’s PR firm may have planned the bombing and arranged the FBI cooperation in the frame-up, but it meshed perfectly with the FBI’s own Operation Thermcon to neutralize Earth First! by trying to connect its best known leaders to explosives, first Dave Foreman, then Judi Bari and Darryl Cherney.
Judi Bari was the redwood timber industry’s most outspoken, brilliant, and effective opponent. The industry would go to any length to defeat Prop. 130, because billions of dollars were at stake. Framing Judi Bari for a bombing would serve that goal. It would be used to demonize Earth First! as violent extremists. Then voters could be turned against the initiative by falsely linking it with Earth First!. And that’s exactly what they did.
The bombing was expertly planned, including the Cloverdale sawmill bomb which the FBI immediately cited as evidence of Bari’s guilt in her own bombing. Both bombs were expertly conceived and built, according to the FBI’s top expert, and the one in Bari’s car functioned as designed. Because of that, Bari believed the bombing was a professional hit.
The bombing happened in the midst of a sophisticated psychological warfare blitz of disinformation, intimidation and death threats, while Bari was organizing the biggest mass demonstrations against corporate overlogging in history, while she was taking on multi-billion dollar corporations and threatening their bottom line, and while she was building a coalition between timber workers and environmentalists by pointing to the corporations as the problem. She had also led Earth First! in her region to disavow tree-spiking and equipment sabotage, and insisted that a strict non-violence code be adhered to during Redwood Summer. The fact that Bari was an outspoken advocate of nonviolence gave all the more sensational impact to framing her as a terrorist bomber.
In depositions the FBI agents involved in the Bari investigation admitted that they never found any evidence whatsoever that she built the bomb that nearly killed her, or any other bomb, But the FBI has never issued any statement of exoneration or any apology. Not only has the FBI not retracted their false charges, they continue to repeat them. Speaking to students at an October 1999 Humboldt State University recruiting event, FBI agent Candice DeLong told the students: “Judi Bari was a terrorist. They were carrying that bomb.” The FBI recently spent $200,000 of the taxpayers’ money paying a U. S. Air Force laboratory to do simulation experiments aimed at showing that the bomb could have been in the back seat of Bari’s car after all.
Regardless who bombed Bari, it is plainly evident that FBI agents made a determined effort to frame her for it. After years of delay by the FBI, Bari’s civil rights suit is set for trial beginning October 1, 2001 in federal court in Oakland.
Footnotes
1 Civil Liberties, no. 273, December 1970; publication of the ACLU.
2 Race, Reform and Rebellion, Marable, pp. 102-3. For more on the Detroit rebellion, see Hersey, John, The Algiers Motel Incident, Alfred A. Knopf Publishers, New York, 1968. Of related interest, see Hayden, Tom, Rebellion in Newark: Official Violence and Ghetto Response, Vintage Books, New York, 1967; and Gilbert, Ben W., et. al., Ten Blocks From the White House: Anatomy of the Washington Riots of 1968, Frederick A. Praeger Publishers, New York, 1968. For an overall appraisal of the motivations underlying the urban rebellions from the perspective of a former CORE field secretary, see Wright, Nathan Jr., Black Power and Urban Unrest: Creative Possibilities, Hawthorn Books, Inc., New York, 1967. In general, see Boesel, David, and Peter H. Rossi (eds.), Cities Under Siege: An Anatomy of the Ghetto Riots, 1964-1968, Basic Books, New York, 1971.
3 Hoover, statement, July 26, 1950 (Harry S. Truman Library, Bontecore Papers), from Ideological Warfare: The FBI’s Path Toward Power, Frank M. Sorrentino, Associated Faculty Press, Inc. 1985.
4 See Memorandum from F.J. Baumgardner to W.C. Sullivan, October 1, 1964; Memorandum from Sullivan to A. Belmont, August 30, 1963; J. Edgar Hoover, chairman, Interdepartmental Intelligence Conference Report to McGeorge Bundy, special assistant to the President, July 25, 1961, enclosing IIC, Status of U.S. Internal Security Programs, July 1, 1960, through June 30, 1961. From Ideological Warfare, op. cit.
5 Special Report of Interagency Committee on Intelligence (Ad Hoc), Chairman J. Edgar Hoover, along with the directors of the CIA, DIA, and NSA, prepared for the President, June 25, 1970, marked “Top Secret.” A censored version was later released. Quotes are from Book 7, Part 1: Summary of Internal Security Threat.
6 C. Gerald Fraser, “F.B.I. Action in 1961 Called Still Harmful to Hopes of Blacks,” New York Times, April 6, 1974. See also Jesse Jackson and Alvin Poussaint. “The Danger Behind FBI Obstruction of Black Movements,” Boston Globe, April 2, 1974.
7
8 Nerve War Against Individuals, forwarded to CIA station in Guatemala City on June 9, 1954 http://www.parascope.com/ds/articles/nervewardoc.htm
9
10 John Kifner, “F.B.I. Gave Chicago Police Plan of Slain Panther’s Apartment,” New York Times, May 25, 1974. Although the act of FBI involvement in the Hampton assassination, along with other details of this major state crime, was not widely publicized outside of Chicago, nevertheless there were a few reports, such as this one. There can be no excuse for the general silence on this matter, which alone overshadows the entire Watergate Affair by a substantial margin.
11 On the significance of the threat, both actual and potential, as perceived at high levels of policy planning, see Noam Chomsky’s review of some of the evidence contained in the “Pentagon Papers” in _For Reasons of State_, chapter 1. For discussion of the impact on the American expeditionary force, see David Cortright, _Soldiers in Revolt_, Doubleday, 1975).
12 January 22, 1969 memo from SAC, Chicago, to Director Hoover, cited in The COINTELPRO Papers, by Ward Churchill and Jim Vander Wall, South End Press.
13 Kelly’s memorandum is reproduced in U.S. Department of Justice, Report of the Justice Department Task Force to Review FBI Martin Luther King, Jr., Security and Assassination Investigations, Washington, D.C., January 11, 1977.
14 Cross is mentioned in a memorandum from Atlanta agent Robert A. Murphy to J. Stanley Pottinger, at FBI headquarters, in July 1958. Interestingly, Murphy suggests the “SWP connection” is not a sufficient basis from which to undertake a COMINFIL investigation. Pottinger apparently did not agree; see Pottinger, J. Stanley, “Martin Luther King Report” (to U.S. Attorney General Edward H. Levi), U.S. Department of Justice, Washington, D.C., April 9,1976.
15 The King file was opened by the New York rather than Atlanta field office. It should be noted that although the Bureau has always maintained that there was no COMINFIL activity directed at King and the SCLC during the 1950s, the code prefixed to the files on both was “100,” indicating they were viewed as “internal security” or “subversive” matters. The numerical file prefix for material accruing from what was considered an investigation of civil rights activities per se would have been “44.”
16 See U.S. Senate, Committee on the Judiciary, FBI Statutory Charter – Appendix to Hearings Before the Subcommittee an Administrative Practice and Procedure, Part 3, 95th Congress, 2d Session, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1979, pp. 33-73.
17 Concerning King see Lee v. Kelly, Civil Action No. 76-1185, U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia, “Memorandum Opinion and Order” (by U.S. District Judge John Lewis Smith, Jr.), January 31, 1977. Certain of the information on both King and Walker was attributed by FBI Associate Director Cartha D. DeLoach to NAACP head Roy Wilkens (see report on the SCLC from Atlanta agent Robert R. Nichols to DeLoach, dated July 1961). Wilkens later vehemently denied any such interaction between himself and the Bureau; see Lardner, George Jr., ‘Wilkens Denies Any Link to FBI Plot to Discredit King,” Washington Post, May 31, 1978.
18 Levison’s CP membership was never established although it was demonstrable that he maintained dose relations with party members from roughly 1949 through ’54. The speech attributed to Wofsy was actually drafted by Levison and can be found in Proceedings of the Fourth Constitutional Convention of the AFL-CIO, Vol. 1, American Federation of Labor – Congress of Industrial Organizations, Washington, D.C., 1962, pp. 282-9. Levison also had much to do with the preparation of the manuscript for King’s first book Stride Toward Freedom (Harper and Brothers Publishers, New York, 1958); see King, Coretta Scott, My Life With Martin Luther King, Jr., Holt, Rinehart and Winston Publishers, New York, 1969.
19 Such Bureau activities with regard to Levison were nothing new and seem to have stemmed largely from reports coming from “Solo,” two brothers – Jack and Morris (Chilofsky) Childs – who served from as early as 1951 as highly placed FBI informants within the CP, USA. It was they who appear to have originally ‘linked” Levison to the party even though they could never attest to his actual membership and essentially stopped referring to him by early 1954. J. Edgar Hoover’s predictable (and quite unsubstantiated) response was to declare Levison a “secret” CP member; see Garrow, op. cit., pp. 21-77.
20 Memorandum, SAC, New York, to Director, FBI, captioned “Martin Luther Kin& Jr., SM-C,” and dated June 21, 1962. Shortly thereafter, the New York field office began to openly affix a COMINFIL caption to correspondence concerning King and the SCLC. The Atlanta field office followed suit on October 23. The designation was officially approved by FBI headquarters supervisor R.J. Rampton in identical letters to the SACs on the latter date.
21 Targeting the SCLC under COINTELPRO-CP, USA was first proposed by the SAC, New York in a memorandum to Hoover dated September 28,1962. The operation was approved by memo in an exchange between Assistant Director William C. Sullivan and one of his aides, Fred J. Baumgardner, on October 8. The initial five newspapers selected for purposes of surfacing the anti-King propaganda were the Long Island Star-Journal, Augusta (GA) Chronicle, Birmingham (AL) News, New Orleans Times-Picayune, and the St. Louis Globe Democrat (where the reporter utilized in spreading the lies was Patrick J. Buchanan, later part of the White House press corps under Presidents Nixon and Reagan, as well as a current host on the Cable News Network Crossfire program).
22 The ELSURS authorization was signed by Kennedy on October 10, 1963 and provided to FBI liaison Courtney A. Evans. The attorney general’s main concern, detailed in the minutes of his meeting with Evans, seems to have been not that the bugging and tapping of King and the SCLC for purely political purposes was wrong but that it might be found out. Once Evans convinced him that this was genuinely improbable, “the Attorney General said he felt [the FBI] should go ahead with the technical coverage of King on a trial basis, and to continue if productive results were forthcoming.” See Denniston, Lyle, “FBI Says Kennedy OKed King Wiretap,” Washington Evening Star, June 18,1969. Also see OLeary, Jeremiah, “King Wiretap Called RFK’s Idea,” Washington Evening Star, June 19, 1969. Concerning continuation of the taps after the “trial period” had concluded, see Rowan, Carl, “FBI Won’t Talk about Additional Wiretappings,” Washington Evening Star, June 20,1969.
23 The New York SAC reported in a memorandum to Hoover, dated November 1, 1963, and captioned ‘Martin Luther Kin& Jr., SM-C; CIRM (JUNE),” that his agents had tapped all three SCLC office lines in his area of operations, with coverage on two lines beginning October 24. He also recommended installation of a tap on the residence line of civil rights leader Bayard Rustin; the tap was approved and installed in early January 1964. On November 27,1963, the Atlanta SAC informed Hoover by a memo captioned “COMINFIL, RM; Martin Luther Kin& Jr., SM-C (JUNE),” that Atlanta operatives had tapped King’s home phone and all four organizational SCLC lines in that city as of November 8.
24 For its disinformation campaign, the Bureau made ample use of “friendly media contacts” such as the nationally syndicated columnist Joseph Alsop, who proved quite willing to smear King in print on the basis of FBI “tips” lacking so much as a shred of supporting evidence. Concerning the IRS, as Garrow (op. cit.) notes at p. 114, ‘in mid-March [1964) the Internal Revenue Service reported that despite careful scrutiny it had been unable to discover any violations in either King’s or SCLC’s tax returns. Director Hoover scrawled ‘what a farce’ on the margin when the disappointing memo reached his desk.”
25
26 The instructions by Sullivan to Whitson and others are summarized in a memorandum from a member of the Internal Security Section named Jones to FBI Associate Director Cartha D. DeLoach on December 1, 1964, captioned simply ‘Martin Luther King, Jr.” For further information, see Lardner, George, Jr., “FBI Bugging and Blackmail of King Bared, Washington Post, November 19,1975. Also see Horrock, Nicholas M., “Ex-Officials Say FBI Harassed Dr. King to Stop His Criticism,” New York Times (March 9,1978), and Kunstler, William, “Writers of the Purple Page,” The Nation (No. 227, December 30, 1978).
27 Garrow, op. cit., p. 127. It appears DeLoach had to content himself with the “contributions” of right-wing hacks like Victor Riesel. However, Bureau efforts to place the “story” in more respectable quarters are known to have included overtures to – at the very least -reporters John Herbers of the New York Times, James McCartney of the Chicago Daily News, David Kraslow of the Los Angeles Times, Eugene Patterson of the Atlanta Constitution, Lou Harris of the Augusta Chronicle, and syndicated columnist Mike Royko. Herbers appears to have passed word of what was happening to civil rights leader James Farmer, who confronted DeLoach with the matter during an appointment on December 2, 1964.
28 There are serious questions concerning the possibility that the FBI might have been involved in the assassination of Martin Luther King. See, for example, Lane, Mark, and Dick Gregory, Code Name “Zorro:” The Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr., Prentice-Hall Publishers, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1977. Also see Lawson, James, “And the Character Assassination That Followed,” Civil Liberties Review, No. 5, July-August 1978. Of further interest, see Lewis, David L., King: A Biography, University of Illinois Press, Urbana, 1979, especially pp. 399-403.
29 Gid Powers, Richard, Secrecy and Power: The Life of J. Edgar Hoover, The Free Press, New York, 1987, p. 4,58.
30 Churchill, Ward, The COINTELPRO Papers, http://www.derechos.net/paulwolf/cointelpropapers/copap4.htm
31 Ibid.
32 Ibid.
33 Ibid.
34 For a review of some of these actions, see Dave Dellinger, More Power than We Know (Garden City, NY: Doubleday, 1975); Gary T. Marx, “Thoughts on a Neglected Category of Social Movement Participant: The Agent Provocateur and the Informant,” American Journal of Sociology, vol. 80, no. 2 (September 1974, pp. 402-42).
35 Ward Churchill and Jim Vander Wall, Agents of Repression: The FBI’s Secret Wars Against the Black Panther Party and the American Indian Movement, South End Press, Boston, MA, 1990.
36 Churchill, Ward, The COINTELPRO Papers, http://www.derechos.net/paulwolf/cointelpropapers/copap7a.htm
37 Kunstler, William, My Life as a Radical Lawyer
38 Voices From Wounded Knee, 1973, (Institute for Policy Studies, Washington, D.C., 1974)p. 81. Warner and Potter were specifically ordered to wear civilian clothes, in order to hide the fact of direct military participation at Wounded Knee. They arranged for supply sergeants, maintenance personnel and medical teams to be present on the federal perimeter throughout the 71-day siege, all similarly attired in civilian garb. Further, the colonels placed a special army assault unit to be placed on 24-hour-a-day alert at Ft. Carson, Colorado for the duration of the siege. See The Nation, November 9,1974. Also see University Review, the same month.
39 Churchill, Ward, The COINTELPRO Papers, http://www.derechos.net/paulwolf/cointelpropapers/copap7b.htm
40
41 Dave Dellinger, More Power than We Know (Garden City, NY: Doubleday, 1975) Many such cases have been exposed throughout the country.
42 For information on these and other FBI actions in Seattle, see Dellinger, op. cit., and Frank J. Donner, “Hoover’s Legacy,” Nation, June 1, 1974.
43 John M. Crewdson, “Ex-Operative Says He Worked for F.B.I. To Disrupt Political Activities up to ’74,” New York Times, February 24, 1975.
44 Donner Frank Donner, Protectors of Privilege: Red Squads and Police Repression in Urban America, University of California Press, Berkeley, 1990, p. , P. 207
45 Ibid.
46 Michael Novick, “BLUE BY DAY, WHITE BY NIGHT: Organized White Supremacist Groups in Law Enforcement Agencies,” People Against Racist Terror (PART), PO BOX 1990, Burbank, CA 91507, Revised and Updated, February 1993, p. 4
47 Ken Lawrence, “Vigilante Repression,” Covert Action Information Bulletin, Washington, D.C., Number 31, Winter 1989
48 Michael Novick, White Lies, White Power. The Fight Against White Supremacy and Reactionary Violence, Common Courage Press, Monroe, Maine, 1995, PP. 35-57
49 For an insider’s account of FBI racism and misogyny, particularly the Bureau’s role in the frame-up of Black Panther Party leader Geronimo ji Jaga [Pratt] see: M. Wesley Swearingen, FBI Secrets: An Agent’s Expose, South End Press, Boston, 1995
50 For a discussion of the nature of the FBI’s “White Hate Groups” COINTELPRO see: Donner 1980, PP. 204-211
51 Donner Frank Donner, Protectors of Privilege: Red Squads and Police Repression in Urban America, University of California Press, Berkeley, 1990, p. 206
52 Frank Donner, Protectors of Privilege: Red Squads and Police Repression in Urban America, University of California Press, Berkeley, 1990, p. 309
53 National Lawyer’s Guild, Counterintelligence: A Documentary Look at America’s Political Police, Volume One, Chicago, 1978, p. 7
54 “Documents detail FBI-Klan links in early rights strife,” Chicago Tribune, August 2,1978
55 Howell Raines, “Police Given Data on Boast by Rowe, The New York Times, July 14, 1978
56 Churchill and Vander Wall, The COINTELPRO Papers, p. 369
57 Elizabeth Wine, “Blacks Hope for Best as Feds Reopen Bombing Case,” Reuters, July 21, 1997
58 The COINTELPRO Papers, p. 170
59 Donner, Protectors of Privilege, p. 214
60
61 Churchill And Vander Wall, op. cit., p. 182
62 Frank Donner, PROTECTORS OF PRIVILEGE: Red Squads and Police Repression in America, University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles, 1990, p. 360
63 ibid.
64 ibid.
65 Novick, op. cit., p. 4
66Donner, op. cit., p. 361
67 ibid.
68 ibid.
69 ibid.
70 Novick, op. cit., p. 4
71 Ridgeway, op. cit. pp. 76-81
72 Peter Biskind, “The FBI’s Secret Soldiers,” New Times, Volume 6, Number 1, January 9, 1976, pp. 21-22
73 Everett R. Holles, “A.C.L.U. Says F.B.I. Funded `Army To terrorize Antiwar Protesters’,” N.Y. Times, June 27, 1975. Information and quotes are from the 18-page single-space report submitted to the Senate Select Committee on June 27, 1975, unless otherwise indicated. See also Steven V. Roberts, “F.B.I. Informer Is Linked to Right-Wing Violence, N.Y. Times, June 24, 1974.
74 Biskind, op. cit., P. 21
75 ibid.
76 CARIC, op. cit., PP. 5-6
77 Biskind, op. cit., P. 23
78 Ibid.
79 Ibid.
80 CARIC, op. cit., p. 6
81 Churchill and Vander Wall, op. cit., p. 182. Also, Godfrey “has testified in a California court that the bureau gave him $10,000 to $20,000 worth of weapons and explosives for use by the [SAO] in addition to his $250-a-month salary as an informant.” John M. Crewdson, “Kelley Discounts F.B.I.’s Link to a Terrorist Group,” N.Y. Times, January 12, 1976.
82 Biskind, op. cit., P. 25
83
84 The Bureau was also busy trying to split up the SNCC leadership during this period. In Agents, op. cit., at p. 50, a document is reproduced proposing a bogus letter designed to achieve this effect vis a vis H. Rap Brown, Stokely Carmichael and James Forman.
85 See Newton, Huey P., To Die for the People, Vintage Books, New York, 1972, p. 191.
86 Current Political Prisoners – Victims of COINTELPRO, roundtable dicsussion of Congresswoman Cynthia McKinney, September 14, 2000 http://www.house.gov/mckinney/news/if_000914_humanrights.htm
87 Churchill, Ward, The COINTELPRO Papers, http://www.derechos.net/paulwolf/cointelpropapers/copap4.htm
88 Ibid.
89 Ibid.
90 Ibid.
91 Ibid.
92
93 Churchill, Ward, The COINTELPRO Papers, http://www.derechos.net/paulwolf/cointelpropapers/copap5a.htm
94 Summary, p. 5.
95 The “Key Black Extremist” tag seems to have been adopted for local use by the LA office COINTELPRO group from at least as early as January 20, 1969, based upon internal office memos. A memo from SAC, Los Angeles to the Director, dated 4/21/69 and captioned BLACK PANTHER PARTY-ARRESTS, RESTS, RACIAL MATTERS, recommended placing both Pratt and his second in command, Roger Lee Lewis, in the National Security Index.
96 Durden-Smith, op. cit., pp. 145-46.
97 This is readily borne out in a Bureau document, LA 157-3436 which, in Section V (MISCELLANEOUS ITEMS RELATING TO ACTIVITIES ASSOCIATED WITH THE BPP), describes how Pratt and several other Panthers, in a private residence, had sawn off the barrels of “15 to 20 weapons” (a legal act, so long as resulting barrel length is not less than 18 inches) during January of 1969; for no apparent reason, it stated that “it was believed the weapons were obtained in a burglary.” The document then goes on to itemize other legal activities in which Pratt had engaged, such as target practice in the Mojave Desert, travel to and from Kansas City, providing a guided tour of the local BPP office for Angela Davis, etc. This is intermixed with suggestions (no reference to evidence of any sort) that Pratt illegally possessed at least one .45 caliber submachinegun and engaged in other criminal behavior.
98 Memo from SCA, Los Angeles to the Director, FBI, dated 5/6/69 and captioned ELMER PRATT, BR–CONSPIRACY states, “As the Bureau is aware, Los Angeles is investigating one bank robbery committed by persons known to be involved in ‘US’ [several words deleted] UNSUBS 131; BANK OF AMERICA, NT & SA, Jefferson HUI Branch, 3320 South Hill Street, Los Angeles, California, 1/10/69, BR’).” The document then goes on, for no logical reason, to announce that BPP members “have possibly been involved in bank robbery matters in the Los Angeles area,” singles Pratt out by name in a heavily deleted passage, and ends with the observation that, “A bank robbery conspiracy case is being opened in the Los Angeles Office on ELMER PRATT … appropriate investigation to attempt to develop a conspiracy case will be conducted [emphasis added].” In a memo to the Director dated 6/5/69 and captioned “ELMER PRATT, BR–CONSPIRACY,” the SAC, Los Angeles, eventually acknowledged that the matter was being dropped because “no information has been developed to indicate that any Black Panther Party (BPP) members have been plotting bank robberies in Los Angeles or elsewhere.” The document concludes that the “captioned case is … subject to being reopened at any time information is received to indicate that Pratt or other members of the BPP are plotting or are responsible for bank robberies.”
99 Los Angeles office Field Report, LA 157-3553, dated 5/14/69. The character of the case reported upon is described as, “RM-SMITH ACT OF 1940; SEDITIOUS CONSPIRACY AND INSURRECTION.”The document was circulated to 8 Bureau offices, the Norton Air Force Base Office of Strategic Intelligence, 115th Military Intelligence Group, and the Secret Service in its initial distribution.
100
101 Summary at p. 6.
102 See Counterintelligence Report from the SAC, Los Angeles, to Director, FBI, (LA 157-17511), dated 6/3/69 and captioned “COUNTERINTELLIGENCE PROGRAM, BLACK NATIONALIST-HATE GROUPS, RACIAL INTELLIGENCE (BLACK PANTHER PARTY).” As to the younger Held’s position in the LA-COINTELPRO operation, see Swearingen deposition, op. cit., p. 1: “1 knew RICHARD WALLACE HELD as head of the COINTELPRO section in Los Angeles [during this period].”
103 Durden-Smith, op. cit., p. 136, quotes Tackwood describing Cotton Smith before the raid, “cutting up this cardboard and making this budding, and he’s putting little dolls with names on them, where they were, and associations and such and such.” The LA version of the O’Neal floorplan in Chicago was thus apparently in three dimensions.
104 Although not so straightforward as the Chicago memoranda in the aftermath of the HamptonClark assassinations, a memo from SAC, Los Angeles to Director, FBI, dated 12/8/69 and captioned BLACK PANTHER PARTY, ARRESTS-RACIAL MATTERS, indicates the Bureau was directly involved in the LA raid and that the local FBI office sought credit for this “success.” Among the BPP members listed in this document as having been arrested on (spurious) attempted murder charges and other offenses as a result of Bureau/police efforts on 12/8 are Robert Bryan, Roland Freeman, Craig Williams, Jackie Johnson, Wayne L. Pharr, Isiah Houston, Elmer Pratt, Sandra Lane Pratt (wife), Willie Stafford, Tommy E. Williams, Renee Moore, Paul Redd, Albert Armor, Melvin Smith and George Young. The situation seems to have sparked substantial interest at the very highest levels of the FBI, as is indicated by a memo on the matter between national COINTELPRO head W.C. Sullivan and his primary operational coordinator, G.C. Moore, dated 12/17/69, in which Moore expresses delight that, “Both Pratts were arrested for their participation in the shooting battle with the Los Angeles Police Department on 12-8-69.”
105 Churchill, Ward, The COINTELPRO Papers, http://www.derechos.net/paulwolf/cointelpropapers/copap5a.htm
106 See “63 Verdicts End Panther Trial”, Los Angeles Times, December 24, 1971.
107 The Glass House Tapes, op. cit., pp. 104-105.
108 Summary at pp. 1-2.
109 Richardson, Lee, “Ex-FBI Agent Exposes Use of Informants to Destroy the BPP,” Freedom Magazine, 18:5, January 1985, P. 31.
110 Summary at P. 3; this was a matter raised in a motion for retrial by Johnnie Cochran, which was denied by trial judge Kathleen Parker.
111 Ibid. at p. 2.
112 Ibid. at pp. 91-93.
113 On prosecution presentation, see ibid. at pp. 2-3; on Newton faction refusal to testify for Pratt, see pp. 94-96.
114 AIRTEL from SAC, Los Angeles, to Acting Director, FBI, dated 7/18/72 (caption deleted), from The COINTELPRO Papers.
115 An “URGENT” Teletype, sent at 1:26 PM, 7-28-72, from the Los Angeles Field Office to the Acting Director, FBI, and reading, “LOS ANGELES SHERIFF’S OFFICE INTELLIGENCE, ADVISED INSTANT DATE ELMER GERARD PRATT FOUND GUILTY FIRST DEGREE MURDER … DETAILS TO FOLLOW,” gives some indication of the ownership and priority the Bureau felt in this case, from The COINTELPRO Papers.
116 See Amnesty International, Proposal for a commission of inquiry into the effect of domestic in telligence activities on criminal trials in the United States of America, Amnesty International, New York, 1980, p. 29: “[The defense obtained] over 7,000 pages of FBI surveillance records dated after 2 January 1969. Elmer Pratt claimed earlier records would reveal that he was at a meeting in Oakland at the time of the murder on 18 December 1968 but the FBI’s initial response to this was that there had been no surveillance before 1969. This was later shown to be untrue.”
117 See Elmer G. Pratt v. William Webster, et al., United States Court of Appeals in the District of Columbia (No. 81 1907) for presentation of the case, and Pratt v. Webster; et. al. (508 F. Supp. 751 [19811) for the ruling. The federal “national security” argument may be found in the reply brief (No. 81-1907).
118 For Judge J. Dunn’s dissenting remarks, see his minority opinion In Re: Pratt, 112 Cal. App. 3d. 795,-Cal. Rptr. (Crim. No. 3 7534. Second Dist., Div. One. 3 December 1980); hereinafter referred to as “Minority’ and “Majority. ”
119 Proposal for a commission of inquiry into the effect of domestic in telligence activities on criminal trials in the United States of America, op. cit., pp. 107-110. Informant Reports and related memoranda on file.
120 Summary at p. 15.
121 Proposal for a commission of inquiry into the effect of domestic in telligence activities on criminal trials in the United States of America, op. cit., p. 25.
122 The document also posits “the absolute necessity for intensive investigative efforts in [political] matters.”
123 Select Committee, Final Report, Book III, OP. cit., p. 517.
124 See New York Times, August 4, 1974, for documents and commentary.
125 This led directly to one of the three post-1971 “COINTELPRO-type” operations:”The leaking of derogatory information about Daniel Ellsberg’s lawyer to Ray McHugh, chief of the Copley News Service.” (Spying on Americans, op. cit., p. 151).
126 The break-in at the Media resident agency, which occurred on the night of March 8, 1971, compromised the secrecy of COINTELPRO and thereby set in motion a process of high level “re-evaluation” of the program’s viability. This led to an April 28 memorandum from Charles D. Brennan, number two man in the COINTELPRO administrative hierarchy, to his boss, FBI Assistant Director William C. Sullivan. Brennan recommended the acronym be dropped, but that the activities at issue be continued under a new mantle “with tight procedures to insure absolute secrecy.” Hoover’s famous “COINTELPRO termination” memo of the following day was merely a toned-down paraphrase of the Brennan missive. In another connection, it should be noted that publication of the COINTELPRO documents taken from the Media office was not in itself sufficient to cause the FBI to admit either the long-term existence or the dimension of its domestic counterintelligence activities. Instead, this required a suit brought by NBC correspondent Carl Stern after the reporter had requested that Attorney General Richard Kleindienst provide him with a copy of any Bureau document which “(i) authorized the establishment of Cointelpro – New Left, (ii) terminated such program, and (iii) ordered or authorized any change in the purpose, scope or nature of such program” on March 20,1972. Kleindienst stalled until January 13, 1973 before denying Stern’s request. Stern then went to court under provision of the 1966 version of the FOIA, with the Justice Department counter-arguing that the judiciary itself “lacks jurisdiction over the subject matter of the complaint.” Finally, on July 16, 1973 U.S. District Judge Barrington Parker ordered the documents delivered to his chambers for in camera review and, on September 25, ordered their release to Stern.
The Justice Department attempted to appeal this decision on October 20, but abandoned the effort on December 6. On the latter date, Acting Attorney General Robert Bork released the first two documents to Stern, an action followed on March 7,1974 by the release of seven more. By this point, there was no way to put the genie back in the bottle, and the Senate Select Committee as well as a number of private attorneys began to force wholesale disclosures of COINTELPRO papers.
127 Examples abound. Early instances come with Jimmy Carter’s Executive Order 12036, signed on January 24,1978, which moved important areas of intelligence/counterintelligence activity under the umbrella of “executive restraint” rather than effective oversight, and the electronic surveillance loopholes imbedded in S. 1566, a draft bill allegedly intended to protect citizens’ rights from such police invasion of privacy, which passed the senate by a vote of 99-1 on April 20,1978. This was followed on December 4,1981 by Ronald Reagan’s Executive Order 12333, expanding the range of activities in which U.S. intelligence agencies might “legally” engage. Then there was the Intelligence Identifies Protection Act of 1982 which made it a “crime” to disclose the identities of FBI informants, infiltrators and provocateurs working inside domestic political organizations. And, in 1983, Reagan followed up with Executive Order 12356, essentially allowing agencies such as the FBI to void the Freedom of Information Act by withholding documents on virtually any grounds they choose. Arguably, things are getting worse, not better.
128 For analysis and texts of the Media documents, see Paul Cowan, Nick Egleson, and Nat Hentoff, State Secrets (Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1973).
129 Henry Steele Commager, “The Constitution Is Alive and Well,” New York Times, August 11, 1974. Commager, who has been forceful in defense of civil liberties and opposition to the Indochina war, states that prior to Nixon, “no President has ever attempted to subvert” the Constitution or “challenged the basic assumptions of our constitutional system itself.” But “the system worked” and the challenge was defeated.
130
131 The classic articulation of how this was rationalized came in the 1974 Justice Department report on COINTELPRO produced by an “investigating committee” headed by Assistant Attorney General Henry Peterson. After reviewing no raw files (innocuously worded FBI “summary reports” were accepted instead), but still having to admit that many aspects of COINTELPRO violated the law, the Peterson committee nonetheless recommended against prosecuting any of the Bureau personnel involved. “Any decision as to whether prosecution should be undertaken must also take into account several other important factors which bear on the events in question. These factors are: first, the historical context in which the programs were conceived and executed by the Bureau in response to public and even Congressional demands for action to neutralize the self-proclaimed revolutionary aims and violence prone activities of extremist groups which posed a threat to the peace and tranquility of our cities in the mid and late sixties; second, the fact that each of the COINTELPRO programs were personally approved and supported by the late Director of the FBI; and third, the fact that the interference with First Amendment rights resulting from individual implemented program actions were insubstantial.” The Senate Select Committee and other bodies went rather further in their research and used much harsher language in describing what had happened under COINTELPRO auspices, but the net result in terms of consequences to the Bureau and its personnel were precisely the same: none.
132 “Charges Over F.B.I.’s Tactics on Subversive Suspects Barred,” Washington Star-News; New York Times, January 4, 1975.
133 For an in-depth analysis of the disinformation campaign at issue, see Weisman, Joel D., “About that ‘Ambush’ at Wounded Knee,” Columbia Journalism Review, September-October 1975.
134
135 David Brion Davis, ed., _The Fear of Conspiracy_ (Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1971). A fifth committed suicide before the sentence of death could be executed. Three others were sentenced to hanging as well, but were not executed. No proof was offered that any of the eight had been involved in the bomb-throwing.
136
137
138
139
140 See excerpts from Palmer in Davis, _op. cit._ On the role of the press, see Levin, _op. cit._.
141 See excerpt in Davis, op.cit.
142
143
144 Proceedings of the Federal-State Conference on Law Enforcement Problems of National Defense, August 5-6, 1940. From Ideological Warfare, op. cit. p. 44.
145 U.S. Congress, House, House Committee on Appropriations, First Deficiency Appropriations Bill, Hearing, February 19, 1941, pp. 188-89. 77th Congress, 1st session. From Ideological Warfare, op. cit. p. 43.
146 Personal and confidential memorandum from Hoover to Attorney General Tom Clark, March 8, 1946. Ibid., p. 44-45.
147
148
149
150
151
152
153 Ross Gelbspan, “Break-ins, Death Threats and the FBI: The Covert War Against the Central American Movement,” South End Press, Boston, MA, 1991, pp. 71-72
154 Ibid.
155 For further information on the FBI’s anti-CISPES operations, see Buitrago, Ann Mari, Report on CISPES Files Maintained by the FBI and Released under the Freedom of Information Act, FOIA, Inc., New York, January 1988.
156 U.S. House of Representatives, Committee on the Judiciary, Subcommittee on Civil and Constitutional Rights, Break-Ins at Sanctuary Churches and Organizations Opposed to Administration Policy in Central America, Serial No. 42, 100th Congress, 1st Session, Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1988, Hearing of February 19 20,1987, pp. 432 ff. Also see Harlan, Christi, “The Informant Left Out in the Cold,” Dallas Morning News, April 6,1986, Gelbspan, Ross, “Documents show Moon group aided FBI,” Boston Globe, April 118,1988; and Ridgeway, James, “Spooking the Left,” Village Voice, March 3, 1987. For more on Varelli’s role and the FBI’s attempt to scapegoat him, see Gelbspan, Ross, “COINTELPRO in the’80s: The ‘New’ FBI,” Covert Action Information Bulletin, No. 31 (Winter 1989), pp. 14-16.
157 See, for example, the FBI teletype on p. 18. Also see Buitrago, Report on CISPES Files Maintained by FBI Headquarters and Released Under the Freedom of Information Act, Fund for Open Information and Accountability, Inc., New York, 1988; Groups Included in the CISPES Files Obtained from FBI Headquarters, Center for Constitutional Rights, 1988; Ridgeway, James, “Abroad at Home: The FBI’s Dirty War,” Village Voice, February 9, 1988.
158 U.S. House of Representatives, Committee on the Judiciary, Subcommittee on Civil and Constitutional Rights, CISPES and FBI Counter-Terrorism Investigations, Serial No. 122, 100th Congress, 2nd Session, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1989, Hearing of September 16,1988, pp. 116-27. The changing public positions taken by Webster and Sessions concerning the FBI’s CISPES operations are well traced in Buitrago, Ann Mari, “Sessions’ Confessions,” Covert Action Information Bulletin, No. 31 (Winter 1989), pp. 17-19.
Bibliography
Books
The COINTELPRO Papers: Documents From the FBI’s Secret Wars Against Dissent in the United States, by Ward Churchill & Jim Vander Wall, South End Press
Agents of Repression: The FBI’s Secret Wars Against the Black Panther Party and the American Indian Movement, by Ward Churchill & Jim Vander Wall, South End Press
COINTELPRO: The FBI’s Secret War on Political Freedom, by Nelson Blackstock, Pathfinder, 1975
FBI Secrets: An Agent’s Expose, by M. Wesley Swearingen, South End Press
War at Home: Covert Action Against U.S. Activists and What We Can Do About It by Brian Glick, South End Press
In the Spirit of Crazy Horse by Peter Matthiessen, 1991, Viking Press
Break-ins, Death Threats and the FBI: The Covert War Against the Central America Movement, by Ross Gelbspan, 1991, South End Press
Are You Now or Have You Ever Been in the FBI FILES: How to Secure and Interpret Your FBI Files by Ann Mari Buitrago and Leon Andrew Immermann, Grove Press Inc.
All Power to the People! The Black Panther Party and Beyond, video by the Electronic News Group
Vincent, Ted, Black Power and the Garvey Movement, Nzinga Publishing House, Oakland, CA, 1987.
Cronon, E. Davis, Black Moses: The Story of Marcus Garvey and the United Negro Improvement Association, University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, 1955.
Frank J. Donner, The Age of Surveillance: The Aims and Methods of America’s Political Intelligence System, New York: Knopf, 1980
Ideological Warfare: The FBI’s Path Toward Power, Frank M. Sorrentino, Associated Faculty Press, Inc. 1985.
Robert J. Goldstein, Political Repression in Modern America, Cambridge: Schenkman, 1978
Morton H. Halperin et. al., The Lawless State, New York: Penguin, 1976
Kenneth O’Reilly, Racial Matters, New York: Free Press, 1989
Hersey, John, The Algiers Motel Incident, Alfred A. Knopf Publishers, New York, 1968
Hayden, Tom, Rebellion in Newark: Official Violence and Ghetto Response, Vintage Books, New York, 1967
Gilbert, Ben W., et. al., Ten Blocks From the White House: Anatomy of the Washington Riots of 1968, Frederick A. Praeger Publishers, New York, 1968
Wright, Nathan Jr., Black Power and Urban Unrest: Creative Possibilities, Hawthorn Books, Inc., New York, 1967.
Boesel, David, and Peter H. Rossi (eds.), Cities Under Siege: An Anatomy of the Ghetto Riots, 1964-1968, Basic Books, New York, 1971
Paul Cowan, Nick Egleson, and Nat Hentoff, State Secrets, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1973
Chomsky, Noam, For Reasons of State, New York: Pantheon, 1973
Chomsky and E.S. Herman, Counterrevolutionary Violence: Bloodbaths in Fact and Propaganda (New York: Warner Modular, 1973), suppressed by order of the parent conglomerate (Warner Brothers) but available in French (Bains de Sang, Paris: Seghers/Laffont, 1974)
Chomsky and Herman, The Political Economy of Human Rights (Boston: South End Press, 1979).
Herman and Chomsky, Manufacturing Consent (New York: Pantheon, 1988).
Zinn, Howard, A People’s History of the United States, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1980.
Johnson, Loch, A Season of Inquiry. The Senate Intelligence Investigation, University of Kentucky Press, Lexington, 1985
Hersh, Seymour, The Price of Power, Simon and Schuster, New York, 1983, p. 295
Barry, John M., The Ambition and the Power: The Fall of Jim Wright, A True Story of Washington, Viking, New York 1989
David Brion Davis, ed., The Fear of Conspiracy, Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1971
Murray B. Levin, Political Hysteria in America: the Democratic Capacity for Repression, New York: Basic Books, 1972
Max Lowenthal, The Federal Bureau of Investigation, William Sloane Associates, Inc., 1950
Novick, Michael, Blue by Day, White by Night: Organized White Supremacist Groups in Law Enforcement Agencies, People Against Racist Terror (PART), PO BOX 1990, Burbank, CA 91507, Revised and Updated, February 1993
Novick, Michael, White Lies, White Power: The Fight Against White Supremacy and Reactionary Violence, Common Courage Press, Monroe, Maine, 1995
Donner, Frank, Protectors of Privilege: Red Squads and Police Repression in Urban America, University of California Press, Berkeley, 1990
National Lawyer’s Guild, Counterintelligence: A Documentary Look at America’s Political Police, Volume One, Chicago, 1978
Newton, Huey P., To Die for the People, Vintage Books, New York, 1972, p. 191.
King, Coretta Scott, My Life With Martin Luther King, Jr., Holt, Rinehart and Winston Publishers, New York, 1969
Lane, Mark, and Dick Gregory, Code Name “Zorro:” The Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr., Prentice-Hall Publishers, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1977.
Lewis, David L., King: A Biography, University of Illinois Press, Urbana, 1979.
Gid Powers, Richard, Secrecy and Power: The Life of J. Edgar Hoover, The Free Press, New York, 1987
Tom Burghardt, “Paramilitary Violence and the State: The ‘Public-Private Partnership’ in Political Repression,” Toronto, Antifa Forum, Number 3, 1998.
Nicholas Wilson, “The Judi Bari Bombing Revisited: Big Timber, Public Relations and the FBI,” The Albion Monitor, http://www.monitor.net/monitor/9905a/jbrevisited.html
Government Reports and Newspaper Articles
Final Report of the Select Committee to Study Governmental Operations with Respect to Intelligence Activities of the United States Senate, Ninety Fourth Congress, First Session,
U.S. Government Printing Office, No. 94-755, April 14, 1976, Vol 1-6.
Hearings Before the Select Committee to Study Governmental Operations with Respect to Intelligence Activities of the United States Senate, Ninety Fourth Congress, First Session,
U.S. Government Printing Office, Sept. 16 – Dec. 5, 1975, Vol 1-7.
U.S. Congress, Joint Committee on Assassinations, Hearings on the Investigation of the Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr., Vol. 6, 95th Congress, 2d Session, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1978
U.S. Senate, Committee on the Judiciary, FBI Statutory Charter – Appendix to Hearings Before the Subcommittee an Administrative Practice and Procedure, Part 3, 95th Congress, 2d Session, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1979
U.S. House of Representatives, Committee on the Judiciary, Subcommittee on Civil and Constitutional Rights, Break-Ins at Sanctuary Churches and Organizations Opposed to Administration Policy in Central America, Serial No. 42, 100th Congress, 1st Session, Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1988, Hearing of February 19 20,1987, pp. 432
U.S. House of Representatives, Committee on the Judiciary, Subcommittee on Civil and Constitutional Rights, CISPES and FBI Counter-Terrorism Investigations, Serial No. 122, 100th Congress, 2nd Session, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1989, Hearing of September 16,1988
Proposal for a commission of inquiry into the effect of domestic intelligence activities on criminal trials in the United States of America, Amnesty International, New York, 1980
Special Report of Interagency Committee on Intelligence (Ad Hoc), Chairman J. Edgar Hoover, along with the directors of the CIA, DIA, and NSA, prepared for the President, June 25, 1970,
Gary T. Marx, “Thoughts on a Neglected Category of Social Movement Participant: The Agent Provocateur and the Informant,” American Journal of Sociology, vol. 80, no. 2, September 1974
Weisman, Joel D., “About that ‘Ambush’ at Wounded Knee,” Columbia Journalism Review, September-October 1975.
See “63 Verdicts End Panther Trial”, Los Angeles Times, December 24, 1971.
Richardson, Lee, “Ex-FBI Agent Exposes Use of Informants to Destroy the BPP,” Freedom Magazine, January 1985
“Charges Over F.B.I.’s Tactics on Subversive Suspects Barred,” Washington Star-News; New York Times, January 4, 1975.
Hill, Robert A., “The Foremost Radical of His Race: Marcus Garvey and the Black Scare, 1918-1920,” Prologue, No. 16, Winter 1984.
Frank Wilkinson, The Era of Libertarian Repression – 1948 to 1973: from Congressman to President, with Substantial Support from the Liberal Establishment, University of Akron, 1974; reprinted from the University of Akron Law Review.
Nicholas M. Horrock, “The F.B.I.’s Appetite for Very Small Potatoes,” New York Times, March 23, 1975.
C. Gerald Fraser, “F.B.I. Action in 1961 Called Still Harmful to Hopes of Blacks,” New York Times, April 6, 1974.
Jesse Jackson and Alvin Poussaint, “The Danger Behind FBI Obstruction of Black Movements,” Boston Globe, April 2, 1974
Henry Steele Commager, “The Constitution Is Alive and Well,” New York Times, August 11, 1974
John M. Crewdson, “Black Pastor Got F.B.I. Threat in ’69,” New York Times, March 17, 1975
Vin McLellan, “FBI Heists Names of 1970 Student Strikers,” Boston Phoenix, March 5, 1974
John Kifner, “F.B.I. Gave Chicago Police Plan of Slain Panther’s Apartment,” New York Times, May 25, 1974.
John Kifner, “Security Aide for Indians Says He Was F.B.I. Informer,” New York Times, March 13, 1975
Harry Kelly, “FBI spurred gang fight in Chicago, Senate says,” Chicago Tribune, November 20, 1975.
Harlan, Christi, “The Informant Left Out in the Cold,” Dallas Morning News, April 6,1986
Ridgeway, James, “Abroad at Home: The FBI’s Dirty War,” Village Voice, February 9, 1988
“Documents detail FBI-Klan links in early rights strife,” Chicago Tribune, August 2,1978
Raines, Howell, “Police Given Data on Boast by Rowe, The New York Times, July 14, 1978
Elizabeth Wine, “Blacks Hope for Best as Feds Reopen Bombing Case,” Reuters, July 21, 1997
Biskind, Peter, “The FBI’s Secret Soldiers,” New Times, January 9, 1976
Everett R. Holles, “A.C.L.U. Says F.B.I. Funded `Army To terrorize Antiwar Protesters’,” N.Y. Times, June 27, 1975
Steven V. Roberts, “F.B.I. Informer Is Linked to Right-Wing Violence, N.Y. Times, June 24, 1974
John M. Crewdson, “Kelley Discounts F.B.I.’s Link to a Terrorist Group,” N.Y. Times, January 12, 1976.
Churchill, Ward, and Jim Vander Wall, “COINTELPRO Against the Black Panthers: The Case of Geronimo Pratt,” Covert Action Information Bulletin, No. 31, January 1989
U.S. Department of Justice, Report of the Justice Department Task Force to Review FBI Martin Luther King, Jr., Security and Assassination Investigations, Washington, D.C., January 11, 1977
Pottinger, J. Stanley, “Martin Luther King Report” (to U.S. Attorney General Edward H. Levi), U.S. Department of Justice, Washington, D.C., April 9,1976
Goldstein, Robert Justin, “The FBI’s Forty Year Plot,” The Nation, No. 227, July 1, 1978
“An American Gulag? Summary Arrest and Emergency Detention of Political Dissidents in the United States,” Columbia Human Rights Law Review, No. 10, 1978
Denniston, Lyle, “FBI Says Kennedy OKed King Wiretap,” Washington Evening Star, June 18,1969.
OLeary, Jeremiah, “King Wiretap Called RFK’s Idea,” Washington Evening Star, June 19, 1969.
Rowan, Carl, “FBI Won’t Talk about Additional Wiretappings,” Washington Evening Star, June 20,1969.
Jacobs, James, “An Overview of National Political Intelligence,” University of Detroit Journal of Urban Law, No. 55, 1978.
Lardner, George, Jr., “FBI Bugging and Blackmail of King Bared, Washington Post, November 19,1975.
Horrock, Nicholas M., “Ex-Officials Say FBI Harassed Dr. King to Stop His Criticism,” New York Times, March 9,1978
Kunstler, William, “Writers of the Purple Page,” The Nation, No. 227, December 30, 1978.
Lawson, James, “And the Character Assassination That Followed,” Civil Liberties Review, No. 5, July-August 1978.


 Rubber bullets can be aimed away from eyes and faces, though an explosive which propels rubber pellets cannot. Any pretense that deputies are avoiding injuring the public is betrayed by the fact that they are aiming their bullets at the faces, groins and kneecaps of protesters. Though media reports state that police are “throwing” these projectiles, witnesses claim all of these are in fact being FIRED on them with launch weapons. Witnesses also report that the stun grenades being against them have their ventilation holes covered with duct-tape. It’s presumed that the tape causes the grenades to explode with greater pressure.
Rubber bullets can be aimed away from eyes and faces, though an explosive which propels rubber pellets cannot. Any pretense that deputies are avoiding injuring the public is betrayed by the fact that they are aiming their bullets at the faces, groins and kneecaps of protesters. Though media reports state that police are “throwing” these projectiles, witnesses claim all of these are in fact being FIRED on them with launch weapons. Witnesses also report that the stun grenades being against them have their ventilation holes covered with duct-tape. It’s presumed that the tape causes the grenades to explode with greater pressure.
 GET THIS. I heard a reverend-person yesterday lecturing newish activists about their need for nonviolence training, which she was volunteering to lead. She was also offering rubber wristbands for her graduates to wear at demonstrations, so that police could differentiate between protesters. She told us she’d ask officers to scrutinize those not wearing bands as being the potential troublemakers. This, she assured everyone, would make it more difficult for outside groups to waylay the action. I kid you not. And she’s a church leader praised locally as something of an activist! HA! That’s a RAT!
GET THIS. I heard a reverend-person yesterday lecturing newish activists about their need for nonviolence training, which she was volunteering to lead. She was also offering rubber wristbands for her graduates to wear at demonstrations, so that police could differentiate between protesters. She told us she’d ask officers to scrutinize those not wearing bands as being the potential troublemakers. This, she assured everyone, would make it more difficult for outside groups to waylay the action. I kid you not. And she’s a church leader praised locally as something of an activist! HA! That’s a RAT!


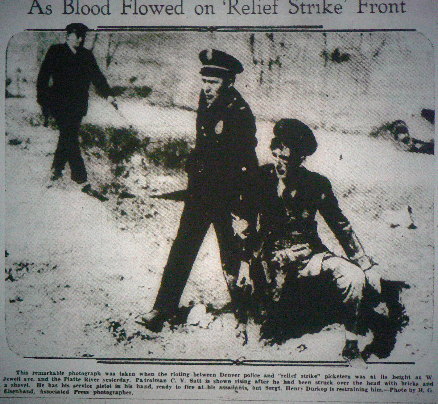

 DENVER, Colo, Oct 30 (UP)– A dark haired, attractive girl led demonstrators into hand to hand battle with police here today, as the picketers, under alleged communist leadership, sought to force a strike of Denver FERA workers.
DENVER, Colo, Oct 30 (UP)– A dark haired, attractive girl led demonstrators into hand to hand battle with police here today, as the picketers, under alleged communist leadership, sought to force a strike of Denver FERA workers.






 According to
According to  By J. D. Hendricks, 2004
By J. D. Hendricks, 2004

 This widely circulated video purported to show uniformed paramilitary thugs in the act of abducting a black-clad protester. The unmarked sedan pulled up, made the grab, and rolled away. Inconsistencies with the perp attire, mode of undress, and odd accessorizing, point to doubt as to whose street theater this was. God Bless ’em.
This widely circulated video purported to show uniformed paramilitary thugs in the act of abducting a black-clad protester. The unmarked sedan pulled up, made the grab, and rolled away. Inconsistencies with the perp attire, mode of undress, and odd accessorizing, point to doubt as to whose street theater this was. God Bless ’em.
 Did you catch it on
Did you catch it on  While she was on the air, the IDF soldiers repeatedly fired gas canisters, until she could no longer speak, and a cameraman had to come to her rescue with a spare gas mask.
While she was on the air, the IDF soldiers repeatedly fired gas canisters, until she could no longer speak, and a cameraman had to come to her rescue with a spare gas mask. Before the National Lawyers Guild issued
Before the National Lawyers Guild issued 
 The police rioters are really too much! Here is a photo spread of their
The police rioters are really too much! Here is a photo spread of their 


